Nine Different Ways That Quantum_Computing Will Change Life For The Better.
Nine Different Ways that Quantum_Computing will change life for the better.
More Posts from Aspergers1044 and Others
Some Possible Models of The Future Evolution of The Cosmos are presented Here.










This Is Why Dark Energy Must Exist, Despite Recent Reports To The Contrary
“We do not do science in a vacuum, completely ignoring all the other pieces of evidence that our scientific foundation builds upon. We use the information we have and know about the Universe to draw the best, most robust conclusions we have. It is not important that your data meet a certain arbitrary standard on its own, but rather that your data can demonstrate which conclusions are inescapable given our Universe as it actually is.
Our Universe contains matter, is at least close to spatially flat, and has supernovae that allow us to determine how it’s expanding. When we put that picture together, a dark energy-dominated Universe is inescapable. Just remember to look at the whole picture, or you might miss out on how amazing it truly is.”
20 years ago, the supernova data came back with an extraordinary surprise: it looked like the Universe wasn’t just expanding, but that the expansion rate was increasing as we head further into the future. While there were many dark energy skeptics to start, the increased flow of improved data from many lines of evidence that all kept pointing to the same conclusion has led to a cosmological consensus: dark energy dominates the Universe today. Last week, a story made waves, as Subir Sarkar and collaborators published their second paper (the first was in 2016) claiming that the evidence from supernovae is not good enough to support the existence of dark energy, and our cosmological foundation for it is extraordinarily shaky.
This is not true. This is demonstrably untrue. And the claim shows a deliberate unwillingness to pay attention to the rest of the field. Find out why dark energy must exist, despite recent reports to the contrary.
Publishers are giving away Bestselling Books for Free!
Last year, Random House decided to give away Dan Brown’s bestselling novel, The Da Vinci Code, for free for one week. The eBook freebie ran on the 10-year anniversary of The Da Vinci Code, and a few weeks before the release of Brown’s new book, Inferno.
Why did Random House give away a...

A Huge_Planet that’s "too big for its Host_Star" has been spotted orbiting a Faint Red_Dwarf Star by some Australian Researchers - with the help of a Backyard Astronomer.
Here are The Top_Ten Star_Wars Planets!
(via https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SqHGZu0DBag)
NASA’s TESS Mission to Search for Lots More EXOPLANETS is now about to be Launched someday really soon!
The Hunt for New Worlds Continues with TESS
We’re getting ready to start our next mission to find new worlds! The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) will find thousands of planets beyond our solar system for us to study in more detail. It’s preparing to launch from our Kennedy Space Center at Cape Canaveral in Florida.

Once it launches, TESS will look for new planets that orbit bright stars relatively close to Earth. We’re expecting to find giant planets, like Jupiter, but we’re also predicting we’ll find Earth-sized planets. Most of those planets will be within 300 light-years of Earth, which will make follow-up studies easier for other observatories.

TESS will find these new exoplanets by looking for their transits. A transit is a temporary dip in a star’s brightness that happens with predictable timing when a planet crosses between us and the star. The information we get from transits can tell us about the size of the planet relative to the size of its star. We’ve found nearly 3,000 planets using the transit method, many with our Kepler space telescope. That’s over 75% of all the exoplanets we’ve found so far!

TESS will look at nearly the entire sky (about 85%) over two years. The mission divides the sky into 26 sectors. TESS will look at 13 of them in the southern sky during its first year before scanning the northern sky the year after.

What makes TESS different from the other planet-hunting missions that have come before it? The Kepler mission (yellow) looked continually at one small patch of sky, spotting dim stars and their planets that are between 300 and 3,000 light-years away. TESS (blue) will look at almost the whole sky in sections, finding bright stars and their planets that are between 30 and 300 light-years away.

TESS will also have a brand new kind of orbit (visualized below). Once it reaches its final trajectory, TESS will finish one pass around Earth every 13.7 days (blue), which is half the time it takes for the Moon (gray) to orbit. This position maximizes the amount of time TESS can stare at each sector, and the satellite will transmit its data back to us each time its orbit takes it closest to Earth (orange).

Kepler’s goal was to figure out how common Earth-size planets might be. TESS’s mission is to find exoplanets around bright, nearby stars so future missions, like our James Webb Space Telescope, and ground-based observatories can learn what they’re made of and potentially even study their atmospheres. TESS will provide a catalog of thousands of new subjects for us to learn about and explore.

The TESS mission is led by MIT and came together with the help of many different partners. Learn more about TESS and how it will further our knowledge of exoplanets, or check out some more awesome images and videos of the spacecraft. And stay tuned for more exciting TESS news as the spacecraft launches!
Watch the Launch + More!

Sunday, April 15 11 a.m. EDT - NASA Social Mission Overview
Join mission experts to learn more about TESS, how it will search for worlds beyond our solar system and what scientists hope to find! Have questions? Use #askNASA to have them answered live during the broadcast.
Watch HERE.
1 p.m. EDT - Prelaunch News Conference
Get an update on the spacecraft, the rocket and the liftoff operations ahead of the April 16 launch! Have questions? Use #askNASA to have them answered live during the broadcast.
Watch HERE.
3 p.m. EDT - Science News Conference
Hear from mission scientists and experts about the science behind the TESS mission. Have questions? Use #askNASA to have them answered live during the broadcast.
Watch HERE.
4 p.m. EDT - TESS Facebook Live
This live show will dive into the science behind the TESS spacecraft, explain how we search for planets outside our solar system and will allow you to ask your questions to members of the TESS team.
Watch HERE.
Monday, April 16 10 a.m. EDT - NASA EDGE: TESS Facebook Live
This half-hour live show will discuss the TESS spacecraft, the science of searching for planets outside our solar system, and the launch from Cape Canaveral.
Watch HERE.
1 p.m. EDT - Reddit AMA
Join us live on Reddit for a Science AMA to discuss the hunt for exoplanets and the upcoming launch of TESS!
Join in HERE.
6 p.m. EDT - Launch Coverage!
TESS is slated to launch at 6:32 p.m. EDT on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from our Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
Watch HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

I remember These! I wonder what has ever happened to Them?
Mixing Salts of Different Metals.
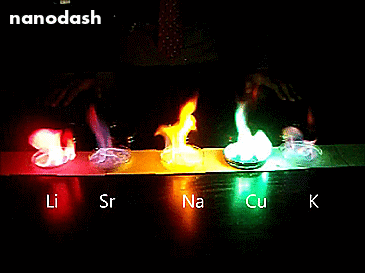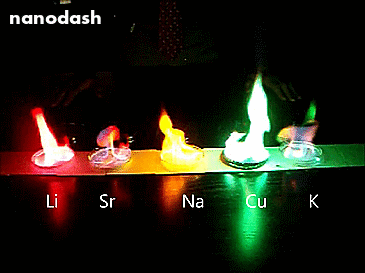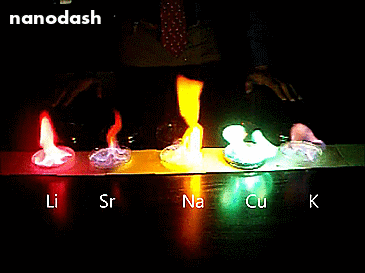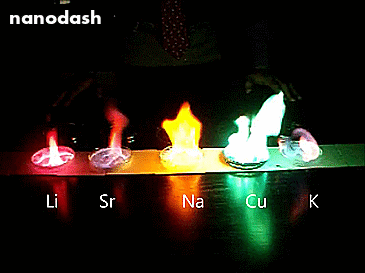
So this is what happens when you mix salts of different metals (Lithium, Strontium, Sodium, Copper, and Potassium) into methanol and then light that sucker.
Pretty colours is what.
Each metal has a different configuration of electrons orbiting in the atom. When the different atoms get energy from the heat, the electrons in the different metals will be excited by a different amount. When they de-excite they release that energy as light. Different metals release different eneriges. Different energies is different colours. The more energy, the violeter the light.
Using different metal salts is also how fireworks do the thing.
See the streetlight yellow in the Sodium (Na)? Well that’s because we use sodium lamps in streetlights
Driving Policy and Driverless Vehicles.
“Communism deprives no man of the power to appropriate the products of society; all that it does is to deprive him of the power to subjugate the labor of others by means of such appropriations.”
— Karl Marx/Friedrich Engels, “The Communist Manifesto”
With Net Neutrality On The Chopping Block, Communities Are Taking Matters Into their Own Hands—And Scaring The Hell Out Of Comcast
