Pick Your Favorite Findings From Fermi’s First Decade
Pick Your Favorite Findings From Fermi’s First Decade
The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope has been observing some of the most extreme objects and events in the universe — from supermassive black holes to merging neutron stars and thunderstorms — for 10 years. Fermi studies the cosmos using gamma rays, the highest-energy form of light, and has discovered thousands of new phenomena for scientists.
Here are a few of our favorite Fermi discoveries, pick your favorite in the first round of our “Fermi Science Playoff.”
Colliding Neutron Stars

In 2017, Fermi detected a gamma ray burst at nearly the same moment ground observatories detected gravitational waves from two merging neutron stars. This was the first time light and ripples in space-time were detected from the same source.
The Sun and Moon in Gamma Rays

In 2016, Fermi showed the Moon is brighter in gamma rays than the Sun. Because the Moon doesn’t have a magnetic field, the surface is constantly pelted from all directions by cosmic rays. These produce gamma rays when they run into other particles, causing a full-Moon gamma-ray glow.
Record Rare from a Blazar

The supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy 3C 279 weighs a billion times the mass of our Sun. In June 2015, this blazar became the brightest gamma-ray source in the sky due to a record-setting flare.
The First Gamma-Ray Pulsar in Another Galaxy

In 2015, for the first time, Fermi discovered a gamma-ray pulsar, a kind of rapidly spinning superdense star, in a galaxy outside our own. The object, located on the outskirts of the Tarantula Nebula, also set the record for the most luminous gamma-ray pulsar we’ve seen so far.
A Gamma-Ray Cycle in Another Galaxy

Many galaxies, including our own, have black holes at their centers. In active galaxies, dust and gas fall into and “feed” the black hole, releasing light and heat. In 2015 for the first time, scientists using Fermi data found hints that a galaxy called PG 1553+113 has a years-long gamma-ray emission cycle. They’re not sure what causes this cycle, but one exciting possibility is that the galaxy has a second supermassive black hole that causes periodic changes in what the first is eating.
Gamma Rays from Novae

A nova is a fairly common, short-lived kind of explosion on the surface of a white dwarf, a type of compact star not much larger than Earth. In 2014, Fermi observed several novae and found that they almost always produce gamma-rays, giving scientists a new type of source to explore further with the telescope.
A Record-Setting Cosmic Blast

Gamma-ray bursts are the most luminous explosions in the universe. In 2013, Fermi spotted the brightest burst it’s seen so far in the constellation Leo. In the first three seconds alone, the burst, called GRB 130427A, was brighter than any other burst seen before it. This record has yet to be shattered.
Cosmic Rays from Supernova Leftovers

Cosmic rays are particles that travel across the cosmos at nearly the speed of light. They are hard to track back to their source because they veer off course every time they encounter a magnetic field. In 2013, Fermi showed that these particles reach their incredible speed in the shockwaves of supernova remains — a theory proposed in 1949 by the satellite’s namesake, the Italian-American physicist Enrico Fermi.
Discovery of a Transformer Pulsar

In 2013, the pulsar in a binary star system called AY Sextanis switched from radio emissions to high-energy gamma rays. Scientists think the change reflects erratic interaction between the two stars in the binary.
Gamma-Ray Measurement of a Gravitational Lens

A gravitational lens is a kind of natural cosmic telescope that occurs when a massive object in space bends and amplifies light from another, more distant object. In 2012, Fermi used gamma rays to observe a spiral galaxy 4.03 billion light-years away bending light coming from a source 4.35 billion light-years away.
New Limits on Dark Matter

We can directly observe only 20 percent of the matter in the universe. The rest is invisible to telescopes and is called dark matter — and we’re not quite sure what it is. In 2012, Fermi helped place new limits on the properties of dark matter, essentially narrowing the field of possible particles that can describe what dark matter is.
‘Superflares’ in the Crab Nebula

The Crab Nebula supernova remnant is one of the most-studied targets in the sky — we’ve been looking at it for almost a thousand years! In 2011, Fermi saw it erupt in a flare five times more powerful than any previously seen from the object. Scientists calculate the electrons in this eruption are 100 times more energetic than what we can achieve with particle accelerators on Earth.
Thunderstorms Hurling Antimatter into Space

Terrestrial gamma-ray flashes are created by thunderstorms. In 2011, Fermi scientists announced the satellite had detected beams of antimatter above thunderstorms, which they think are a byproduct of gamma-ray flashes.
Giant Gamma-Ray Bubbles in the Milky Way

Using data from Fermi in 2010, scientists discovered a pair of “bubbles” emerging from above and below the Milky Way. These enormous bubbles are half the length of the Milky Way and were probably created by our galaxy’s supermassive black hole only a few million years ago.
Hint of Starquakes in a Magnetar

Neutron stars have magnetic fields trillions of times stronger than Earth’s. Magnetars are neutron stars with magnetic fields 1,000 times stronger still. In 2009, Fermi saw a storm of gamma-ray bursts from a magnetar called SGR J1550-5418, which scientists think were related to seismic waves rippling across its surface.
A Dark Pulsar

We observe many pulsars using radio waves, visible light or X-rays. In 2008, Fermi found the first gamma-ray only pulsar in a supernova remnant called CTA 1. We think that the “beam” of gamma rays we see from CTA 1 is much wider than the beam of other types of light from that pulsar. Those other beams never sweep across our vision — only the gamma-rays.

Have a favorite Fermi discovery or want to learn more? Cast your vote in the first of four rounds of the Fermi Science Playoff to help rank Fermi’s findings. Or follow along as we celebrate the mission all year.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
More Posts from Primordialbitch and Others
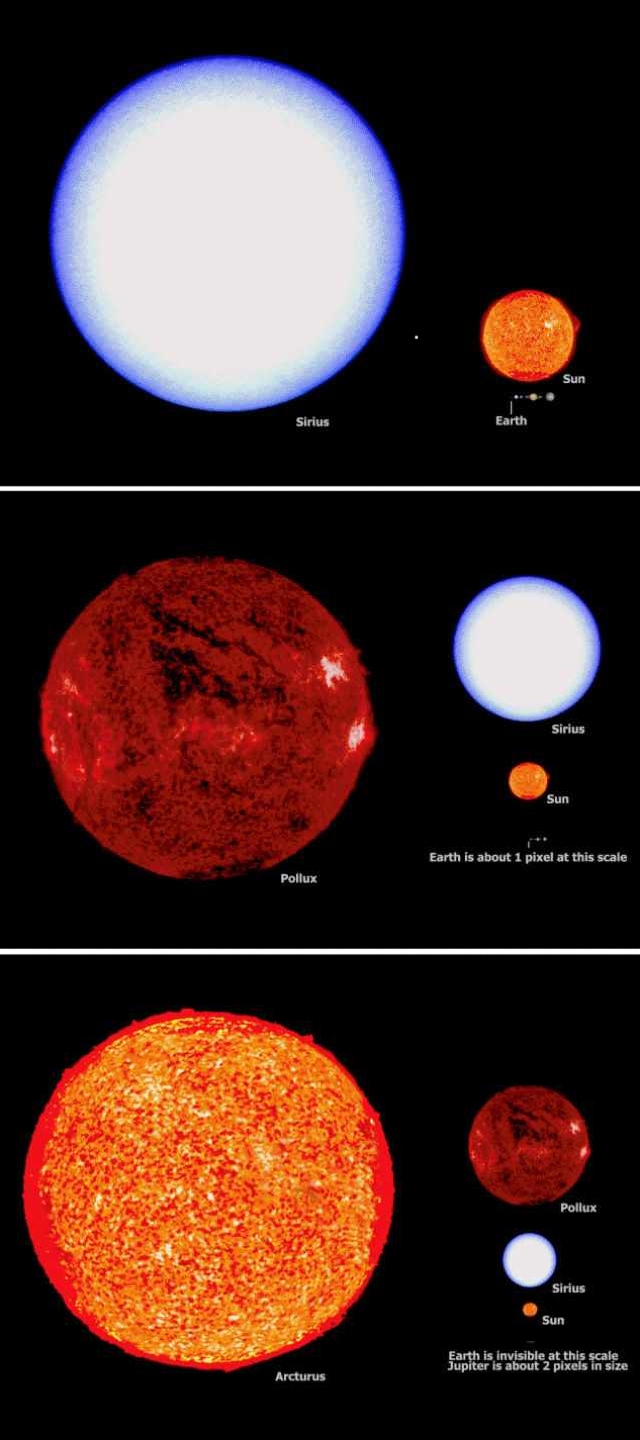







Hubble fortuitously discovers a new galaxy in the cosmic neighborhood
Astronomers using the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope to study some of the oldest and faintest stars in the globular cluster NGC 6752 have made an unexpected finding. They discovered a dwarf galaxy in our cosmic backyard, only 30 million light-years away. The finding is reported in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters.

An international team of astronomers recently used the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope to study white dwarf stars within the globular cluster NGC 6752. The aim of their observations was to use these stars to measure the age of the globular cluster, but in the process they made an unexpected discovery.
Keep reading
Unveiling the Center of Our Milky Way Galaxy

We captured an extremely crisp infrared image of the center of our Milky Way galaxy. Spanning more than 600 light-years, this panorama reveals details within the dense swirls of gas and dust in high resolution, opening the door to future research into how massive stars are forming and what’s feeding the supermassive black hole at our galaxy’s core.

Among the features coming into focus are the jutting curves of the Arches Cluster containing the densest concentration of stars in our galaxy, as well as the Quintuplet Cluster with stars a million times brighter than our Sun. Our galaxy’s black hole takes shape with a glimpse of the fiery-looking ring of gas surrounding it.
The new view was made by the world’s largest airborne telescope, the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, or SOFIA.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
did humans invent math or did we discover it
does math even exist
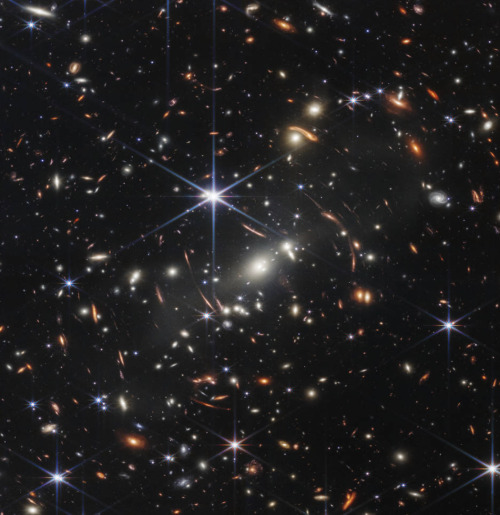

This first image from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is the deepest and sharpest infrared image of the distant universe to date. Known as Webb’s First Deep Field, this image of galaxy cluster SMACS 0723 is overflowing with detail. Thousands of galaxies – including the faintest objects ever observed in the infrared – have appeared in Webb’s view for the first time. This slice of the vast universe covers a patch of sky approximately the size of a grain of sand held at arm’s length by someone on the ground.










Could invisible aliens really exist among us? An astrobiologist explains
by Samantha Rolfe

They probably won’t look anything like this. Martina Badini/Shutterstock
Life is pretty easy to recognise. It moves, it grows, it eats, it excretes, it reproduces. Simple. In biology, researchers often use the acronym “MRSGREN” to describe it. It stands for movement, respiration, sensitivity, growth, reproduction, excretion and nutrition.
But Helen Sharman, Britain’s first astronaut and a chemist at Imperial College London, recently said that alien lifeforms that are impossible to spot may be living among us. How could that be possible?
Keep reading
10 Amazing Space Discoveries by the World’s Largest Flying Observatory

On the night of May 26, 2010, the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, or SOFIA, the world’s largest flying observatory, first peered into the cosmos. Its mission: to study celestial objects and astronomical phenomena with infrared light. Many objects in space emit almost all their energy at infrared wavelengths. Often, they are invisible when observed in ordinary, visible light. Over the last decade, the aircraft’s 106-inch telescope has been used to study black holes, planets, galaxies, star-forming nebulas and more! The observations have led to major breakthroughs in astronomy, revolutionizing our understanding of the solar system and beyond. To celebrate its 10 years of exploration, here’s a look at the top 10 discoveries made by our telescope on a plane:
The Universe’s First Type of Molecule

Scientists believe that around 100,000 years after the big bang, helium and hydrogen combined to make a molecule called helium hydride. Its recent discovery confirms a key part of our basic understanding of the early universe.
A New View of the Milky Way

More than a pretty picture, this panorama of cosmic scale reveals details that can help explain how massive stars are born and what’s feeding our Milky Way galaxy’s supermassive black hole.
When Planets Collide

A double-star system that is more than 300 light-years away likely had an extreme collision between two of its rocky planets. A similar event in our own solar system may have formed our Moon.
How A Black Hole Feasts

Fear not, the dark, my friend. And let the feast begin! Magnetic fields in the Cygnus A galaxy are trapping material where it is close enough to be devoured by a hungry black hole.
Somewhere Like Home

The planetary system around Epsilon Eridani, a star located about 10 light-years away, has an architecture remarkably similar to our solar system. What’s more, its central star is a younger, fainter version of our Sun.
A Quiet Place

Black holes in many galaxies are actively consuming material, but our Milky Way galaxy’s central black hole is relatively quiet. Observations show magnetic fields may be directing material around, not into, the belly of the beast.
The Great Escape

Ever wonder how material leaves a galaxy? The wind flowing from the center of the Cigar Galaxy is so strong it’s pulling a magnetic field — and the mass of 50 to 60 million Suns — with it.
Exploding Star, New Worlds

What happens when a star goes boom? It turns out that supernova explosions can produce a substantial amount of material from which planets like Earth can form.
Stellar Sibling Rivalry

They say siblings need time and space to grow, but here’s one that really needs some room. A newborn star in the Orion Nebula is clearing a bubble of space around it, preventing any new luminous family members from forming nearby.
Clues to Life’s Building Blocks

Radiation from stars is making organic molecules in nebula NGC 7023, also known as the Iris Nebula, larger and more complex. The growth of these molecules is one of the steps that could lead to the emergence of life under the right circumstances.
SOFIA is a modified Boeing 747SP aircraft that allows astronomers to study the solar system and beyond in ways that are not possible with ground-based telescopes. Find out more about the mission at www.nasa.gov/SOFIA.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Faint starlight in Hubble images reveals distribution of dark matter
Astronomers using data from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope have employed a revolutionary method to detect dark matter in galaxy clusters. The method allows astronomers to “see” the distribution of dark matter more accurately than any other method used to date and it could possibly be used to explore the ultimate nature of dark matter. The results were published in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.

In recent decades astronomers have tried to understand the true nature of the mysterious substance that makes up most of the matter in the Universe – dark matter – and to map its distribution in the Universe. Now two astronomers from Australia and Spain have used data from the Frontier Fields programme of the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope to accurately study the distribution of dark matter.
Keep reading
-
 mountaingoat0112 liked this · 2 months ago
mountaingoat0112 liked this · 2 months ago -
 elizasoulmate liked this · 1 year ago
elizasoulmate liked this · 1 year ago -
 jouelacommelara liked this · 1 year ago
jouelacommelara liked this · 1 year ago -
 asabargerthe liked this · 1 year ago
asabargerthe liked this · 1 year ago -
 1-800-forget-me-not liked this · 1 year ago
1-800-forget-me-not liked this · 1 year ago -
 gsunny6 liked this · 2 years ago
gsunny6 liked this · 2 years ago

