What Have Eclipses Ever Done For Science? Quite A Lot, Actually!
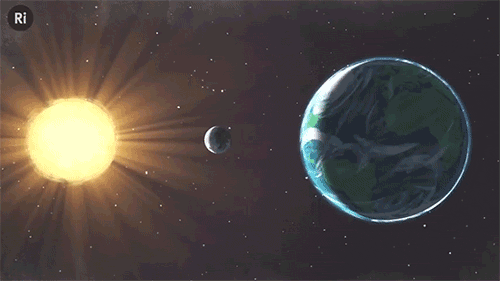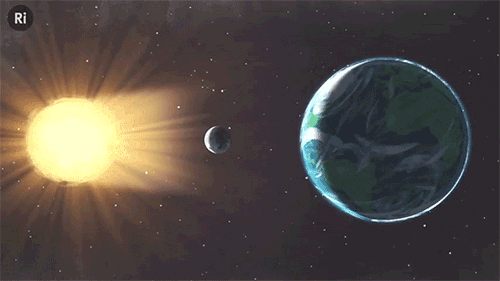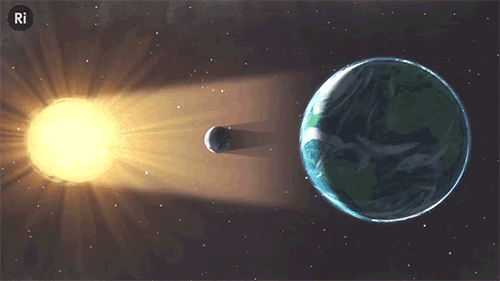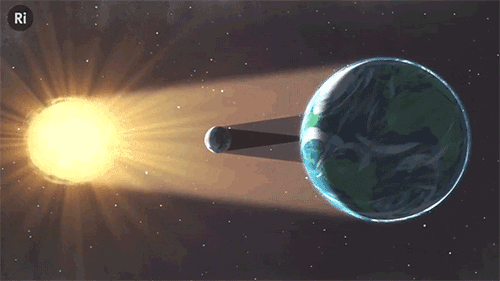
What have eclipses ever done for science? Quite a lot, actually!
The first measurement of the width of the Atlantic ocean in the 16th Century



When British settlers arrived in Virginia in the US, they weren’t sure how far across the globe they’d gone. They recorded the local time of a total eclipse of the moon - which is seen all across the night-time side of the planet. Their colleagues in London did the same, and when the travellers returned they could figure out the five hour time difference.
Edmond Halley discovered that the moon is moving away from the Earth


Halley realised you could back-calculate when previous eclipses would have occurred. But he noticed a mismatch between his predictions and the history books. The reason, he discovered, what that he was assuming the moon stayed the same distance from the Earth. It is actually getting further at about the rate your fingernails grow. And that means that one day (in a few million years, that is), the moon will be too far away to create any more total solar eclipses.
In 1919 a solar eclipse proved Einstein’s theory of relativity

Einstein’s theory predicted that the sun’s gravity should bend the light of nearby stars, meaning that in theory we should be able to see stars that are hidden just behind the sun. However, sunlight always blocks our view of these stars, and it was only during a solar eclipse that there was a short window to see if hidden stars were visible, as predicted. Astronomer Arthur Eddington travelled to West Africa and took photos that proved Einstein right.
Scientists still use solar eclipses today
It’s very hard to study the sun’s corona - a tenuous hot gas, which just one millionth of the light intensity of the sun. The shapes and lines of the corona show the nature of the sun’s magnetic field, and are only visible to study during an eclipse. NASA are also using this opportunity to help create the first thermal map of Mercury!
Want to know more? Watch our full video.
More Posts from T-sci-eng and Others

Superstretchable, supercompressible supercapacitors
Flexible, wearable electronics require equally flexible, wearable power sources. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, Chinese scientists have introduced an extraordinarily stretchable and compressible polyelectrolyte which, in combination with carbon nanotube composite paper electrodes, forms a supercapacitor that can be stretched to 1000 percent in length and compressed to 50 percent in thickness with even gaining, not losing capacity.
Supercapacitors bridge the gap between batteries, which are merely energy-storing devices, and normal capacitors, which release and take up electric energy very quickly but cannot store so much energy. With their ability to charge and release large amounts of electric power in a very short time, supercapacitors are preferably used in regenerative braking, as power buffers in wind turbines, and, increasingly, in consumer electronics such as laptop computers and digital cameras. To make supercapacitors fit for future electrics demands like, for example, wearables and paper electronics, Chunyi Zhi from the City University of Hong Kong and his colleagues are searching for ways to endow them with mechanical flexibility. It can be achieved with a new electrolyte material: they developed a polyelectrolyte that can be stretched more than 10 times its length and compressed to half its thickness retaining full functionality, without breakage, cracking, or other damage to its material.
Read more.






Just imagine a world full of beautiful stained glass windows which also generate electricity…
[Oxford Photovoltaics]




Ceramics: Aluminum Nitride
First synthesized in the late 1800s, aluminum nitride’s potential wasn’t realized until a hundred years later in the late 1900s. AlN is a ceramic with high thermal conductivity but is an electrical insulator. It is classified as a covalent compound, the only stable compound in the binary Al-N system.
AlN is similar in properties to beryllium oxide (BeO), but is cheaper and has less of a potential to be toxic. In addition to the properties mentioned above, this ceramic also has high chemical resistance and exhibits piezoelectric properties.
Thanks to its thermal and electrical conductivity properties, AlN is useful in microelectronics. It is used in microelectronic packaging, surface acoustic wave sensors, in RF filters, as a crucible for the growth of gallium arsenide crystals, in piezoelectric MEMs applications, and many more. In addition, the wurtzite phase of aluminum nitride, w-AlN, is a wide band gap semiconductor material, with potential applications in deep ultraviolet optoelectronics.
Because AlN is a covalent compound, high pressures or sintering aids are required to assist densification during production. Typical additives include rare-earth or alkaline-earth oxides, such as yttrium compounds. The additives and sintering conditions used can alter the properties of commercially available grades of AlN.
Sources: ( 1 ) ( 2 - images 2 and 3 ) ( 3 - images 1 and 4 ) ( 4 )
More Than You Ever Wanted to Know About Mechanical Engineering, Part 33: Stress Concentrations With Fluctuating Stresses
There’s one last complication to consider with fluctuating stresses. When we looked at the case of fully reversed stresses (that is, σ_m = 0, σ_a ≠ 0) we found a fatigue stress concentration factor based on the stress concentration factor for a static situation.
With a fluctuating stress, the situation is a little different. Since the mean stress is non-zero, the part is always under some kind of load. We can consider the effects of this constant mean stress separately from the effects of the momentary alternating stress and assign them a separate fatigue stress concentration factor, which we’ll call K_fm.
Let’s think about what’s actually physically happening to a part being subjected to a fluctuating stress. Let’s say we’re dealing with a plate with a slot in it subjected to fluctuating tension.

There’s obviously a large stress concentration at the slot that we’ll have to take into account.
There’s three different scenarios which can occur here. The first is that the maximum stress the plate sees (the largest value of combined mean and alternating stress, taking stress concentrations into account) never approaches the yield strength of the material. The plate just stretches and contracts elastically. This isn’t really any different from our previous situation with fatigue stress concentration factors - we can use the K_f factor we got earlier here.

But suppose the yield strength is exceeded. What happens then? If the maximum stress is greater than the yield strength, then the plate must deform plastically at that point of maximum stress - the slot must widen. If the slot is wider, then the stress concentration is relieved - there’s more room for movement before the geometry stops you. If other words, the fatigue stress concentration factor is lessened.
If it’s just your maximum stress that exceeds the yield strength but your minimum stress is still below it, this localized yielding will be one-sided - you’ll get a slot that’s widened on one side, but you’ll still have some overall mean stress. If this is the case, you base your stress concentration factor on the relationship of the mean and alternating stresses to the yield strength.

If both your minimum and maximum stresses exceed the yield strength of the material, you get a situation where you’ve widened the slot as far as you can without actually breaking the part on both sides and you’re experiencing a stress of magnitude equal to the yield strength at either extreme of the fluctuation. Since you now have a fluctuation with equal and opposite extremes, your mean stress is zero - the mean fatigue stress concentration factor is zero. The scenario is now one of fully reversed loading and the mean stress drops right out of it.





Elevated Bus That Drives Above Traffic Jams
10 “Spinoffs of Tomorrow” You Can License for Your Business
The job of the our Technology Transfer Program is pretty straight-forward – bring NASA technology down to Earth. But, what does that actually mean? We’re glad you asked! We transfer the cool inventions NASA scientists develop for missions and license them to American businesses and entrepreneurs. And that is where the magic happens: those business-savvy licensees then create goods and products using our NASA tech. Once it hits the market, it becomes a “NASA Spinoff.”
If you’re imagining that sounds like a nightmare of paperwork and bureaucracy, think again. Our new automated “ATLAS” system helps you license your tech in no time — online and without any confusing forms or jargon.
So, sit back and browse this list of NASA tech ripe for the picking (well, licensing.) When you find something you like, follow the links below to apply for a license today! You can also browse the rest of our patent portfolio - full of hundreds of available technologies – by visiting technology.nasa.gov.

1. Soil Remediation with Plant-Fungal Combinations
Ahh, fungus. It’s fun to say and fun to eat—if you are a mushroom fan. But, did you know it can play a crucial role in helping trees grow in contaminated soil? Scientists at our Ames Research Center discovered that a special type of the fungus among us called “Ectomycorrhizal” (or EM for short) can help enhance the growth of trees in areas that have been damaged, such as those from oil spills.

2. Preliminary Research Aerodynamic Design to Lower Drag
When it comes to aircraft, drag can be, well…a drag. Luckily, innovators at our Armstrong Flight Research Center are experimenting with a new wing design that removes adverse yaw (or unwanted twisting) and dramatically increases aircraft efficiency by reducing drag. Known as the “Preliminary Research Aerodynamic Design to Lower Drag (PRANDTL-D)” wing, this design addresses integrated bending moments and lift to achieve drag reduction.

3. Advancements in Nanomaterials
What do aircraft, batteries, and furniture have in common? They can ALL be improved with our nanomaterials. Nanomaterials are very tiny materials that often have unique optical, electrical and mechanical properties. Innovators at NASA’s Glenn Research Center have developed a suite of materials and methods to optimize the performance of nanomaterials by making them tougher and easier to process. This useful stuff can also help electronics, fuel cells and textiles.

4. Green Precision Cleaning
Industrial cleaning is hard work. It can also be expensive when you have to bring in chemicals to get things squeaky. Enter “Green Precision Cleaning,” which uses the nitrogen bubbles in water instead. The bubbles act as a scrubbing agent to clean equipment. Goddard Space Flight Center scientists developed this system for cleaning tubing and piping that significantly reduces cost and carbon consumption. Deionized water (or water that has been treated to remove most of its mineral ions) takes the place of costlier isopropyl alcohol (IPA) and also leaves no waste, which cuts out the pricey process of disposal. The cleaning system quickly and precisely removes all foreign matter from tubing and piping.

5. Self-Contained Device to Isolate Biological Samples
When it comes to working in space, smaller is always better. Innovators at our Johnson Space Center have developed a self-contained device for isolating microscopic materials like DNA, RNA, proteins, and cells without using pipettes or centrifuges. Think of this technology like a small briefcase full of what you need to isolate genetic material from organisms and microorganisms for analysis away from the lab. The device is also leak-proof, so users are protected from chemical hazards—which is good news for astronauts and Earth-bound scientists alike.

6. Portable, Rapid, Quiet Drill
When it comes to “bringing the boom,” NASA does it better than anyone. But sometimes, we know it’s better to keep the decibels low. That’s why innovators at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory have developed a new handheld drilling device, suitable for a variety of operations, that is portable, rapid and quiet. Noise from drilling operations often becomes problematic because of the location or time of operations. Nighttime drilling can be particularly bothersome and the use of hearing protection in the high-noise areas may be difficult in some instances due to space restrictions or local hazards. This drill also weighs less than five pounds – talk about portable power.

7. Damage Detection System for Flat Surfaces
The ability to detect damage to surfaces can be crucial, especially on a sealed environment that sustains human life or critical equipment. Enter Kennedy Space Center’s damage detection system for flat composite surfaces. The system is made up of layered composite material, with some of those layers containing the detection system imbedded right in. Besides one day potentially keeping humans safe on Mars, this tech can also be used on aircrafts, military shelters, inflatable structures and more.

8. Sucrose-Treated Carbon Nanotube and Graphene Yarns and Sheets
We all know what a spoonful of sugar is capable of. But, who knew it could help make some materials stronger? Innovators at NASA’s Langley Research Center did! They use dehydrated sucrose to create yarns and woven sheets of carbon nanotubes and graphene.
The resulting materials are lightweight and strong. Sucrose is inexpensive and readily available, making the process cost-effective. Makes you look at the sweet substance a little differently, doesn’t it?

9. Ultrasonic Stir Welding
NASA scientists needed to find a way to friction weld that would be gentler on their welding equipment. Meet our next tech, ultrasonic stir welding.
NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center engineers developed ultrasonic stir welding to join large pieces of very high-strength, high-melting-temperature metals such as titanium and Inconel. The addition of ultrasonic energy reduces damaging forces to the stir rod (or the piece of the unit that vibrates so fast, it joins the welding material together), extending its life. The technology also leaves behind a smoother, higher-quality weld.

10. A Field Deployable PiezoElectric Gravimeter (PEG)
It’s important to know that the fuel pumping into rockets has remained fully liquid or if a harmful chemical is leaking out of its container. But each of those things, and the many other places sensors are routinely used, tends to require a specially designed, one-use device.
That can result in time-consuming and costly cycles of design, test and build, since there is no real standardized sensor that can be adapted and used more widely.
To meet this need, the PiezoElectric Gravimeter (PEG) was developed to provide a sensing system and method that can serve as the foundation for a wide variety of sensing applications.

See anything your business could use? Did anything inspire you to start your own company? If so, head to our website at technology.nasa.gov to check them out.
When you’ve found what you need, click, “Apply Now!” Our licensing system, ATLAS, will guide you through the rest.
If the items on this round-up didn’t grab you, that’s ok, too. We have hundreds of other technologies available and ready to license on our website.
And if you want to learn more about the technologies already being used all around you, visit spinoff.nasa.gov.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com



Alloys: 300 series Stainless Steel
When chromium is added to steel in sufficient amounts, it reacts with oxygen on the surface of the metal, creating a thin transparent layer that prevents further oxidation such as rusting. The layer is even self-healing, when damaged by scratches or wear. Steels that have over ten percent chromium added are classified as stainless steels, with high strength and toughness, in addition to the corrosion resistance - and there are hundreds of varieties of stainless steel.
As such, these alloys are divided into types, or series, often defined by their compositions or the methods of forming and working them. The 300 series of stainless steels are austenitic stainless steels, with an austenitic or face-centered cubic crystal structure. They contain anywhere from about 15-30% chromium, as well as up to about 20% nickel and other elements such as molybdenum. The nickel stabilizes the austenitic structure and increases ductility as well as high temperature strength and corrosion resistance.
The 300 series alloys are non-magnetic in the annealed condition, though they can become slightly magnetic when cold worked, depending on the nickel content. Comparatively, these steels have high ductility, low yield stress, and high tensile strengths.
Commonly used 300 series stainless steels include 301, 302, 304, and 316, as well as the low carbon variations of these types, designated with an L, such as 316L. 304 stainless steel is also often called 18/8 stainless steel, given that it has 18% Cr and 8% Ni, or A2 stainless. The 316 grade is also know as A4, or marine grade stainless.
In the photos above, the Gateway Arch in St. Louis is clad in type 304 SS, while the Chrysler Building in New York is clad with Nirosta stainless steel, a form of type 302.
Sources: ( 1 ) ( 2 ) ( 3 ) ( 4 - images 1 and 2 ) ( 5 - image 3 )

How did the Greeks know ?
Greeks had a strong geometric approach towards problems and as a result their methods are very intuitive.
In this post, we will look at the Method of exhaustion formulated by Archimedes that stands out as a milestone in the history of mathematics
Method of Exhaustion - Archimedes

Source
In order to find the bounds of pi, Archimedes came up with a remarkably elegant ‘algorithm’, which is as follows:
Lower bound
Inscribe a n-sided polygon in a circle —> Measure its perimeter(p) —> Measure its diameter(d) —> pi_min = p/d —-> Repeat with n+1 sides.
Upper bound
Circumscribe a n-sided polygon in a circle —> Measure its perimeter(p) —> Measure its diameter(d) —> pi_max = p/d —-> Repeat with n+1 sides.
And by following this procedure one could obtain the upper and lower bounds of pi !
Heres an animation made on geogebra for a circle of diameter 1. Watch how the lower and upper bounds vary.

Archimedes did this for a 96 sided polygon and found the value of pi to be between 3.14103 and 3.1427. This is a good enough approximation for most of the calculations that we do even today!

Happy Holidays !
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Reaching out into space yields benefits on Earth. Many of these have practical applications — but there’s something more than that. Call it inspiration, perhaps, what photographer Ansel Adams referred to as nature’s “endless prospect of magic and wonder.“
Our ongoing exploration of the solar system has yielded more than a few magical images. Why not keep some of them close by to inspire your own explorations? This week, we offer 10 planetary photos suitable for wallpapers on your desktop or phone. Find many more in our galleries. These images were the result of audacious expeditions into deep space; as author Edward Abbey said, "May your trails be crooked, winding, lonesome, dangerous, leading to the most amazing view.”

1. Martian Selfie
This self-portrait of NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover shows the robotic geologist in the “Murray Buttes” area on lower Mount Sharp. Key features on the skyline of this panorama are the dark mesa called “M12” to the left of the rover’s mast and pale, upper Mount Sharp to the right of the mast. The top of M12 stands about 23 feet (7 meters) above the base of the sloping piles of rocks just behind Curiosity. The scene combines approximately 60 images taken by the Mars Hand Lens Imager, or MAHLI, camera at the end of the rover’s robotic arm. Most of the component images were taken on September 17, 2016.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

2. The Colors of Pluto
NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft captured this high-resolution, enhanced color view of Pluto on July 14, 2015. The image combines blue, red and infrared images taken by the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC). Pluto’s surface sports a remarkable range of subtle colors, enhanced in this view to a rainbow of pale blues, yellows, oranges, and deep reds. Many landforms have their own distinct colors, telling a complex geological and climatological story that scientists have only just begun to decode.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

3. The Day the Earth Smiled
On July 19, 2013, in an event celebrated the world over, our Cassini spacecraft slipped into Saturn’s shadow and turned to image the planet, seven of its moons, its inner rings — and, in the background, our home planet, Earth. This mosaic is special as it marks the third time our home planet was imaged from the outer solar system; the second time it was imaged by Cassini from Saturn’s orbit, the first time ever that inhabitants of Earth were made aware in advance that their photo would be taken from such a great distance.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

4. Looking Back
Before leaving the Pluto system forever, New Horizons turned back to see Pluto backlit by the sun. The small world’s haze layer shows its blue color in this picture. The high-altitude haze is thought to be similar in nature to that seen at Saturn’s moon Titan. The source of both hazes likely involves sunlight-initiated chemical reactions of nitrogen and methane, leading to relatively small, soot-like particles called tholins. This image was generated by combining information from blue, red and near-infrared images to closely replicate the color a human eye would perceive.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

5. Catching Its Own Tail
A huge storm churning through the atmosphere in Saturn’s northern hemisphere overtakes itself as it encircles the planet in this true-color view from Cassini. This picture, captured on February 25, 2011, was taken about 12 weeks after the storm began, and the clouds by this time had formed a tail that wrapped around the planet. The storm is a prodigious source of radio noise, which comes from lightning deep within the planet’s atmosphere.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

6. The Great Red Spot
Another massive storm, this time on Jupiter, as seen in this dramatic close-up by Voyager 1 in 1979. The Great Red Spot is much larger than the entire Earth.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

7. More Stormy Weather
Jupiter is still just as stormy today, as seen in this recent view from NASA’s Juno spacecraft, when it soared directly over Jupiter’s south pole on February 2, 2017, from an altitude of about 62,800 miles (101,000 kilometers) above the cloud tops. From this unique vantage point we see the terminator (where day meets night) cutting across the Jovian south polar region’s restless, marbled atmosphere with the south pole itself approximately in the center of that border. This image was processed by citizen scientist John Landino. This enhanced color version highlights the bright high clouds and numerous meandering oval storms.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

8. X-Ray Vision
X-rays stream off the sun in this image showing observations from by our Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, overlaid on a picture taken by our Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). The NuSTAR data, seen in green and blue, reveal solar high-energy emission. The high-energy X-rays come from gas heated to above 3 million degrees. The red channel represents ultraviolet light captured by SDO, and shows the presence of lower-temperature material in the solar atmosphere at 1 million degrees.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

9. One Space Robot Photographs Another
This image from NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows Victoria crater, near the equator of Mars. The crater is approximately half a mile (800 meters) in diameter. It has a distinctive scalloped shape to its rim, caused by erosion and downhill movement of crater wall material. Since January 2004, the Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity has been operating in the region where Victoria crater is found. Five days before this image was taken in October 2006, Opportunity arrived at the rim of the crater after a drive of more than over 5 miles (9 kilometers). The rover can be seen in this image, as a dot at roughly the “ten o'clock” position along the rim of the crater. (You can zoom in on the full-resolution version here.)
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

10. Night Lights
Last, but far from least, is this remarkable new view of our home planet. Last week, we released new global maps of Earth at night, providing the clearest yet composite view of the patterns of human settlement across our planet. This composite image, one of three new full-hemisphere views, provides a view of the Americas at night from the NASA-NOAA Suomi-NPP satellite. The clouds and sun glint — added here for aesthetic effect — are derived from MODIS instrument land surface and cloud cover products.
Full Earth at night map
Americas at night
Discover more lists of 10 things to know about our solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com








Are Cloaking Devices Coming? Metalens-Shaped Light May Lead The Way
“The biggest challenge facing a real-life cloak has been the incorporation of a large variety of wavelengths, as the cloak’s material must vary from point-to-point to bend (and then unbend) the light by the proper amount. Based on the materials discovered so far, we haven’t yet managed to penetrate the visible light portion of the spectrum with a cloak. This new advance in metalenses, however, seems to indicate that if you can do it for a single, narrow wavelength, you can apply this nanofin technology to extend the wavelength covered tremendously. This first application to achromatic lenses covered nearly the full visible-light spectrum (from 470 to 670 nm), and fusing this with advances in metamaterials would make visible-light cloaking devices a reality.”
What would it take to have a true cloaking device? You’d need some way to bend the light coming from all across the electromagnetic spectrum around your cloaked object, and have it propagate off in the same direction once it moved past you. To an outside observer, it would simply seem like the cloaked object wasn’t there, and they’d only view the world in front of and behind them. Even with the recent advances that have been made in metamaterials, we have not yet been able to realize this dream in three dimensions, covering the entire electromagnetic spectrum, and from all directions. But a new advance in metalens technology might get you the full electromagnetic spectrum after all, as they appear to have solved the problem of chromatic aberration with a light, small, and inexpensive solution. If we can combine these two technologies, metalenses and metamaterials, we just might realize the dream of a true invisibility cloak.
Whether you’re a Star Trek or Harry Potter fan, the ability to turn yourself invisible would be Earth-shattering. Come see how transformation optics might transform the world!
-
 wings-scales-fire reblogged this · 5 months ago
wings-scales-fire reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 neuronium liked this · 2 years ago
neuronium liked this · 2 years ago -
 sharkeys-miscellaneous reblogged this · 5 years ago
sharkeys-miscellaneous reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 karyll-axolotl liked this · 5 years ago
karyll-axolotl liked this · 5 years ago -
 percbth liked this · 5 years ago
percbth liked this · 5 years ago -
 marlunaroja liked this · 5 years ago
marlunaroja liked this · 5 years ago -
 dharmatica reblogged this · 5 years ago
dharmatica reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 moonie139 reblogged this · 5 years ago
moonie139 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 progettomorte liked this · 6 years ago
progettomorte liked this · 6 years ago -
 astraasper liked this · 6 years ago
astraasper liked this · 6 years ago -
 noeticlistener19 liked this · 6 years ago
noeticlistener19 liked this · 6 years ago -
 diamondsforlife liked this · 6 years ago
diamondsforlife liked this · 6 years ago -
 bansheenut reblogged this · 6 years ago
bansheenut reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 shadhavar1126 reblogged this · 6 years ago
shadhavar1126 reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 passionfrvttt liked this · 6 years ago
passionfrvttt liked this · 6 years ago -
 destrudovassago liked this · 6 years ago
destrudovassago liked this · 6 years ago -
 n2light432-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
n2light432-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 bitchimabroad-blog liked this · 6 years ago
bitchimabroad-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 misentropy liked this · 6 years ago
misentropy liked this · 6 years ago -
 alt-89 reblogged this · 6 years ago
alt-89 reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 atomiclarka liked this · 6 years ago
atomiclarka liked this · 6 years ago -
 cara-linea reblogged this · 6 years ago
cara-linea reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 marbleowl reblogged this · 6 years ago
marbleowl reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 myparti reblogged this · 6 years ago
myparti reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 thestusci reblogged this · 6 years ago
thestusci reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 imtoohighbabe reblogged this · 6 years ago
imtoohighbabe reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 cnovakw liked this · 6 years ago
cnovakw liked this · 6 years ago -
 syntheticorange liked this · 7 years ago
syntheticorange liked this · 7 years ago -
 brokenmanx reblogged this · 7 years ago
brokenmanx reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 brokenmanx liked this · 7 years ago
brokenmanx liked this · 7 years ago -
 bearmythology liked this · 7 years ago
bearmythology liked this · 7 years ago -
 antonio-teixeira liked this · 7 years ago
antonio-teixeira liked this · 7 years ago -
 ullamars reblogged this · 7 years ago
ullamars reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 ullamars liked this · 7 years ago
ullamars liked this · 7 years ago -
 sharkey1964 liked this · 7 years ago
sharkey1964 liked this · 7 years ago -
 egl74722 reblogged this · 7 years ago
egl74722 reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 nikolaeftimov-blog liked this · 7 years ago
nikolaeftimov-blog liked this · 7 years ago