GUIDE: NAMING A TOWN OR CITY
GUIDE: NAMING A TOWN OR CITY
This post was originally from a FAQ, but since the original link is now defunct, I am re-posting it here.
There are many things to keep in mind when naming the town or city in your novel:
1) Genre/Theme/Tone
It’s very important to consider the genre and theme of your story when choosing a town name. Take these names for example, each of which indicates the genre or theme of the story: King’s Landing (sounds fantastical) Cloud City (sounds futuristic) Silent Hill (sounds scary) Sweet Valley (sounds happy and upbeat) Bikini Bottom (sounds funny) Radiator Springs (sounds car-related) Halloween Town (sounds Halloween-related) Storybrooke (sounds fairytale-related) 2) Time/Place It’s also important to consider the time and place where your story takes place. For example, you wouldn’t use “Vista Gulch” as a name for a town in Victorian England. You probably wouldn’t use it for a town in modern day North Carolina, either. Vista is a Spanish word and would normally be found in places where Spanish names are common, like Spain, Central and South America, the southwest United States (including southern California), Cuba, Puerto Rico, Dominican Republic, and Florida. 3) Size/Settlement Type An isolated town of 300 people probably won’t be Valley City, but a sprawling metropolis of 30 million could be called Windyville, because it could have started out as a small town and grew into a large city. 4) Geography Words like gulch, butte,and bayou tend to be regional terms. You probably wouldn’t find Berle’s Bayou in Idaho, or Windy Butte in Rhode Island. Words like mount, cape, and valley are dependent upon terrain. Most of the time, you won’t have a town named “mount” something unless there are hills or mountains nearby. You wouldn’t use “cape” unless the town was on a cape, which requires a large body of water. 5) History Is there a historical person or event that your town might be named after? The Simpsons’ hometown of Springfield is ironically named after its founder, Jebediah Springfield. Chattanooga, Tennessee is named after the Cherokee town that was there first. Nargothrond, in The Lord of the Rings, is an Elvish town with an Elvish name. 6) Combination of Words
person name + geographical term = Smithfield, Smith Creek
group name + geographical term = Pioneer Valley, Settlers’ Ridge
descriptive word + geographical term = Mystic Falls, Smoky Hill
person name + settlement type = Smithton, Claraville
landmark + settlement type = Bridgton, Beaconville
Word Lists
Types of Settlements

Geographical Features
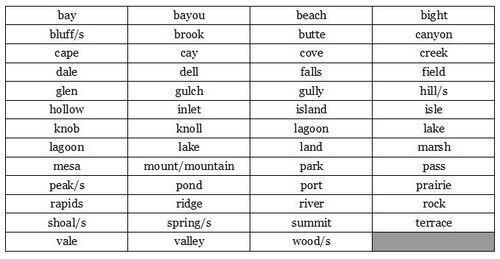
Place Words

Common Suffixes
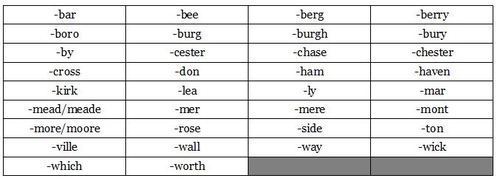
Other Descriptors
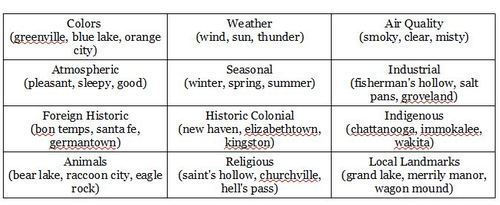
More Posts from Sparklingsilvermagnolias and Others
When Should You Describe a Character’s Appearance? (And When You Really, Really Shouldn’t)
It’s one of the first instincts writers have: describe your character. What they look like, what they wear, how they move. But the truth is — readers don’t need to know everything. And more importantly, they don’t want to know everything. At least, not all at once. Not without reason.
Let’s talk about when to describe a character’s appearance, how to do it meaningfully, and why less often says more.
1. Ask: Who Is Seeing Them? And Why Now?
The best descriptions are filtered through a perspective. Who’s noticing this character, and what do they see first? What do they expect to see, and what surprises them?
She looked like someone who owned every book you were supposed to have read in school. Glasses slipping down her nose. Sharp navy coat, sensible shoes, and an air of knowing too much too soon.
Now we’re not just learning what she looks like — we’re learning how she comes across. That tells us more than eye color ever could.
2. Use Appearance to Suggest Character, Not List Facts
Avoid long physical checklists. Instead, choose a few details that do double work — they imply personality, history, class, mood, or context.
Ineffective: She had long, wavy brown hair, green eyes, a small nose, and full lips. She wore jeans and a white shirt.
Better: Her hair was tied back like she hadn’t had time to think about it. Jeans cuffed, a shirt buttoned wrong. Tired, maybe. Or just disinterested.
You don’t need to know her exact features — you feel who she is in that moment.
3. Know When It’s Not the Moment
Introducing a character in the middle of action? Emotion? Conflict? Don’t stop the story for a physical description. It kills momentum.
Instead, thread it through where it matters.
He was pacing. Long-legged, sharp-shouldered — he didn’t seem built for waiting. His jaw kept twitching like he was chewing on the words he wasn’t allowed to say.
We learn about his build and his mood and his internal tension — all in motion.
4. Use Clothing and Gesture as Extension of Self
What someone chooses to wear, or how they move in it, says more than just what’s on their body.
Her sleeves were too long, and she kept tucking her hands inside them. When she spoke, she looked at the floor. Not shy, exactly — more like someone used to being half-disbelieved.
This is visual storytelling with emotional weight.
5. Finally: Describe When It Matters to the Story, Not Just the Reader
Are they hiding something? Trying to impress? Standing out in a crowd? Use appearance when it helps shape plot, stakes, or power dynamics.
He wore black to the funeral. Everyone else in grey. And somehow, he still looked like the loudest voice in the room.
That detail matters — it changes how we see him, and how others react to him.
TL;DR:
Don’t info-dump descriptions.
Filter visuals through a point of view.
Prioritize impression over inventory.
Describe only what tells us more than just what they look like — describe what shows who they are.
Because no one remembers a checklist.
But everyone remembers the girl who looked like she’d walked out of a forgotten poem.
Reading fantasy again, I've started thinking about how odd it is how in books like that, the non-human races invariably scoff at human frailty and vulnerability, even those that they'll call friends. Like that's mean?? Why would you be a dick to your friend who you know is not capable of as much as you are, and it's not their fault they were born like that. That's mean.
Like consider the opposite: Characters of non-human races treating their human companions like frail little old dogs. Worrying about small wounds being fatal - humans die of small injuries all the time - or being surprised that humans can actually eat salt, even if they can't stomach other spicy rocks. Being amazed that a human friend they haven't seen in 10 years still looks so young, they've hardly aged at all! And when the human tries to explain that they weren't going to just unexpectedly shrivel into a raisin in 10 years, the longer-lifespan friend dismisses this like no, he's seen it happen, you don't see a human for 10 or 20 years and they've shriveled in a blink.
Elves arguing with each other like "you can't take her out there, she will die!" and when the human gets there to ask what they're talking about, they explain to her that the journey will take them through a passage where it's going to be sunny out there. Humans burn in the sun. And she will have to clarify that no, actually, she'll be fine. They fight her about it, until she manages to convince them that it's not like vampires - humans only burn a little bit in the sun, not all the way through. She'll be fine if she just wears a hat.
Meanwhile dwarves are reluctant to allow humans in their mines and cities, not just out of being secretive, but because they know that you cannot bring humans underground, they will go insane if they go too long without seeing the sun. Nobody is entirely sure how long that is, but the general consensus is three days. One time a human tries to explain their dwarf companion that this is not true, there are humans that endure much longer darkness than that. As a matter of fact, in the furthest habited corners of the lands of the Northmen, the winter sun barely rises at all. Humans can survive three weeks of darkness, and not just once, but every single year.
"Then how do they sane?" Asks the dwarf, and just as he does, the conversation gets interrupted by the northland human, who had been eavesdropping, and turns to look at them with an unnerving glint in her colourless grey eyes, grinning while saying
"That's the neat part, we don't."
the problem with addiction is not that it's pleasurable. it's not "having too much fun" disease. it's not even a requirement for addiction that you have fun at any point in the process at all and to be honest it is incredibly common that no pleasure is gained from substance use. imagining that addiction is about pleasure does two things: 1) demonises feeling good (there is nothing wrong with wanting to be happy/comfortable/etc), and 2) frames addicts as people who Like Having Fun Too Much. it's simply not useful to frame things this way as well as just fundamentally not being true
Avoiding the “Mary Sue” trap while creating characters.
A “Mary Sue” is that charact. Perfect; bends the story to their will, faces no meaningful struggles, and often feels too idealized to be relatable. The thing I like most is when an author makes a character, a situation, a scene, realistic. I like heavy realism in my books. I know we read to escape reality, but there's a way to do that.
1. Give Them Flaws Not the checklist kind. Not "clumsy" or "bad at math" unless that genuinely bleeds into who they are and how they move through the world. I mean the kind of flaws that crack open relationships. That drive certain choices. That make you want to shake them. Flaws should cost them something. Otherwise, they’re decoration.
2. Let Them Fail Failure is the most human thing. It brings shame, doubt, growth, all the stuff that makes a character feel alive. Let them try, and stumble. Let them mess up something important. Let them hurt people and not know how to fix it. Failure opens narrative doors that perfection just slams shut.
3. Don’t Make Everyone Love Them If every side character is just there to admire your MC, you’re not writing a story—you’re writing propaganda. Let people mistrust them. Let some hate them. Not everyone sees the same version of a person. Maybe someone sees behind their act, maybe someone’s immune to their charm. That gives perspective.
4. Make Their Skills Believable A skill with no backstory is just plot armor. If they're good at something, show why. Time. Training. Failure. Maybe they’re not even the best—just someone who works harder than they should have to. That’s infinitely more compelling than someone who just is talented for no reason.
5. Avoid Overloading Them With Traits They don’t need to be smart, funny, hot, tragic, a prodigy, a rebel, and an empath who bakes when sad. Choose what matters. Strip it down to the few traits that define them, the ones they carry into every scene. Complexity is about layers, not a pile of labels.
6. Give Them Internal Conflict We all contradict ourselves. That’s the beauty of it. Your character should wrestle with decisions. Regret them. Say one thing and feel another. Inner conflict is what separates a walking trope from a person we believe in.
7. Let the Plot Push Back The world shouldn’t bend for your character. The plot should push them, break them, make them bleed for the win. Their goals should cost something. The story isn’t just their playground—it’s the pressure cooker where they get tested. If they’re never cornered, what’s the point?
8. Ensure They Don’t Eclipse the Entire Cast Other characters are not props. Give them wants, voices, limits. They don’t exist to spotlight the protagonist—they exist to breathe life into the story. And your MC is more interesting when they’re surrounded by people who push them, contradict them, challenge them.
9. Avoid Unrealistic Morality Nobody’s always right. And honestly, it’s annoying when they are. Let them justify things that aren’t justifiable. Let them fail to see another perspective. Let them believe they’re in the right—until they’re not. Give them a compass that doesn’t always point true north.
10. Make Them Struggle to Earn Trust Trust is a slow build. People remember hurt. They hesitate. Let your MC do the work—prove themselves, fail, rebuild. Trust earned over time is more satisfying than instant loyalty that comes out of nowhere.
I hate perfect characters. Especially when it’s pretend perfection. Like what do you mean he has abs when he has no time to workout? Like what do you mean she is so put together all the time? In this economy?
let's write something raw, something realistic.
Struggling with emotional scenes? Here are some tips for writing emotion!
=========
1. While you’re writing, try to build an explanation for their feelings. What triggered their emotion? Is their reaction rational or are they overreacting? Do they fight, flight, fawn or freeze when provoked? Do they feel threatened?
=========
2. Show, don’t tell. Describe what is happening instead of plainly stating the situation. Try not to use words like sad, happy, devastated, in pain, angry, nervous, scared, or worried. They cut back on the emotional integrity of the scene and make it hard for readers to connect with your characters. Here are some different behaviors for different emotions.
-Eager-
Bouncing up and down
Unable to sit still
Breathing deeply
Fidgeting
Pretending to do something
Trying to stay busy
Constantly looking at the clock
-Nervous-
Red and hot face
Sweaty palms
Voice cracks
Shaky hands
Biting nails
Biting lips/inside of cheek
Wide eyes
Shallow breathing
Heart racing
-Excited-
Wide smile
Squeal/scream
Bouncing up and down
Fidgeting
Playing with hands
Tapping foot
Talking fast
Tapping pencil
Pacing back and forth
-Scared-
Curling up/bringing knees to head
Closing eyes
Covering ears
Stop breathing or breathing quickly
Biting nails
Shaking
Gritting teeth
Hugging/squeezing something tight
-Frustrated-
Stomping
Grunting/mumbling/yelling
Deep breaths
Red and hot face
Hitting/kicking something
Pointing
Straining/veins become more visible
-Sobbing-
Eyes filling up with tears
Eyes burn/turn red
Red cheeks
Face becomes puffy
Pursed lips
Holding head down
Hyperventilating
Fast blinking
Trying not to blink/holding back tears
-Happy-
Smiling wide
Laughing loudly
Cheeks hurting
Talking loudly
Higher pitched voice
Animated/expressive
-Upset-
Walking slowly/shuffling feet
Head down/avoiding eye contact
Biting inside of cheek
Dissociation
Keeping quiet
Fidgeting
-Bored-
Pacing back and forth
Sighing loudly
Complaining
Fidgeting
Blank face
Looking for something to do
Making up stories
Talking about random topics
=========
3. Try and bring some trauma into your character’s emotions. For example, something might happen that reminds them of a suppressed/traumatic memory. This is an easy way to hook your reader and have them really feel like your character is a real person with real emotions. They might have some internal conflict they need to work through and a certain situation reminds them of that. They might become irritable at the thought of their traumatic experience and they might snap at whoever is nearby.
=========
4. Most characters won’t dump their entire backstory or feelings in a conversation. Try and reserve your character’s emotions to make more interesting scenes later on. For example, your character may be triggered and someone may ask them what’s wrong. Will they give in, soften up and share? Or will they cut themself off and say they’re fine? Also take into account that your character might not know the other character very well and won’t be comfortable sharing personal information with them, like details regarding their trauma.
=========
5. Last but not least, you don’t need to have a major event happen to connect emotionally with your audience. You don’t have to kill off a character every time you need to spice up your story, even simple interactions can just help your readers understand your character better. Show how they react to certain topics or situations. Describe their feelings, their surroundings, their body language. Their defense mechanisms will help the audience to better understand what kind of person they are.
=========
Writing Description Notes:
Updated 9th September 2024 More writing tips, review tips & writing description notes
Facial Expressions
Masking Emotions
Smiles/Smirks/Grins
Eye Contact/Eye Movements
Blushing
Voice/Tone
Body Language/Idle Movement
Thoughts/Thinking/Focusing/Distracted
Silence
Memories
Happy/Content/Comforted
Love/Romance
Sadness/Crying/Hurt
Confidence/Determination/Hopeful
Surprised/Shocked
Guilt/Regret
Disgusted/Jealous
Uncertain/Doubtful/Worried
Anger/Rage
Laughter
Confused
Speechless/Tongue Tied
Fear/Terrified
Mental Pain
Physical Pain
Tired/Drowsy/Exhausted
Eating
Drinking
Warm/Hot
hi dhaaruni! i want to learn about radical feminism, could you rec some books/texts? thank you <3

YES.
Right-Wing Women, Woman Hating, and Letters From a War Zone by Andrea Dworkin
Are women human?, Only Words, and Toward a Feminist Theory of the State by Catharine A. MacKinnon
The Second Sex by Simone de Beauvoir
The Politics of Reality: Essays in Feminist Theory by Marilyn Frye
Sexual Politics by Kate Millett
Sister Outsider by Audre Lorde
The Feminine Mystique by Betty Friedan
Women, Race, & Class by Angela Davis
Invisible Women: Data Bias in a World Designed for Men by Caroline Criado Pérez
This Bridge Called My Back by Cherríe Moraga and Gloria E. Anzaldúa
The Industrial Vagina: The Political Economy of the Global Sex Trade by Sheila Jeffreys
Against Our Will: Men, Women, and Rape by Susan Brownmiller
We Should All Be Feminists by Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie
Material Girls: Why Reality Matters for Feminism by Kathleen Stock
Of Woman Born: Motherhood as Experience and Institution by Adrienne Rich
The Beauty Myth by Naomi Wolf (it was published in 1990 before Wolf went cuckoo for cocoa puffs)
On Rape and Sex and Destiny: The Politics of Human Fertility by Germaine Greer
Bad Feminist by Roxane Gay (just never look at her Twitter if you haven't already since this book really is very good and her Twitter ensured I'm never reading another book of hers ever)
And thank you for enjoying my newsletter!!
Vibes for Softly Tortured Characters
For the ones who make you want to wrap them in a blanket and also scream “JUST TALK TO SOMEONE.”
Always looks like they didn’t sleep (because they didn’t)
Talks like they’re about to say something else, but never does
Constantly touches their sleeves/jewelry/lip, like if they’re not holding something, they’ll fall apart
Laughs too easily, but it never quite reaches their eyes
Over-apologizes for things no one noticed
Craves affection but flinches when they get it
Body language = trying to take up as little space as possible
Flashes of unexpected rage, like pressure finally cracking glass
Always says “I’m fine” in a tone that screams “Please ask again”
Cries alone, then wipes their face like it’s a secret
Feels safest in chaos because stillness feels like waiting for pain
Thinks being loved means being a burden
Cannot remember the last time they were truly, fully relaxed
Keeps people at arm’s length, but is the first to drop everything if someone else needs help
Treats their own joy like it's a luxury they didn’t earn
-
 0ncem0rew1thfeel1ng reblogged this · 1 week ago
0ncem0rew1thfeel1ng reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 sparklingsilvermagnolias reblogged this · 1 week ago
sparklingsilvermagnolias reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 deobfuscated-duck liked this · 2 weeks ago
deobfuscated-duck liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 justnerdy15 liked this · 2 weeks ago
justnerdy15 liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 lacependragon liked this · 2 weeks ago
lacependragon liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 thatndginger reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
thatndginger reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 jesterswritingblog reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
jesterswritingblog reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 breneli0-asoiaf-lover liked this · 3 weeks ago
breneli0-asoiaf-lover liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 soupscold liked this · 1 month ago
soupscold liked this · 1 month ago -
 zombiemantises liked this · 1 month ago
zombiemantises liked this · 1 month ago -
 soupscold reblogged this · 1 month ago
soupscold reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 oogelyboogely reblogged this · 1 month ago
oogelyboogely reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 oogelyboogely liked this · 1 month ago
oogelyboogely liked this · 1 month ago -
 newdawnhorizon reblogged this · 1 month ago
newdawnhorizon reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 petrock-rambles reblogged this · 1 month ago
petrock-rambles reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 sarifel-corrisafid-ilxhel liked this · 1 month ago
sarifel-corrisafid-ilxhel liked this · 1 month ago -
 starlantern reblogged this · 1 month ago
starlantern reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 basilandbitter reblogged this · 1 month ago
basilandbitter reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 thegroovygroupie liked this · 1 month ago
thegroovygroupie liked this · 1 month ago -
 writeshine reblogged this · 1 month ago
writeshine reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 rebirthresource reblogged this · 1 month ago
rebirthresource reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 hellooocaffeine reblogged this · 2 months ago
hellooocaffeine reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 ha-im-gonna-die-alone reblogged this · 2 months ago
ha-im-gonna-die-alone reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 alkdfkkslaldkjdka reblogged this · 2 months ago
alkdfkkslaldkjdka reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 futuristicallyclever42 liked this · 2 months ago
futuristicallyclever42 liked this · 2 months ago -
 mudwizardbignaturals reblogged this · 2 months ago
mudwizardbignaturals reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 dark-academia-lair reblogged this · 2 months ago
dark-academia-lair reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 g0ddamnb0x liked this · 2 months ago
g0ddamnb0x liked this · 2 months ago -
 elxaine liked this · 2 months ago
elxaine liked this · 2 months ago -
 dirt-and-wyrms liked this · 2 months ago
dirt-and-wyrms liked this · 2 months ago -
 arsonstick liked this · 2 months ago
arsonstick liked this · 2 months ago -
 toomanyfandomsstuff reblogged this · 2 months ago
toomanyfandomsstuff reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 toomanyfandomsstuff liked this · 2 months ago
toomanyfandomsstuff liked this · 2 months ago -
 jedi-bird reblogged this · 2 months ago
jedi-bird reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 exalteranima reblogged this · 2 months ago
exalteranima reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 ahb-writes liked this · 2 months ago
ahb-writes liked this · 2 months ago -
 furiousphoenix reblogged this · 2 months ago
furiousphoenix reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 gallery-mg liked this · 2 months ago
gallery-mg liked this · 2 months ago -
 spamforwritingstuff reblogged this · 2 months ago
spamforwritingstuff reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 completelyconfusing liked this · 2 months ago
completelyconfusing liked this · 2 months ago -
 demimachia reblogged this · 2 months ago
demimachia reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 demimachia liked this · 2 months ago
demimachia liked this · 2 months ago -
 wordwizards reblogged this · 2 months ago
wordwizards reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 scribblesandscratches reblogged this · 2 months ago
scribblesandscratches reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 thebookwyrm liked this · 2 months ago
thebookwyrm liked this · 2 months ago -
 ninjasmudge liked this · 2 months ago
ninjasmudge liked this · 2 months ago -
 misswhatsit reblogged this · 2 months ago
misswhatsit reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 grandmasickomode reblogged this · 2 months ago
grandmasickomode reblogged this · 2 months ago -
 errorcritical reblogged this · 2 months ago
errorcritical reblogged this · 2 months ago

119 posts


