A Slow-motion Animation Of The Crab Pulsar Taken At 800 Nm Wavelength (near-infrared) Using A Lucky Imaging

A slow-motion animation of the Crab Pulsar taken at 800 nm wavelength (near-infrared) using a Lucky Imaging camera from Cambridge University, showing the bright pulse and fainter interpulse.
Credit: Cambridge University Lucky Imaging Group
More Posts from Xyhor-astronomy and Others

Neptune Clouds
This Voyager 2 high resolution color image, taken 2 hours before closest approach, provides obvious evidence of vertical relief in Neptune’s bright cloud streaks.
Credit: NASA / Voyager 2
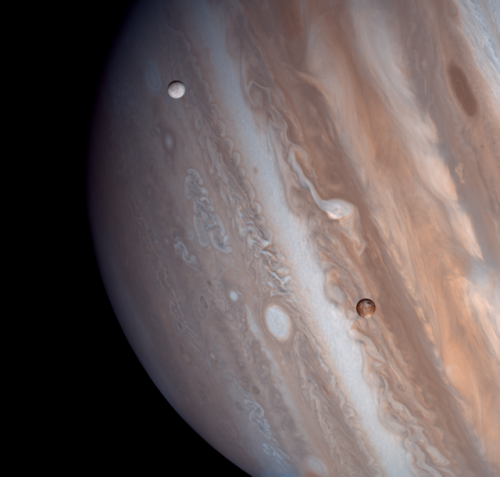

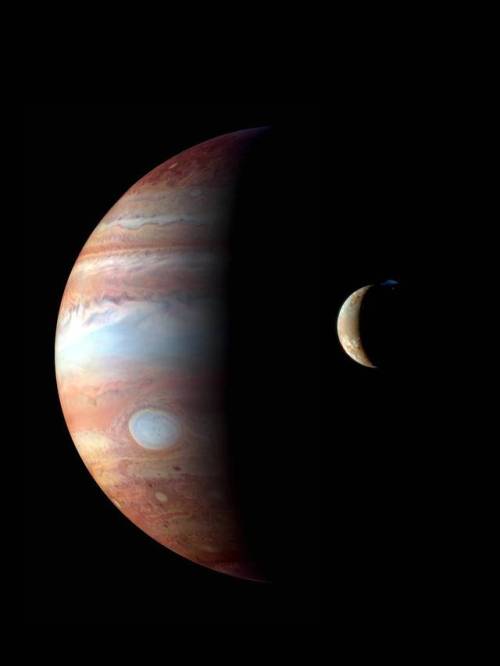
Io and Europa taken by the Voyager 1 spacecraft in 1979
Image credit: Justin Cowart
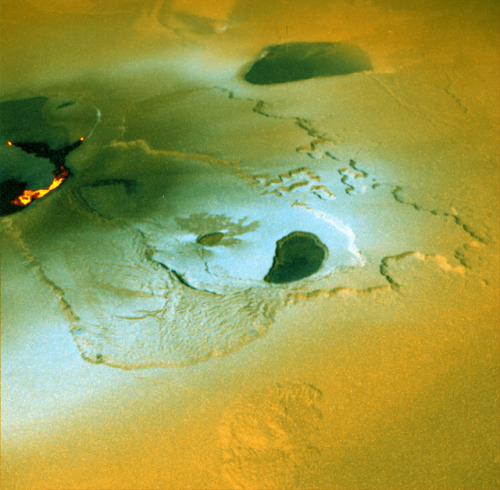
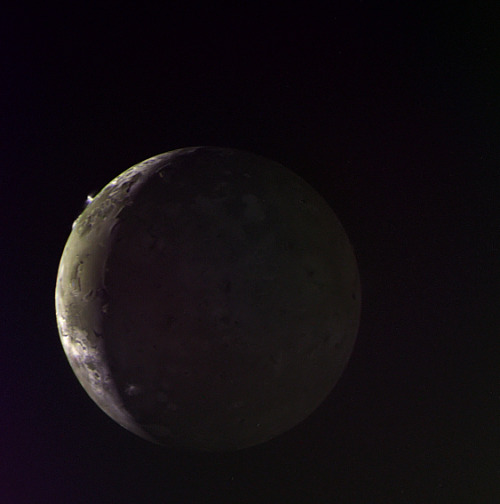
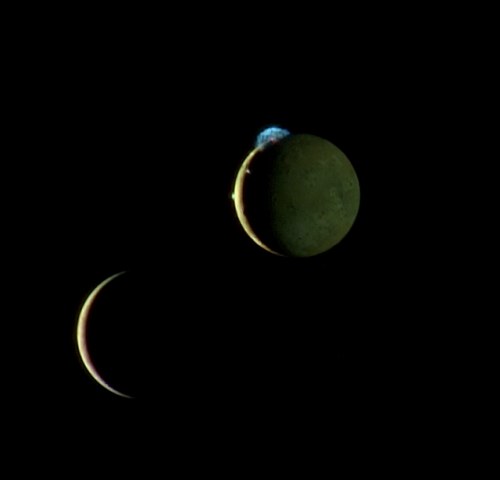
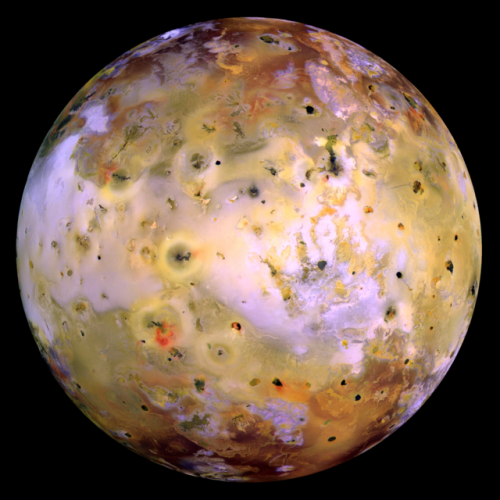


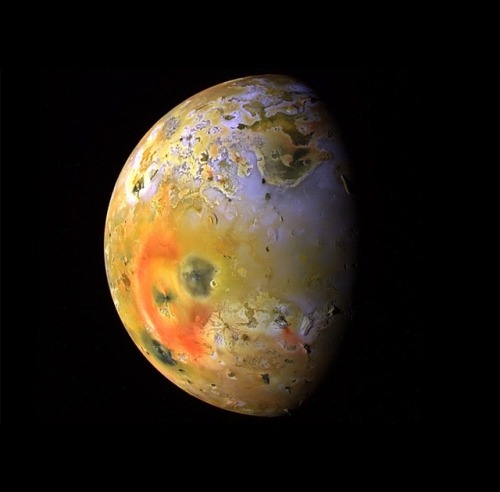





Io - The Volcanic Moon
Looking like a giant pizza covered with melted cheese and splotches of tomato and ripe olives, Io is the most volcanically active body in the solar system. Volcanic plumes rise 300 km (190 miles) above the surface, with material spewing out at nearly half the required escape velocity.
A bit larger than Earth’s Moon, Io is the third largest of Jupiter’s moons, and the fifth one in distance from the planet.
Although Io always points the same side toward Jupiter in its orbit around the giant planet, the large moons Europa and Ganymede perturb Io’s orbit into an irregularly elliptical one. Thus, in its widely varying distances from Jupiter, Io is subjected to tremendous tidal forces. These forces cause Io’s surface to bulge up and down (or in and out) by as much as 100 m (330 feet)! Compare these tides on Io’s solid surface to the tides on Earth’s oceans. On Earth, in the place where tides are highest, the difference between low and high tides is only 18 m (60 feet), and this is for water, not solid ground!
This tidal pumping generates a tremendous amount of heat within Io, keeping much of its subsurface crust in liquid form seeking any available escape route to the surface to relieve the pressure. Thus, the surface of Io is constantly renewing itself, filling in any impact craters with molten lava lakes and spreading smooth new floodplains of liquid rock. The composition of this material is not yet entirely clear, but theories suggest that it is largely molten sulfur and its compounds (which would account for the varigated coloring) or silicate rock (which would better account for the apparent temperatures, which may be too hot to be sulfur). Sulfur dioxide is the primary constituent of a thin atmosphere on Io. It has no water to speak of, unlike the other, colder Galilean moons. Data from the Galileo spacecraft indicates that an iron core may form Io’s center, thus giving Io its own magnetic field.
Io was discovered on 8 January 1610 by Galileo Galilei. The discovery, along with three other Jovian moons, was the first time a moon was discovered orbiting a planet other than Earth.

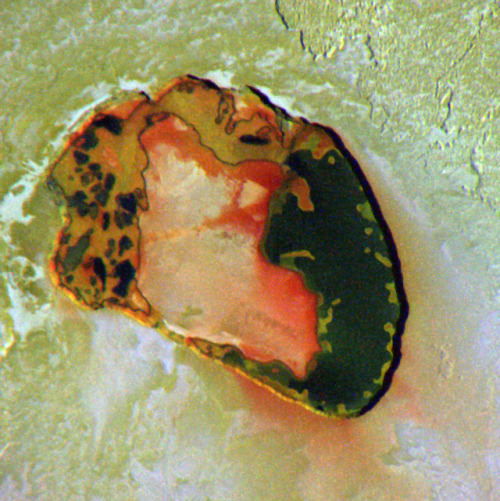
Eruption of the Tvashtar volcano on Jupiter’s moon Io, photographed by New Horizons.
Image credit: NASA/JPL/Galileo/New Horizons ( Stuart Rankin | Kevin Gill)
Source: NASA



(Causus maculatus) - Common names include forest rhombic night adder, West African night adder and spotted night adder.

Remnant of supernova toward the constellation of Vela, which exploded 11,000 years ago.
Image credit: NASA / Chandra x-ray Observatory









5 Questions You Were Too Embarrassed To Ask About The Expanding Universe
“5.) Are there galaxies moving away faster than the speed of light, and isn’t that forbidden? From our point of view, the space in between us and any distant point is expanding. The farther away something is, the faster it appears to recede from us. Even if the expansion rate were tiny, an object far enough away would eventually cross that threshold of any finite speed, since an expansion rate (a speed-per-distance) multiplied by a great enough distance will give you a speed as fast as you want. But this is okay in General Relativity! The law that nothing can travel faster than the speed of light only applies to an object’s motion through space, not to the expansion of space itself. In reality, the galaxies themselves only move around at speeds that are hundreds or thousands of km/s, much lower than the 300,000 km/s speed limit set by the speed of light. It’s the expansion of the Universe that causes this recession and the redshift, not a true galactic motion.”
The idea that the spatial fabric of the Universe itself is expanding, and that’s what’s behind the observed relationship between redshift and distance has long been controversial, and also long-misunderstood. After all, if more distant objects appear to recede more quickly, couldn’t there be a different explanation, like an explosion that flung many things outward? As it turns out, this isn’t a mere difference in interpretation, there are observations we can make that tell us the answer! The Universe is not expanding ‘into’ anything, despite what your intuition might tell you. The Hubble ‘constant’ isn’t actually a constant, but is rather decreasing as time goes on. The Universe looks like it’s going to expand forever, but even that scientific conclusion is subject to revision depending on what data shows in the future. And although 97% of the galaxies in the Universe are already unreachable, it isn’t a violation of relativity or a faster-than-light phenomenon that’s to blame.
Come learn the answers to five questions about the expanding Universe that many are too embarrassed to ask!
Resupply Mission Brings Mealworms and Mustard Seeds to Space Station
Orbital ATK will launch its Cygnus cargo spacecraft to the International Space Station on November 11, 2017 from Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. It will be packed with cargo and scientific experiments for the six humans currently living and working on the orbiting laboratory.

The cargo spacecraft is named the S.S. Gene Cernan after former NASA astronaut Eugene Cernan, who is the last man to have walked on the moon.

Here are some of the really neat science and research experiments that will be delivered to the station:
What’s Microgravity Got to do with Bacterial Antibiotics?
Antibiotic resistance could pose a danger to astronauts, especially since microgravity has been shown to weaken human immune response. E. coli AntiMicrobial Satellite (EcAMSat) will study microgravity’s effect on bacterial antibiotic resistance.

Results from this experiment could help us determine appropriate antibiotic dosages to protect astronaut health during long-duration human spaceflight and help us understand how antibiotic effectiveness may change as a function of stress on Earth.
Laser Beams…Not on Sharks…But on a CubeSat
Traditional laser communication systems use transmitters that are far too large for small spacecraft. The Optical Communication Sensor Demonstration (OCSD) tests the functionality of laser-based communications using CubeSats that provide a compact version of the technology.

Results from OCSD could lead to improved GPS and other satellite networks on Earth and a better understanding of laser communication between small satellites in low-Earth orbit.
This Hybrid Solar Antenna Could Make Space Communication Even Better
As space exploration increases, so will the need for improved power and communication technologies. The Integrated Solar Array and Reflectarray Antenna (ISARA), a hybrid power and communication solar antenna that can send and receive messages, tests the use of this technology in CubeSat-based environmental monitoring.

ISARA may provide a solution for sending and receiving information to and from faraway destinations, both on Earth and in space.
More Plants in Space!
Ready for a mouthful…The Biological Nitrogen Fixation in Microgravity via Rhizobium-Legume Symbiosis…aka the Biological Nitrogen Fixation experiment, will examine how low-gravity conditions affect the nitrogen fixation process of the Microclover legume (a plant in the pea family). Nitrogen fixation is a process where nitrogen in the atmosphere is converted into ammonia. This crucial element of any ecosystem is also a natural fertilizer that is necessary for most types of plant growth.

This experiment could tell us about the space viability of the legume’s ability to use and recycle nutrients and give researchers a better understanding of this plant’s potential uses on Earth.
What Happens When Mealworms Live in Space?
Mealworms are high in nutrients and one of the most popular sources of alternative protein in developing countries. The Effects of Microgravity on the Life Cycle of Tenebrio Molitor (Tenebrio Molitor) investigation studies how the microgravity environment affects the mealworm life cycle.

In addition to alternative protein research, this investigation will provide information about animal growth under unique conditions.
Mustard Seeds in Microgravity
The Life Cycle of Arabidopsis thaliana in Microgravity experiment studies the formation and functionality of the Arabidopsis thaliana, a mustard plant with a genome that is fully mapped, in microgravity conditions.

The results from this investigation could contribute to an understanding of plant and crop growth in space.
Follow @ISS_Research on Twitter for more information about the science happening on space station.
Watch the launch live HERE on Nov. 11, liftoff is scheduled for 7:37 a.m. EDT!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Black Holes are not so Black (Part 3) - Gravitational Waves
The existence of Gravitational Waves have been confirmed. But you probably have heard that. In this post, we will break down this profound discovery into comprehend-able chunks.
This is going to be a amazing journey. Ready ?
Redefining Gravity
When we usually talk of Gravitation we are bound to think like Newton, where objects are assumed to exerting a force upon each other.
Like imaginary arrows of force in space. But this picture, although good for high school crumbled, with the advent of Einstein’s theory of Relativity.
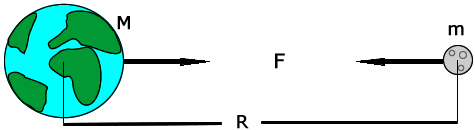
What is the Space-Time Fabric?
Think of space-time fabric as an actual cloth of fabric. ( An analogy )

When you place an object on the fabric, the cloth curves. This is exactly what happens in the solar system as well.

The sun with such a huge mass bends the space-time fabric. And the earth and all the planets are kept in orbit by following this curvature that has been made by the sun.
Attributing to the various masses of objects, the way they bend this fabric also varies.
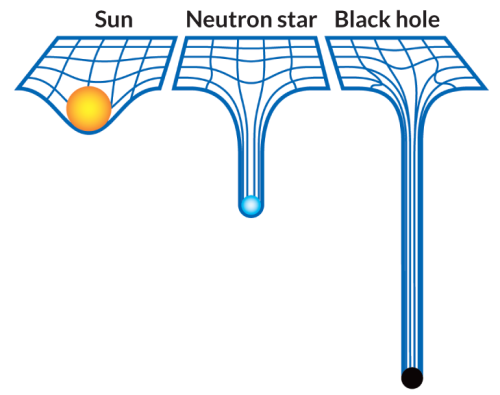
What are Gravitational Waves?
If you drop an object in a medium such as water, they produce ripples that propagate as waves through the medium.

Similarly, Gravitational waves are ripples in space-time fabric produced when you drag heavy objects through space time.
And the nature of these waves is that they don’t require a medium to propagate.
How do you make one?
Everything with mass/energy can create these waves.

Source
Two persons dancing around each other in space too can create gravitational waves. But the waves would be extremely faint.
You need something big and massive accelerating through space-time in order to even detect them.

And orbiting binary stars/black holes are valuable in this retrospect.
How can you detect them?
Let’s turn to the problem to detecting them assuming you do find binary stars/black-holes in the wondrous space to suite your needs.
Well, for starters you cannot use rocks/ rulers to measure them because as the space expands and contracts, so do the rocks. ( the distances will remain same in both the cases )

Here’s where the high school fact that the speed of Light is a constant no matter what plays an important and pivotal role.
If the space expands, the time taken for light to reach from A to B would be longer. And if it contracts, the time taken for it to reach from A to B would be smaller.

PC: PHDComics
By allowing the light waves from the contraction and expansion to interfere with each other, such as done in any interferometry experiment we can detect the expansion or contraction. Voila!
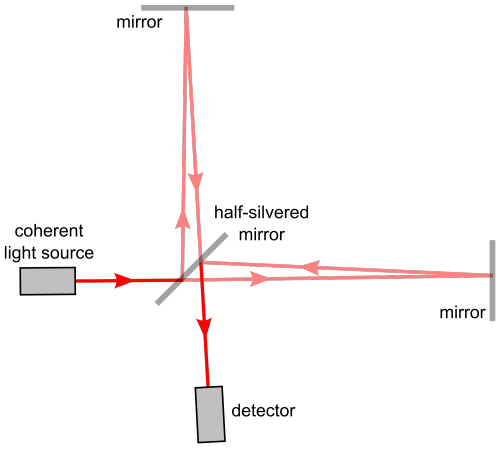
And this is exactly what they did! ( on a macroscopic level ) at LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory)
14 September 2015

Two Black Holes with masses of 29 and 36 solar masses merged together some 1.3 Billion light years away.
Two Black Holes colliding is the header animation of the ‘Black Holes are not so Black Series’, in case if you haven’t noticed.

The merger of these two black holes results in the emission of energy equivalent to 3 solar masses as Gravitational Waves.
This signal was seen by both LIGO detectors, in Livingston and Hanford, with a time difference of 7 milliseconds.
And with the measurement of this time difference, physicists have pronounced the existence of Gravitational Waves.

Source
All this is most certainly easily said than done and requires meticulous and extensive research, not to mention highly sensitive instruments.
Had they not have measured this time difference, we might have had to wait for the merger for more massive black holes to collide and maybe even build more sensitive instruments to detect these waves.
And Einstein predicted this a 100 years back!

Mind Blown!
Note: Hope you are able to understand and appreciate the profundity of the discovery done by mankind.
** All animations used here are merely for Educational purposes. If you have any issues, please write to us at : 153armstrong@gmail.com
How to Discover a Planet: A short step-by-step guide on how each of our planetary neighbors were originally discovered.

Comet Lovejoy is visible near Earth’s horizon in this nighttime image photographed by NASA astronaut Dan Burbank, Expedition 30 commander, onboard the International Space Station on Dec. 21, 2011.
Image credit: NASA
-
 thisworldisntrealhoney liked this · 1 year ago
thisworldisntrealhoney liked this · 1 year ago -
 demichrising liked this · 1 year ago
demichrising liked this · 1 year ago -
 ravexandxlust liked this · 1 year ago
ravexandxlust liked this · 1 year ago -
 sparkyairstuff liked this · 3 years ago
sparkyairstuff liked this · 3 years ago -
 uglyasfstudyblr reblogged this · 3 years ago
uglyasfstudyblr reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 chopinguy liked this · 3 years ago
chopinguy liked this · 3 years ago -
 leitharstjarna liked this · 3 years ago
leitharstjarna liked this · 3 years ago -
 undertheladdder liked this · 3 years ago
undertheladdder liked this · 3 years ago -
 hath-thee-in-thrall reblogged this · 3 years ago
hath-thee-in-thrall reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 johnbitchsociety reblogged this · 3 years ago
johnbitchsociety reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 johnbitchsociety liked this · 3 years ago
johnbitchsociety liked this · 3 years ago -
 jescache reblogged this · 3 years ago
jescache reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 jescache liked this · 3 years ago
jescache liked this · 3 years ago -
 jonbinary-archive reblogged this · 3 years ago
jonbinary-archive reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 nealmcclure liked this · 4 years ago
nealmcclure liked this · 4 years ago -
 ti-star liked this · 5 years ago
ti-star liked this · 5 years ago -
 astrobio-logy liked this · 5 years ago
astrobio-logy liked this · 5 years ago -
 gulusgammapussy liked this · 5 years ago
gulusgammapussy liked this · 5 years ago -
 pinkclamllamafish liked this · 5 years ago
pinkclamllamafish liked this · 5 years ago -
 nobodylistenstolucy liked this · 5 years ago
nobodylistenstolucy liked this · 5 years ago -
 gia-is-a-punk-rocker liked this · 5 years ago
gia-is-a-punk-rocker liked this · 5 years ago -
 metalzoic liked this · 5 years ago
metalzoic liked this · 5 years ago -
 gingerfan24 liked this · 5 years ago
gingerfan24 liked this · 5 years ago -
 notisaidthechicken liked this · 5 years ago
notisaidthechicken liked this · 5 years ago -
 fagdykefrank liked this · 5 years ago
fagdykefrank liked this · 5 years ago -
 ted-blogs-blog liked this · 5 years ago
ted-blogs-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 oldfayth liked this · 5 years ago
oldfayth liked this · 5 years ago -
 krdiboy-blog-blog liked this · 5 years ago
krdiboy-blog-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 caughtin-flux liked this · 5 years ago
caughtin-flux liked this · 5 years ago -
 queen-of-alagaesia liked this · 5 years ago
queen-of-alagaesia liked this · 5 years ago -
 thepizzalovingnerd liked this · 5 years ago
thepizzalovingnerd liked this · 5 years ago
For more content, Click Here and experience this XYHor in its entirety!Space...the Final Frontier. Let's boldly go where few have gone before with XYHor: Space: Astronomy & Spacefaring: the collection of the latest finds and science behind exploring our solar system, how we'll get there and what we need to be prepared for!
128 posts