Https://iglovequotes.net/

https://iglovequotes.net/
More Posts from Tonimichelleluttrell and Others

“To go wrong in one’s own way is better than to go right in someone else’s.”
— Fyodor Dostoyevsky, Crime and Punishment (via books-n-quotes)










Did You Know?
The most professional Feiyue shoes Australia on http://www.icnbuys.com/feiyue-shoes-australia.
“Now that I am in my third year of medical school, I have started to see how health care disparities can have significant impacts on the management and prevention of disease. It is my hope that as the culture of medicine changes ever so slowly more physicians will be aware of the disparities and develop cultural humility to better serve their patient populations.”
An article on health disparities in medicine, by Stephanie Dreikorn at University of California, Riverside School of Medicine

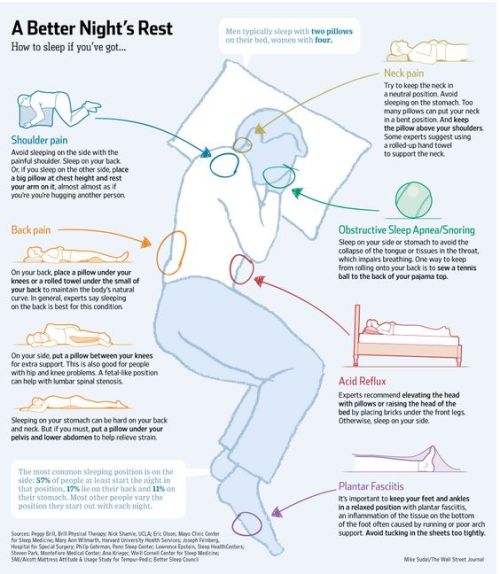





Do you know that your sleeping position are ruining you?
Incorrect sleeping posture leads to six major severe pains.
The easiest way to improve the quality of life.
Click here to learn the correct position for sleep.

Scientists discover schizophrenia gene roles in brain development
A USC research team identified 150 proteins affecting cell activity and brain development that contribute to mental disorders, including schizophrenia, bipolar condition and depression.
It’s the first time these molecules, which are associated with the disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) protein linked to mental disorders, have been identified. The scientists developed new tools involving stem cells to determine chemical reactions the proteins use to influence cell functions and nerve growth in people.
“This moves science closer to opportunities for treatment for serious mental illness,” said Marcelo P. Coba, the study author and professor of psychiatry at the Zilkha Neurogenetic Institute at the Keck School of Medicine of USC.
The findings appear in Biological Psychiatry.
Schizophrenia affects less than 1 percent of the U.S. population, but has an outsized impact on disability, suicide and premature deaths.
The DISC1 gene was linked to schizophrenia nearly 20 years ago. It controls how nerve cells called neurons develop, as well as how the brain matures. DISC1 also directs a network of signals across cells that can contribute to the disease. Scientists say errors in these chemical reactions contribute to schizophrenia.
But the identity of proteins that DISC1 can regulate is poorly understood, prompting the USC researchers and colleagues from the State University of New York Downstate Medical Center to undertake the research. The challenge was to simulate conditions inside the human brain, Coba explained.
Using stem cells, they conducted assays resembling habitat where DISC1 does its work. They then used gene editing to insert a molecular tag on DISC1, allowing them to extract it from brain cells and identify the proteins with which it associates.
Identifying the proteins that interact with DISC1 in brain cells could lead to understanding how the risk factors for psychiatric diseases are connected to specific molecular functions, Coba explained. The discovery enables researchers to determine specific processes that differ in patients suffering from specific mental illnesses.
“This gives researchers specific trails to follow within cells from both healthy patients and those diagnosed with disorders,” Coba said.
Schizophrenia research
Schizophrenia is one of the top 15 leading causes of disability worldwide. People with schizophrenia live an average of nearly 29 years less than those without the disorder, according to the National Institutes of Mental Health (NIMH).
The illness is often accompanied by conditions such as heart disease and diabetes, which contribute to the high premature mortality rate among people with schizophrenia. About 5 percent of people with schizophrenia die by suicide, a rate far greater than the general population, with the highest risk in the early stages of illness, according to the NIMH.

I love the fact my oldest son still goofs with his momma! So Blessed and thankful. (at Liberty, Kentucky)




✨ Follow @psych2go for more! ✨
✧ Check out our website here ✧
“Once, there stood a tree by the road. High… proud… strong. It stood away from everyone, doing neither good nor harm to anyone. It had never loved anyone, nor had it ever flowered. It was dependent on no-one, and no-one was dependent on it. The tree knew how to keep everyone at bay. The forest, the field… and the road with all its travelers. And it had always been like this. “Say, tree… are you alone here?” asked the cat. “Completely alone,” answered the tree indifferently. “And you are not lonely?” “Not lonely at all,” rustled the tree just as indifferently. “And you never experience sadness, fear or loneliness?” “Never” “I don’t wait for anyone. I don’t need anyone.” “Ah…” said the cat, “how I wish to be independent, live alone, and not grieve for anyone.” “Well now,” said the tree with dignity, “this is not too hard to learn.” “Live with me, observe…” “and when you learn, you will leave and be able to live alone.” “Thank you,” said the cat, and she stayed there. “Where are you going?” moaned the tree. “Goodbye! Now I can live alone,” answered the cat. “Don’t go! You have taught me a lot.” “Stay…” And that is the whole story about the tree. Or rather, about the tree and the cat. Because if not for the cat, the tree would not have had a story to tell.”
— The Tree and the Cat, Written by I. GLEBOVA, Director EVGENII SIVOKON. (via amargedom)
-
 xshycowboyx reblogged this · 5 years ago
xshycowboyx reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 lunajames reblogged this · 5 years ago
lunajames reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 fakesociety reblogged this · 5 years ago
fakesociety reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 fakesociety liked this · 5 years ago
fakesociety liked this · 5 years ago -
 hopefulinstability liked this · 5 years ago
hopefulinstability liked this · 5 years ago -
 sad-enigma reblogged this · 5 years ago
sad-enigma reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 wowmoods reblogged this · 5 years ago
wowmoods reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 slowlyfallinggx reblogged this · 5 years ago
slowlyfallinggx reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 though-i-fall-i-will-rise reblogged this · 5 years ago
though-i-fall-i-will-rise reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 downhomedirtyblonde reblogged this · 5 years ago
downhomedirtyblonde reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 womanlygoddess liked this · 5 years ago
womanlygoddess liked this · 5 years ago -
 sarahsparkles5sos reblogged this · 5 years ago
sarahsparkles5sos reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 hekeepsitalltohimself reblogged this · 5 years ago
hekeepsitalltohimself reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 fabulously-mistaken liked this · 5 years ago
fabulously-mistaken liked this · 5 years ago -
 chasethesunset21 reblogged this · 5 years ago
chasethesunset21 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 b-beyourself liked this · 5 years ago
b-beyourself liked this · 5 years ago -
 ela-endale reblogged this · 5 years ago
ela-endale reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 jjdreamin reblogged this · 5 years ago
jjdreamin reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 jjdreamin liked this · 5 years ago
jjdreamin liked this · 5 years ago -
 ifeeldizzyy reblogged this · 5 years ago
ifeeldizzyy reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 ifeeldizzyy liked this · 5 years ago
ifeeldizzyy liked this · 5 years ago -
 perfectlybadone reblogged this · 5 years ago
perfectlybadone reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 incendiaivocare reblogged this · 5 years ago
incendiaivocare reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 incendiaivocare liked this · 5 years ago
incendiaivocare liked this · 5 years ago -
 purple-is-my-happy-colour liked this · 5 years ago
purple-is-my-happy-colour liked this · 5 years ago -
 kiss-me-sober liked this · 5 years ago
kiss-me-sober liked this · 5 years ago -
 fucked-u-stuff liked this · 5 years ago
fucked-u-stuff liked this · 5 years ago -
 swimming-tears liked this · 5 years ago
swimming-tears liked this · 5 years ago -
 belladonnalust reblogged this · 5 years ago
belladonnalust reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 yung-dark-siren liked this · 5 years ago
yung-dark-siren liked this · 5 years ago -
 justyouraveragemassgirl reblogged this · 5 years ago
justyouraveragemassgirl reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 0xygenz reblogged this · 5 years ago
0xygenz reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 zendegimx reblogged this · 5 years ago
zendegimx reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 zendegimx liked this · 5 years ago
zendegimx liked this · 5 years ago -
 sei-da reblogged this · 5 years ago
sei-da reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 sei-da liked this · 5 years ago
sei-da liked this · 5 years ago -
 justneedhope-02-06-14 reblogged this · 5 years ago
justneedhope-02-06-14 reblogged this · 5 years ago
