I Want To Live With SOFIA In The Sky
I want to live with SOFIA in the sky
What's Inside SOFIA? High Flying Instruments

Our flying observatory, called SOFIA, carries a 100-inch telescope inside a Boeing 747SP aircraft. Having an airborne observatory provides many benefits.

It flies at 38,000-45,000 feet – above 99% of the water vapor in Earth’s atmosphere that blocks infrared light from reaching the ground!

It is also mobile! We can fly to the best vantage point for viewing the cosmos. We go to Christchurch, New Zealand, nearly every year to study objects best observed from the Southern Hemisphere. And last year we went to Daytona Beach, FL, to study the atmosphere of Neptune’s moon Triton while flying over the Atlantic Ocean.

SOFIA’s telescope has a large primary mirror – about the same size as the Hubble Space Telescope’s mirror. Large telescopes let us gather a lot of light to make high-resolution images!

But unlike a space-based observatory, SOFIA returns to our base every morning.

Which means that we can change the instruments we use to analyze the light from the telescope to make many different types of scientific observations. We currently have seven instruments, and new ones are now being developed to incorporate new technologies.
So what is inside SOFIA? The existing instruments include:

Infrared cameras that can peer inside celestial clouds of dust and gas to see stars forming inside. They can also study molecules in a nebula that may offer clues to the building blocks of life…

…A polarimeter, a device that measures the alignment of incoming light waves, that we use to study magnetic fields. The left image reveals that hot dust in the starburst galaxy M82 is magnetically aligned with the gas flowing out of it, shown in blue on the right image from our Chandra X-ray Observatory. This can help us understand how magnetic fields affect how stars form.

…A tracking camera that we used to study New Horizon’s post-Pluto flyby target and found that it may have its own moon…

…A spectrograph that spreads light into its component colors. We’re using one to search for signs of water plumes on Jupiter’s icy moon Europa and to search for signs of water on Venus to learn about how it lost its oceans…

…An instrument that studies high energy terahertz radiation with 14 detectors. It’s so efficient that we made this map of Orion’s Horsehead Nebula in only four hours! The map is made of 100 separate views of the nebula, each mapping carbon atoms at different velocities.

…And we have an instrument under construction that will soon let us study how water vapor, ice and oxygen combine at different times during planet formation, to better understand how these elements combine with dust to form a mass that can become a planet.

Our airborne telescope has already revealed so much about the universe around us! Now we’re looking for the next idea to help us use SOFIA in even more new ways.
Discover more about our SOFIA flying observatory HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
More Posts from Duxgregis and Others
Ain't we?


6/10 favorite quotes - Big damn heroes, sir.




(via BoringEnormous)










Delicate Temporary Tattoos That Look Like Real Watercolor Illustrations
London-based brand and temporary tattoo designers PAPERSELF prides itself in the creation of artistic temporary tattoos. Adorned with soft pastels and inspired by nature, the watercolor-like temporary tattoos are unique. They follow the new trend of artistic temporary tattoos, which mimic the delicacy of watercolor paintings. Find their entire collection in their Etsy shop.
View similar posts here!
Gifts for every budget
Personalized and custom jewelry
Jewelry shop
Gifts for her
Home gallery
Topic: Etsy, Illustration, Temporary Tattoos, Tattoos || by STAFF

Neil 2020





8.28.17
Happy 4th of July… From Space!
In Hollywood blockbusters, explosions and eruptions are often among the stars of the show. In space, explosions, eruptions and twinkling of actual stars are a focus for scientists who hope to better understand their births, lives, deaths and how they interact with their surroundings. Spend some of your Fourth of July taking a look at these celestial phenomenon:

Credit: NASA/Chandra X-ray Observatory
An Astral Exhibition
This object became a sensation in the astronomical community when a team of researchers pointed at it with our Chandra X-ray Observatory telescope in 1901, noting that it suddenly appeared as one of the brightest stars in the sky for a few days, before gradually fading away in brightness. Today, astronomers cite it as an example of a “classical nova,” an outburst produced by a thermonuclear explosion on the surface of a white dwarf star, the dense remnant of a Sun-like star.

Credit: NASA/Hubble Space Telescope
A Twinkling Tapestry
The brilliant tapestry of young stars flaring to life resemble a glittering fireworks display. The sparkling centerpiece is a giant cluster of about 3,000 stars called Westerlund 2, named for Swedish astronomer Bengt Westerlund who discovered the grouping in the 1960s. The cluster resides in a raucous stellar breeding ground located 20,000 light-years away from Earth in the constellation Carina.
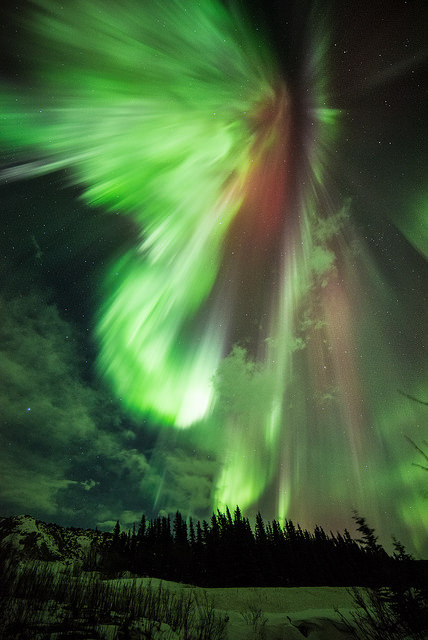

Credit: NASA/THEMIS/Sebastian Saarloos
An Illuminating Aurora
Sometimes during solar magnetic events, solar explosions hurl clouds of magnetized particles into space. Traveling more than a million miles per hour, these coronal mass ejections, or CMEs, made up of hot material called plasma take up to three days to reach Earth. Spacecraft and satellites in the path of CMEs can experience glitches as these plasma clouds pass by. In near-Earth space, magnetic reconnection incites explosions of energy driving charged solar particles to collide with atoms in Earth’s upper atmosphere. We see these collisions near Earth’s polar regions as the aurora. Three spacecraft from our Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms (THEMIS) mission, observed these outbursts known as substorms.

Credit: NASA/Hubble Space Telescope//ESA/STScI
A Shining Supermassive Merger
Every galaxy has a black hole at its center. Usually they are quiet, without gas accretions, like the one in our Milky Way. But if a star creeps too close to the black hole, the gravitational tides can rip away the star’s gaseous matter. Like water spinning around a drain, the gas swirls into a disk around the black hole at such speeds that it heats to millions of degrees. As an inner ring of gas spins into the black hole, gas particles shoot outward from the black hole’s polar regions. Like bullets shot from a rifle, they zoom through the jets at velocities close to the speed of light. Astronomers using our Hubble Space Telescope observed correlations between supermassive black holes and an event similar to tidal disruption, pictured above in the Centaurus A galaxy.

Credit: NASA/Hubble Space Telescope/ESA
A Stellar Explosion
Supernovae can occur one of two ways. The first occurs when a white dwarf—the remains of a dead star—passes so close to a living star that its matter leaks into the white dwarf. This causes a catastrophic explosion. However most people understand supernovae as the death of a massive star. When the star runs out of fuel toward the end of its life, the gravity at its heart sucks the surrounding mass into its center. At the turn of the 19th century, the binary star system Eta Carinae was faint and undistinguished. Our Hubble Telescope captured this image of Eta Carinae, binary star system. The larger of the two stars in the Eta Carinae system is a huge and unstable star that is nearing the end of its life, and the event that the 19th century astronomers observed was a stellar near-death experience. Scientists call these outbursts supernova impostor events, because they appear similar to supernovae but stop just short of destroying their star.

Credit: NASA/GSFC/SDO
An Eye-Catching Eruption
Extremely energetic objects permeate the universe. But close to home, the Sun produces its own dazzling lightshow, producing the largest explosions in our solar system and driving powerful solar storms.. When solar activity contorts and realigns the Sun’s magnetic fields, vast amounts of energy can be driven into space. This phenomenon can create a sudden flash of light—a solar flare.The above picture features a filament eruption on the Sun, accompanied by solar flares captured by our Solar Dynamics Observatory.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
My kind of lady

Happy birthday, Marie Curie! In 1903, Curie and her husband shared a Nobel Prize in Physics for the discovery of radium and polonium. She was the first woman to win this award and later, the first woman to become a professor at the University of Paris. In 1911 she won another Nobel Prize, this time in chemistry, for producing radium as a pure metal and for further studies on radioactive elements. During World War I, she devoted herself to using radioactivity to help people. She set up mobile x-ray vehicles for soldiers in France, which were nicknamed petites Curies (“little Curies”). In the 1920s, radium was considered a miracle cure—you could even buy “Radium” brand butter, cigarettes, and beer. We now know that radioactivity itself causes cancer, but thanks to Curie, radiation therapy is still used today as an effective way to target cancerous tissues. Photo: Tekniska museet
Sonnet for President Trump
Shall I compare thee to a Shakespeare play? Thou art less clever and less literate, But how else should poor poets have their say? Alas, our leader lacks a donkey’s wit! Sometime too fierce the fire of ego burns, And when a man is made to look a fool, He rages ’gainst the mockery he earns, As little boys will cry when teas’d at school. But thy eternal tantrums shall not wane, Nor shalt thou e’er unclench thy tiny fists, Nor listen when the people dare to say, “’Tis you, dear sir, who made a scene of this.” So long as men can breathe and speech is free, The Bard shall speak and show thy shame to thee.
(4 July 2017, in honor and defense of freedom of artistic expression)
It’s so beautiful. It’s so beautiful it makes me want to cry. It’s the fulfillment of dozens, hundreds, thousands of people’s efforts, but it’s also the fulfillment of an idea suddenly becoming real.
Peter Saulson of Syracuse University, who has spent more than three decades working on the detection of gravitational waves.
Astronomers Strike Gravitational Gold In Colliding Neutron Stars
(via npr)
Au in some stars many, many, many AUs away.
I second this
petition to ban “slideshow” as an article format on the internet
-
 velovelo liked this · 4 years ago
velovelo liked this · 4 years ago -
 hardfarmcroissantskeleton liked this · 4 years ago
hardfarmcroissantskeleton liked this · 4 years ago -
 rodeolex liked this · 4 years ago
rodeolex liked this · 4 years ago -
 murciegalito liked this · 4 years ago
murciegalito liked this · 4 years ago -
 craymor1 reblogged this · 5 years ago
craymor1 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 craymor1 liked this · 5 years ago
craymor1 liked this · 5 years ago -
 brieflyinstantruins liked this · 5 years ago
brieflyinstantruins liked this · 5 years ago -
 oblivious-chaos reblogged this · 5 years ago
oblivious-chaos reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 docfotcho liked this · 5 years ago
docfotcho liked this · 5 years ago -
 ca1iban liked this · 5 years ago
ca1iban liked this · 5 years ago -
 3rdlegend liked this · 5 years ago
3rdlegend liked this · 5 years ago -
 89845aaa liked this · 5 years ago
89845aaa liked this · 5 years ago -
 chinoagogo liked this · 5 years ago
chinoagogo liked this · 5 years ago -
 rostenkowsky liked this · 5 years ago
rostenkowsky liked this · 5 years ago -
 innertracklist liked this · 5 years ago
innertracklist liked this · 5 years ago -
 paprikazz liked this · 5 years ago
paprikazz liked this · 5 years ago -
 misfitwashere liked this · 5 years ago
misfitwashere liked this · 5 years ago -
 7thgenscot liked this · 5 years ago
7thgenscot liked this · 5 years ago -
 truth-of-words liked this · 5 years ago
truth-of-words liked this · 5 years ago -
 thismustbetheplace2be reblogged this · 5 years ago
thismustbetheplace2be reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 mevoyalwerto reblogged this · 5 years ago
mevoyalwerto reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 mevoyalwerto liked this · 5 years ago
mevoyalwerto liked this · 5 years ago -
 repalakiedomer liked this · 5 years ago
repalakiedomer liked this · 5 years ago -
 mechanicalreaper88 liked this · 5 years ago
mechanicalreaper88 liked this · 5 years ago -
 wildlandman liked this · 5 years ago
wildlandman liked this · 5 years ago -
 traveler733 reblogged this · 5 years ago
traveler733 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 grapnel liked this · 5 years ago
grapnel liked this · 5 years ago -
 kogenzen reblogged this · 5 years ago
kogenzen reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 cadoretjerome liked this · 5 years ago
cadoretjerome liked this · 5 years ago -
 nelvaz25 liked this · 5 years ago
nelvaz25 liked this · 5 years ago