We-are-all-paranoid - Microbe Nerd Alert

More Posts from We-are-all-paranoid and Others
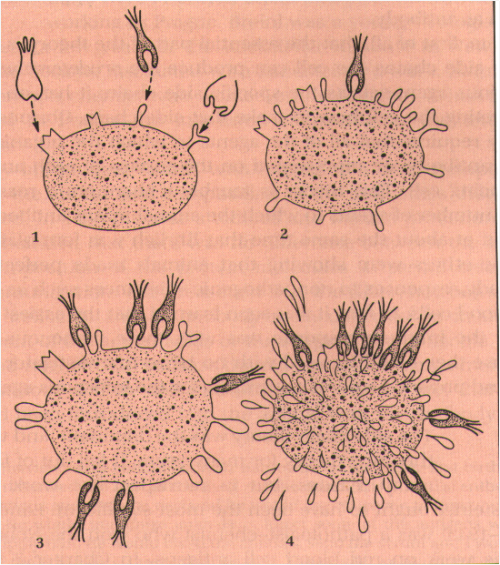
Antibodies are the secreted form of B-lymphocyte receptors and are a part of adaptive immunity, but how are these proteins formed?
Above is a diagram illustrating Paul Ehlrich’s Side Chain Theory of Antibody Formation. Ehlrich proposed that immunoglobulin molecules, a fundamental component of adaptive immunity, served as membrane bound proteins that bound to particular threats, similarly to the former “key in lock” view of enzymes in catalyzing biological reactions. Ehrlich also suggested that the action of binding a pathogenic molecule to the receptor would generate a signal to stimulate the production of more receptors of the same specificity. These “side chains” that were added on would then break off from the cell surface and become what we call antibodies.
We now know, however, that soluble immunoglobulin receptors are specially manufactured to be secreted as antibody, rather than just “breaking off” of the lymphocyte, even though they have the same specificity as their membrane-bound counterparts.
Remember, folks, never pay to access a scientific article. Use a site like Sci-Hub, or failing that, e-mail the authors and request the data you need. Elsevier and their ilk are hoarders and thieves of knowledge, and they don’t deserve one cent more. Poach and pirate away; it is entirely justified.


Stop the ban on blood donation of gay men


Hey... what the fuck???
So I read the article, and this is super cool. Basically what happened is that they let a drop of butyl alcohol out from a syringe onto the surface of another liquid, and it just... hung out there? For a very significant amount of time, too. In the past, this type of "droplet levitation" has only lasted a few milliseconds max, but this droplet was staying levitated without any external forces applied for tens of minutes.
The reason this happens is because of Solutocapilllary convection, which as far as I can tell essentially boosts the surface tension of that one spot in the underlying liquid using vapor molecules, so that the butyl alcohol molecule can't sink in.
Also, the reason why I specified that the reason this was cool is because it was done without external forces is that APPARENTLY we've been able to levitate things using sound waves since like... the 1930s. And it makes sense that you can do that, in principle, but it still looks absolutely wild to see.


i found another specimen of a super rare organism yesterday!
this is a rare and remarkable ciliate, a single-celled organism called Metopus verrucosus.
a few neat facts about it:
it’s an anaerobic organism! this means it prefers to live without oxygen
it lives deep in the mud of sulfur- & methane-rich bodies of saltwater. this one was found in the salt marsh estuary on the side of the garden state pkwy in south New Jersey!
it couldn’t survive in these noxious conditions by itself, though! the fuzzyness covering it’s cell is actually a type of bacteria that symbiotically lives on M. verrucosus.
this bacteria has the ability to metabolize sulfur and/or methane, processing these volatile stinky chemicals and turning it into energy, that it then shares with M. verrucosus!
i’m the only known person with this kind of footage of M. verrucosus! the paper The Santa Barbara Basin is an Oasis of Symbiosis has the only other photo i’ve seen of this organism, and it’s actually an HVEM (electron microscope) photo of a cross-section of the cell showing it’s endosymbiotic bacteria.


here are some more photos i took of other specimens:







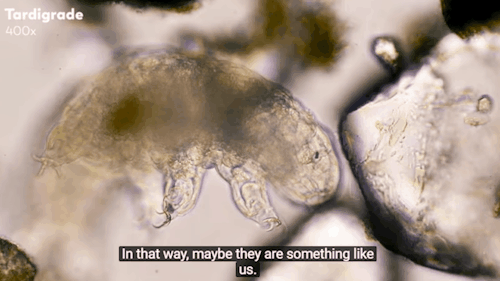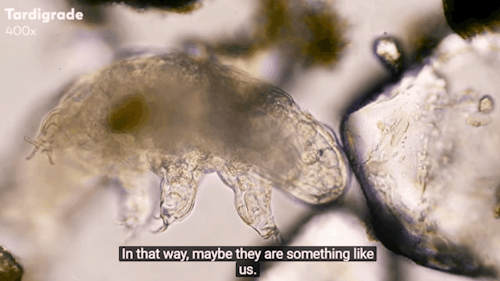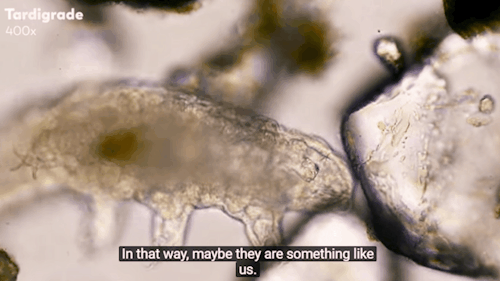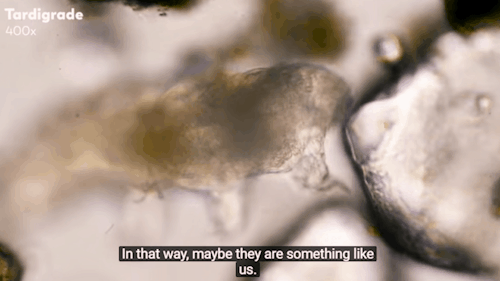


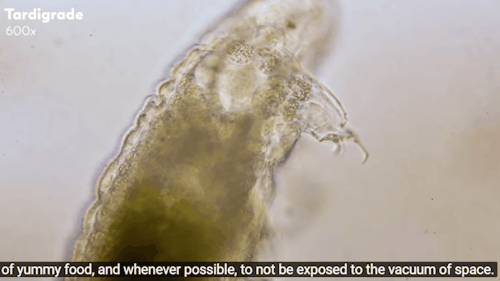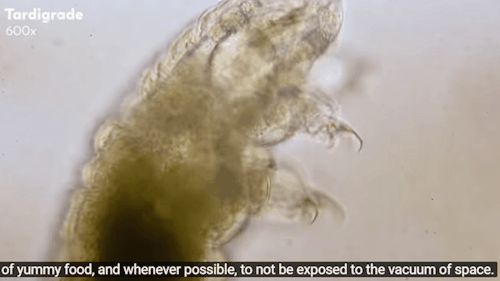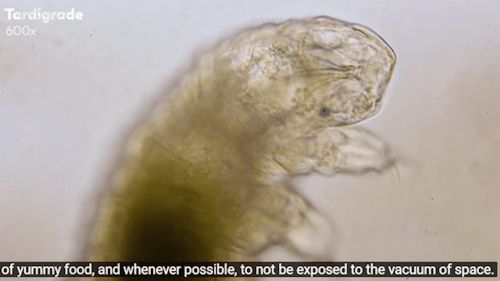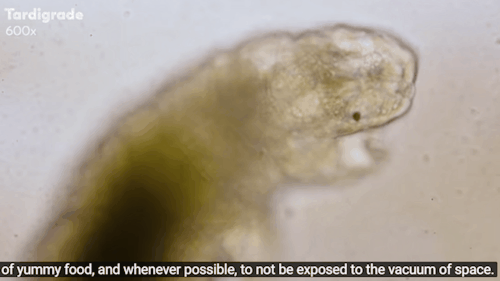
Journey to the Microcosmos: Tardigrades: Chubby, Misunderstood, & Not Immortal
Images originally captured by Jam’s Germs
Thank you @airyearthgirl for inspiring me to gif these amazing lines
-
 bellewintersroe liked this · 4 days ago
bellewintersroe liked this · 4 days ago -
 andrabeets liked this · 4 days ago
andrabeets liked this · 4 days ago -
 saint-petah-the-good liked this · 4 days ago
saint-petah-the-good liked this · 4 days ago -
 msmercury84 reblogged this · 4 days ago
msmercury84 reblogged this · 4 days ago -
 msmercury84 liked this · 4 days ago
msmercury84 liked this · 4 days ago -
 moiraifate liked this · 4 days ago
moiraifate liked this · 4 days ago -
 kath-666 liked this · 4 days ago
kath-666 liked this · 4 days ago -
 the-ill-omen-of-hope liked this · 5 days ago
the-ill-omen-of-hope liked this · 5 days ago -
 softguarnere reblogged this · 5 days ago
softguarnere reblogged this · 5 days ago -
 burnt-out-toast-with-jam liked this · 5 days ago
burnt-out-toast-with-jam liked this · 5 days ago -
 nooramee reblogged this · 5 days ago
nooramee reblogged this · 5 days ago -
 thekinginjello liked this · 6 days ago
thekinginjello liked this · 6 days ago -
 drastic-schmastic reblogged this · 1 week ago
drastic-schmastic reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 excellent-desert liked this · 1 week ago
excellent-desert liked this · 1 week ago -
 werewuff liked this · 1 week ago
werewuff liked this · 1 week ago -
 theliloleme reblogged this · 1 week ago
theliloleme reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 au79burger liked this · 1 week ago
au79burger liked this · 1 week ago -
 zositoki6317 liked this · 1 week ago
zositoki6317 liked this · 1 week ago -
 sungbeen liked this · 1 week ago
sungbeen liked this · 1 week ago -
 livingmydopelife liked this · 1 week ago
livingmydopelife liked this · 1 week ago -
 adleid liked this · 1 week ago
adleid liked this · 1 week ago -
 kissingonyou reblogged this · 1 week ago
kissingonyou reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 greentealycheejelly reblogged this · 1 week ago
greentealycheejelly reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 vickylynntwin2 reblogged this · 1 week ago
vickylynntwin2 reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 vickylynntwin2 liked this · 1 week ago
vickylynntwin2 liked this · 1 week ago -
 syderium liked this · 1 week ago
syderium liked this · 1 week ago -
 paperroxas reblogged this · 1 week ago
paperroxas reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 paperroxas liked this · 1 week ago
paperroxas liked this · 1 week ago -
 pridemoth1 reblogged this · 1 week ago
pridemoth1 reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 saga-project reblogged this · 1 week ago
saga-project reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 thethingwiththefeathers liked this · 1 week ago
thethingwiththefeathers liked this · 1 week ago -
 crypticphysicist liked this · 1 week ago
crypticphysicist liked this · 1 week ago -
 lily0sanchez liked this · 2 weeks ago
lily0sanchez liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 rah11dongsongposts reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
rah11dongsongposts reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 shehuntsinshadow reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
shehuntsinshadow reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 shehuntsinshadow liked this · 2 weeks ago
shehuntsinshadow liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 impetusofadream reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
impetusofadream reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 impetusofadream liked this · 2 weeks ago
impetusofadream liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 theunluckylistenermusician liked this · 2 weeks ago
theunluckylistenermusician liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 ef-tu-brute liked this · 2 weeks ago
ef-tu-brute liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 itallstartedwithharry reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
itallstartedwithharry reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 blueelectricangels liked this · 2 weeks ago
blueelectricangels liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 starsharks liked this · 2 weeks ago
starsharks liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 silvergryphon reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
silvergryphon reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 ruin-cain liked this · 2 weeks ago
ruin-cain liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 whocanbelieve reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
whocanbelieve reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 whocanbelieve liked this · 2 weeks ago
whocanbelieve liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 otheliame liked this · 2 weeks ago
otheliame liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 xue-mei reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
xue-mei reblogged this · 2 weeks ago


