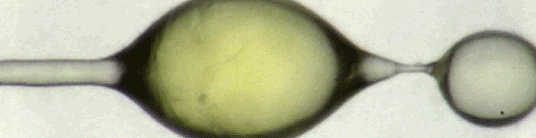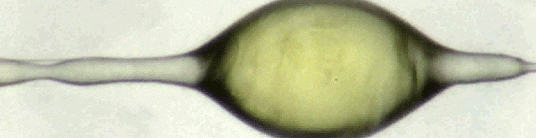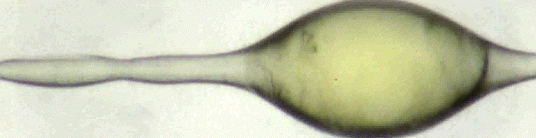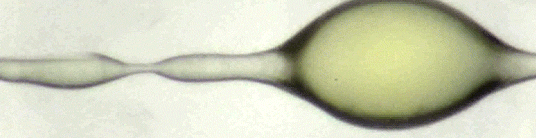
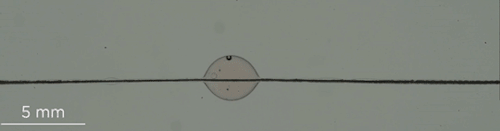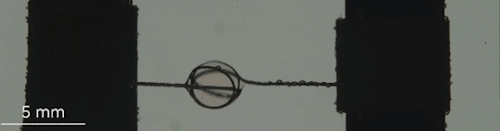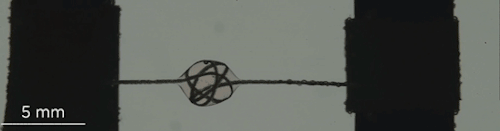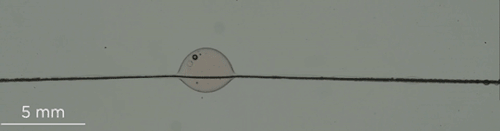
Can You Lick The Science? An abbreviated list.
Can you lick the science? An abbreviated list.
Genetics: Do not. Unless cheek swabs?
Chemistry: NO!!!!! DO NOT!!!!!!
Archaeology: Perhaps. But might be human bone.
Geology: Sometimes needed, sometimes dangerous
Psychology: Best not.
Physics: ????????? How??????
Zoology: In zoology, science licks you.
More Posts from Drunkscience4u and Others
https://www.facebook.com/drunkscience4u/videos/1418162364863308/
We all know this struggle, Cylinder. We all know. March 4, we make their dreams come true on YouTube! Tune in!

Old but gold 💛







This Black History Month, let’s celebrate the first African-American woman who traveled in space.

Let’s celebrate black people, who made history! This is so important to know that some of us didn’t give up and were strong enough to achieve something great like this. These stories are inspirational , but we don’t see them in our history books. Even though she was told women can’t go into space, she never stopped believing in her dreams.
“As a little girl, I was excited, and people kept trying to explain to me why women couldn’t go into space,” Jemison said, according to the university’s student newspaper, The Plainsman. “I always thought they were full of it.”
She’s the role model for every black kid, who has big dreams! She is a living proof everything’s possible!
#BlackHistoryMonth

Chop a magnet in two, and it becomes two smaller magnets. Slice again to make four. But the smaller magnets get, the more unstable they become; their magnetic fields tend to flip polarity from one moment to the next. Now, however, physicists have managed to create a stable magnet from a single atom.
The team, who published their work in Nature on 8 March1, used their single-atom magnets to make an atomic hard drive. The rewritable device, made from 2 such magnets, is able to store just 2 bits of data, but scaled-up systems could increase hard-drive storage density by 1,000 times, says Fabian Natterer, a physicist at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (EPFL) in Lausanne, and author of the paper.
“It’s a landmark achievement,” says Sander Otte, a physicist at Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands. “Finally, magnetic stability has been demonstrated undeniably in a single atom.”
Continue Reading.

The Juno mission has been revealing angles of Jupiter we’ve never seen before. This photo shows Jupiter’s northern temperate latitudes and NN-LRS-1, a.k.a. the Little Red Spot (lower left), the third largest anticyclone on Jupiter. The Little Red Spot is a storm roughly the size of the Earth and was first observed in 1993. As an anticyclone, it has large-scale rotation around a core of high pressure and rotates in a clockwise direction since it is in the northern hemisphere. Jupiter’s anticyclones seem to be powered by merging with other storms; in 1998, the Little Red Spot merged with three other storms that had existed for decades. (Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS/Gerald Eichstaedt/John Rogers; via Bad Astronomy)
-
 bajiion liked this · 6 days ago
bajiion liked this · 6 days ago -
 jollycooperative liked this · 1 week ago
jollycooperative liked this · 1 week ago -
 seidmadr-secrets reblogged this · 1 week ago
seidmadr-secrets reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 qualitymoonsuit reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
qualitymoonsuit reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 crazyworldhuh reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
crazyworldhuh reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 spiritwholovesart liked this · 3 weeks ago
spiritwholovesart liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 pandaheart333 liked this · 3 weeks ago
pandaheart333 liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 the-dumpster-fire-of-anxiety reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
the-dumpster-fire-of-anxiety reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 bunnyliquefaction reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
bunnyliquefaction reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 incidentalsynthesis reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
incidentalsynthesis reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 tanuki1029 reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
tanuki1029 reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 furry-with-too-many-fox-ocs reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
furry-with-too-many-fox-ocs reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 james-the-axew reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
james-the-axew reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 james-the-axew liked this · 3 weeks ago
james-the-axew liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 wwwwyamd reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
wwwwyamd reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 wwwwyamd liked this · 3 weeks ago
wwwwyamd liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 fishfrommars reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
fishfrommars reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 fishfrommars liked this · 3 weeks ago
fishfrommars liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 therearenouniquenames reblogged this · 4 weeks ago
therearenouniquenames reblogged this · 4 weeks ago -
 punch-facists liked this · 1 month ago
punch-facists liked this · 1 month ago -
 corvidcrafts273 reblogged this · 1 month ago
corvidcrafts273 reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 noattentionsstuff liked this · 1 month ago
noattentionsstuff liked this · 1 month ago -
 ardentteadrinker liked this · 1 month ago
ardentteadrinker liked this · 1 month ago -
 pikertwoelectricboogaloo reblogged this · 1 month ago
pikertwoelectricboogaloo reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 pikerthedog liked this · 1 month ago
pikerthedog liked this · 1 month ago -
 starrybobatea liked this · 1 month ago
starrybobatea liked this · 1 month ago -
 tiramewsu-xx reblogged this · 1 month ago
tiramewsu-xx reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 tiramewsu-xx liked this · 1 month ago
tiramewsu-xx liked this · 1 month ago -
 spaceenthusiastgremlin liked this · 2 months ago
spaceenthusiastgremlin liked this · 2 months ago -
 rayvenwithawhy liked this · 2 months ago
rayvenwithawhy liked this · 2 months ago -
 radio-show liked this · 3 months ago
radio-show liked this · 3 months ago -
 healerqueen reblogged this · 3 months ago
healerqueen reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 keeperofbloodpuding reblogged this · 3 months ago
keeperofbloodpuding reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 keeperofbloodpuding liked this · 3 months ago
keeperofbloodpuding liked this · 3 months ago -
 gumbootrambles liked this · 3 months ago
gumbootrambles liked this · 3 months ago -
 proud-memer reblogged this · 3 months ago
proud-memer reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 red-winter-is-coming liked this · 3 months ago
red-winter-is-coming liked this · 3 months ago -
 red-winter-is-coming reblogged this · 3 months ago
red-winter-is-coming reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 wisekoalanightmare reblogged this · 3 months ago
wisekoalanightmare reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 alexthespaceace liked this · 3 months ago
alexthespaceace liked this · 3 months ago -
 ohaiiipinkelephants liked this · 4 months ago
ohaiiipinkelephants liked this · 4 months ago -
 midi-san liked this · 4 months ago
midi-san liked this · 4 months ago -
 booklover4211 liked this · 4 months ago
booklover4211 liked this · 4 months ago -
 astralnexus432 liked this · 4 months ago
astralnexus432 liked this · 4 months ago -
 brilledcheese reblogged this · 4 months ago
brilledcheese reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 sirkazum liked this · 5 months ago
sirkazum liked this · 5 months ago -
 unsupervisedweirdo reblogged this · 5 months ago
unsupervisedweirdo reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 unsupervisedweirdo liked this · 5 months ago
unsupervisedweirdo liked this · 5 months ago -
 sketching-and-digital-artist liked this · 5 months ago
sketching-and-digital-artist liked this · 5 months ago
The official page of Drunk Science! An enthusiastic host performs simple experiments and then humorously explains the science behind the result, all while visibly drunk.
126 posts