T-b-a-blr-blog - Untitled

More Posts from T-b-a-blr-blog and Others

Palmoplantar Rash - Secondary Syphilis
classically a generalised polymorphic rash
usually non-itchy, often affecting palms + soles
important to exclude HIV seroconversion
similar appearance to “target lesions” of erythema multiforme
diagnosis —> syphilis serology

A fib = no p wave
hey! could you do a study tips post on studying w friends who aren't doing the same subjects? like, how to make good flashcards/questions and answers etc so they can quiz you and give you hints etc even if they don't know the content?
How to Effectively Study with Friends
Using Flash Cards
Oh easy peasy! Simply write examination style questions on your flashcards - that way when your friends read the questions out to you, you’ll be testing yourself in a way that might show up on the easier exam questions. Reason being that in order to cover all the topics, your questions will tend to be somewhat simple e.g. describe the different components of x, explaining how they related to y. Obviously, flash cards aren’t the best way to study more complex interrelationships between ideas/concepts, which should be explored more in a mind map fashion. For tips on mind maps, you can check out my briefing here.
Using Your Existing Study Notes
Other than flash cards, if you intend to study in groups for most subjects, one of the best ways to do that is to use the Cornell Notetaking System (which you can read about with my personal tips here). Writing the questions out as you study saves you the trouble of writing out questions for your friends to test you on, and as well as that, means you can test yourself almost as well without them for any times when you’re studying solitary.
Using Essay or Long Response Questions
For long response essays, it’s better to use principles like the rubber duck method, i.e. explaining how concepts relate to each other as if the other person doesn’t know anything about it. So give your friends a list of essay questions and explain part by part in a logical sequential order how you would answer that question e.g. I would talk about the involvement of person A in event B, and explain their impact through examples C, D and E, etc.
Choosing the Right Study Group
Most of all, make sure you rally and encourage each other. Work with people who are like-minded, rotate between each other and have someone who will keep the others on task when you start getting too carried away when studying. Having a goal on what you intend to get finished during a group study session will make sure you always get more out of the session than studying alone!

Hope that helps! ^_^
Cysteine Growth Requirements
MICROBIOLOGY MNEMONIC
BoyFriend Lost Penis
B rucella
F rancisella
L egionella
P asteurella
or….
The four sisters “Ella” worship in the “cystein” chapel
Brucella
Francisella
Legionella
Pasteurella
Anaerobic ABC
A ctinomyces
B acteroides
C lostridium




11.19.17
2 more days until break
Music mood: Mili - Miracle Milk

DNA viruses Mnemonic
NOT MINE!!!! This brilliant mnemonic was created by the youtuber 100lyric. Here are the videos explaining this super useful visual aid:
“Easy ways to remember DNA viruses”
“Easy ways to remember DNA viruses part 2”
I just recreated the drawing she made and added a couple of things, to remember detaiIs better.
All DNA viruses are ds except Parvovirus = the viruses that have 2 lines, are double stranded.
All DNA viruses are linear except Polyomavirus, Papilomavirus, Hepadnavirus= Not drawn with straight lines (Polyoma, Papiloma: circular; Hepadna: semicircular)
All DNA viruses are icosahedral except Poxvirus= that’s why is in a different color (green). This virus is a complex, diamond shape virus.
All DNA viruses replicate in the nucleus except Poxvirus = that’s why I drew something inside the diamond shape virus, to represent the DNA-dependant RNA polymerase.
Like I said, this is NOT MY MNEMONIC! But it helped me a lot, and now it’s so easy for me to remember this viruses! Please, go subscribe to her channel, is amazing!!!! 100lyric
And If you need a mnemonic to remember RNA viruses, click here and here.
Hope this helps!
Hi :) I'm considering doing optom at unsw next year and I was wondering how the job prospects are currently? I've heard that it'll be a saturated job market in the next few years so I'm not if its a worthwhile investment, as I'm from WA and although I'm genuinely interested, a really big factor is the $ ahaha. Also I was wondering what the community life at the uni, since I'm a bit worried I wont make any friends lmaoo? Also how difficult is the workload as compared to year 12? Thanks so much <3
Job Market re: Australia
Hey! Keep in mind, this is what info I’ve been hearing from colleagues as well as some optometrists who are hiring. If you’re from WA, then I would say that you don’t have to worry about saturated job markets if you’re going to return to your home state after graduating. I’ve heard you can get $100K starting salary even relatively close to the city. Melbourne and Sydney though are probably closer to hitting saturation, but they’re capping university take ins next year, so again it could be a completely different ballgame by the time you get out in Sydney and Melbourne. WA though is totally safe, I believe they’re underserviced because there are no optometry schools there. And of course, anywhere that is regional or rural, regardless of state is underserviced, so if you’re cool with moving out to learn a bit more about using your therapeutic skills and ocular disease, then there should be absolutely no problem. Job prospects are only a bit riskier staying with Syd/Melb metro.
Student Life re: UNSW
Pretty friendly on the whole, I believe that because UNSW is one of the newer universities, even the aura here is a bit more cosmopolitan. We definitely have many international students, and also there are a lot of 1st years who are super bubbly because 1) it’s a new experience and they’re excited and 2) it’s a new environment and they’re apprehensive about making friends. So literally everyone feels the same way and as long as you make a little effort to get to know someone, it’ll be more than reciprocated. Just large cliques of high school friends may be trickier to break, because it’s difficult to broach friendship with someone who’s already 6 years deep in friendship with others and still not interested in making new friends.
Also, see these posts that I’ve written about making friends because I keep getting questions about it somehow LOL
Making Conversation - a guide for introverts!
Making Friends
Part 4 Extra-Curriculars
Part 6 Social Life
High School vs. University Workload
As a precursor, no matter what the degree, studying anything at a tertiary level is going to be a challenge, not necessarily difficult. Particular degrees might be easy/hard to particular people, etc. If you’d like to know more about university I have a whole series on it.
Read this for a summary: Transitioning from High School to University
Part 0 Choosing a Degree
Part 1 Administration
Part 2 Getting to Class - pros and cons of attending class, when you should choose not to attend, laptop and notebook recommendations, advice about choosing a backpack and other essential equipment.
> Laptop Considerations and Recommendations
Part 3 Studying
Part 4 Extra-Curriculars
Part 5 Exams
Part 6 Social Life
Part 7 Part Time Work
Part 8 Four Secrets The Uni Tells You
Part 9 Best Study Spots On Campus
Part 10 Saving Money 1 - Food, Transport, Entertainment
Part 10 Saving Money 2 - Textbooks, Tax, Scholarships
Part 11 Adapting to Uni Study popular!!
Part 12 How to Study From Textbooks in Uni
Part 13 Dealing with Lazy Group Members
But granted, I’m going to say that optometry is hard. Personally I would say, and I’ve also had someone describe to me, that it’s like doing 2 HSC exams every year because of the amount of info that you have to cram into 13 weeks of a semester. I’ve had a guest lecturer who was an ophthalmologist who originally graduated as an optometrist, worked for a while and then did the GAMSAT and post-grad medicine and he told us that optometry was more difficult than the generalist medical degree. I’ve also heard from numerous other people in the field, relatives, and also heard about families with children studying both optometry and medicine saying that optom undergrad is more difficult. This is most likely because the 5 year degree is meant to give you complete training, compared with medicine where you have a 6-7 year undergrad followed by the 3 year hospital training before another 5 years of specialisation.
Be prepared for hard work and long hours. I said this in a previous ask but at the end of the day, the job that you do as an optometrist requires you to keep an eye out for sight-threatening and life-threatening conditions, as well as to deal with common eye problems day to day, so you need to learn a lot about anatomy and physiology, anatomy of the eye/head/brain and the innervation/blood supply, as well as the diseases that can arise, and how to manage and treat them. Refraction and getting an actual prescription is a skill that needs a lot of practice and refinement too.
See these asks for more details about optometry:
Optometry Prerequisites and Difficulty (yes someone’s asked before :)
Why I Chose Optometry and Comparisons to Other Health Sciences
Entry Requirements at UNSW
Format of the Degree and 1st Year Contact Hours
+ general tag for all optometry related asks
Hope that helps! ^_^
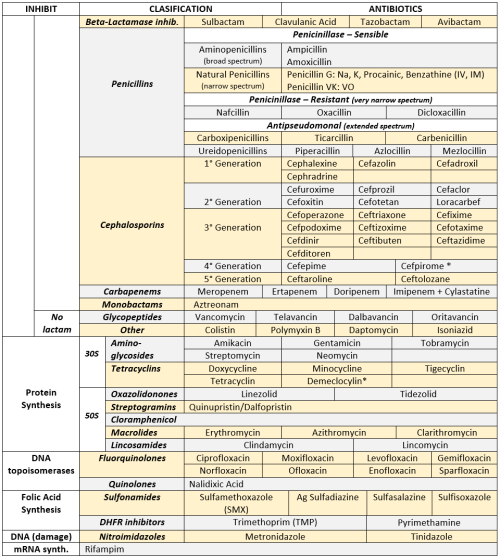
ANTIBIOTICS CHEAT SHEET :)
Also, REMEMBER!!!!
* Sulfonamides compete for albumin with:
Bilirrubin: given in 2°,3°T, high risk or indirect hyperBb and kernicterus in premies
Warfarin: increases toxicity: bleeding
* Beta-lactamase (penicinillase) Suceptible:
Natural Penicillins (G, V, F, K)
Aminopenicillins (Amoxicillin, Ampicillin)
Antipseudomonal Penicillins (Ticarcillin, Piperacillin)
* Beta-lactamase (penicinillase) Resistant:
Oxacillin, Nafcillin, Dicloxacillin
3°G, 4°G Cephalosporins
Carbapenems
Monobactams
Beta-lactamase inhibitors
* Penicillins enhanced with:
Clavulanic acid & Sulbactam (both are suicide inhibitors, they inhibit beta-lactamase)
Aminoglycosides (against enterococcus and psedomonas)
* Aminoglycosides enhanced with Aztreonam
* Penicillins: renal clearance EXCEPT Oxacillin & Nafcillin (bile)
* Cephalosporines: renal clearance EXCEPT Cefoperazone & Cefrtriaxone (bile)
* Both inhibited by Probenecid during tubular secretion.
* 2°G Cephalosporines: none cross BBB except Cefuroxime
* 3°G Cephalosporines: all cross BBB except Cefoperazone bc is highly highly lipid soluble, so is protein bound in plasma, therefore it doesn’t cross BBB.
* Cephalosporines are "LAME“ bc they do not cover this organisms
L isteria monocytogenes
A typicals (Mycoplasma, Chlamydia)
M RSA (except Ceftaroline, 5°G)
E nterococci

* Disulfiram-like effect: Cefotetan & Cefoperazone (mnemonic)
* Cefoperanzone: all the exceptions!!!
All 3°G cephalosporins cross the BBB except Cefoperazone.
All cephalosporins are renal cleared, except Cefoperazone.
Disulfiram-like effect
* Against Pseudomonas:
3°G Cef taz idime (taz taz taz taz)
4°G Cefepime, Cefpirome (not available in the USA)
Antipseudomonal penicillins
Aminoglycosides (synergy with beta-lactams)
Aztreonam (pseudomonal sepsis)
* Covers MRSA: Ceftaroline (rhymes w/ Caroline, Caroline the 5°G Ceph), Vancomycin, Daptomycin, Linezolid, Tigecycline.
* Covers VRSA: Linezolid, Dalfopristin/Quinupristin
* Aminoglycosides: decrease release of ACh in synapse and act as a Neuromuscular blocker, this is why it enhances effects of muscle relaxants.
* DEMECLOCYCLINE: tetracycline that’s not used as an AB, it is used as tx of SIADH to cause Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus (inhibits the V2 receptor in collecting ducts)
* Phototoxicity: Q ue S T ion?
Q uinolones
Sulfonamides
T etracyclines

* p450 inhibitors: Cloramphenicol, Macrolides (except Azithromycin), Sulfonamides
* Macrolides SE: Motilin stimulation, QT prolongation, reversible deafness, eosinophilia, cholestatic hepatitis
* Bactericidal: beta-lactams (penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams, carbapenems), aminoglycosides, fluorquinolones, metronidazole.
* Baceriostatic: tetracyclins, streptogramins, chloramphenicol, lincosamides, oxazolidonones, macrolides, sulfonamides, DHFR inhibitors.
* Pseudomembranous colitis: Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Clindamycin, Lincomycin.
* QT prolongation: macrolides, sometimes fluoroquinolones
-
 seowens88 liked this · 4 years ago
seowens88 liked this · 4 years ago -
 t-b-a-blr-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
t-b-a-blr-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 t-b-a-blr-blog liked this · 6 years ago
t-b-a-blr-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 shreyareddy1111 liked this · 6 years ago
shreyareddy1111 liked this · 6 years ago -
 mahajkhan liked this · 6 years ago
mahajkhan liked this · 6 years ago -
 lumumanandhar-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
lumumanandhar-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 optimisticnachocollector-fd-blog liked this · 8 years ago
optimisticnachocollector-fd-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 paolocabeza-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
paolocabeza-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 paolocabeza-blog liked this · 8 years ago
paolocabeza-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 sofiajamilb-blog liked this · 8 years ago
sofiajamilb-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 dr-pritosh liked this · 8 years ago
dr-pritosh liked this · 8 years ago -
 radhaheidi-blog liked this · 8 years ago
radhaheidi-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 curiosityneverkilled liked this · 9 years ago
curiosityneverkilled liked this · 9 years ago -
 enarmeandoando liked this · 9 years ago
enarmeandoando liked this · 9 years ago -
 alexthesociologist liked this · 10 years ago
alexthesociologist liked this · 10 years ago -
 herrcobaltblue reblogged this · 10 years ago
herrcobaltblue reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 herrcobaltblue liked this · 10 years ago
herrcobaltblue liked this · 10 years ago -
 lockstockbro reblogged this · 10 years ago
lockstockbro reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 ozzies-world liked this · 10 years ago
ozzies-world liked this · 10 years ago -
 princesskatlyn reblogged this · 10 years ago
princesskatlyn reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 ilove-countrygirl liked this · 10 years ago
ilove-countrygirl liked this · 10 years ago -
 e-m-3-l liked this · 10 years ago
e-m-3-l liked this · 10 years ago -
 liruiyu-blog liked this · 10 years ago
liruiyu-blog liked this · 10 years ago -
 secretqueerpersona liked this · 10 years ago
secretqueerpersona liked this · 10 years ago -
 skysurfer-world liked this · 10 years ago
skysurfer-world liked this · 10 years ago -
 terry-may liked this · 10 years ago
terry-may liked this · 10 years ago -
 xuanyirousmle reblogged this · 10 years ago
xuanyirousmle reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 drramit29 liked this · 10 years ago
drramit29 liked this · 10 years ago -
 cacajao reblogged this · 10 years ago
cacajao reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 butternutgutterslut reblogged this · 10 years ago
butternutgutterslut reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 pistachito reblogged this · 10 years ago
pistachito reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 johana--world reblogged this · 10 years ago
johana--world reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 celestialmedicine reblogged this · 10 years ago
celestialmedicine reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 --dopamine reblogged this · 10 years ago
--dopamine reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 abpandanguyen liked this · 10 years ago
abpandanguyen liked this · 10 years ago -
 abpandanguyen reblogged this · 10 years ago
abpandanguyen reblogged this · 10 years ago -
 ah-thenah reblogged this · 10 years ago
ah-thenah reblogged this · 10 years ago