119 posts
Latest Posts by sparklingsilvermagnolias - Page 4
🍀 21 Plot Twist Ideas 🍀
Stuck on your WIP? Unsure of how a scene should go? Feel as though your story is lacking substance? Enduring with the frustrations of writer’s block?
Why not try throwing in a plot twist?
A messenger brings bad news
Something important is stolen
Someone vanishes without a trace
An important item is damaged
Protagonist recognizes a face in the crowd
Someone seems to intentionally fail
Protagonist finds an item thought lost
A charitable act has a harmful result
A cruel act has a beneficial outcome
Someone unexpectedly returns the favour
A raging storm moves across town
A gift makes a character the target of a murderer
A fallen enemy makes one last attack
Only one character in danger can be saved
An enemy saves the life of Protagonist’s friend
A will from a long-lost relative appears
A secret rival seeks to replace Protagonist
A thief makes Protagonist their next target
An obscure law suddenly becomes important
Strangers mistake Protagonist for a fugitive
A tool breaks when needed most
How I improved my writing style... without actually writing.
Intro : It's just a clickbait title to talk about theory and side techniques - before actually practicing, of course.
LINGUISTIC ISN'T GRAMMAR - AND IT'S BETTER TO KNOW ABOUT BOTH. It's useful for writing impactful dialogue and giving your characters depth. Your characters' language should (ideally) take into account: their social position (rich or poor), the locality (local expressions?) and sometimes their age (different cultural references). And this is best transcribed with linguistic knowledge. In short: linguistics is descriptive, grammar is prescriptive.
The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages), phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language, and analogous systems of sign languages), and pragmatics (how the context of use contributes to meaning). (Linguistics, Wikipedia)
Literary theory isn't as boring as it sounds. Learn more about internal criteria of the text (figure of speech, style, aesthetic...) and external criteria of the text (the author's persona and responsability, the role of the reader and what is left to interpretation...). I refer you to the French Wikipedia page, which you can translate directly via your browser in case you need more information. (Make sure you translate the page not switch language, because the content isn't the same).
Listening to Youtube Video about the analysis of film sequences and/or scenario. Remember when I told you to read historical fiction to learn how to describe a castle properly ? Same vibe.
Novel adaptations of movies. = when the movie exists before the book, and not the other way around. e.g : The Shape of Water ; Pan's Labyrinth. In line with tip n°3, it allows us to see how emotions, scenes and descriptions have been translated into writing - and thus to better visualize concepts that may have been abstract.
Read books about authors' writing experiences. e.g : Stephen King, On Writing: A Memoir of the Craft. Everyone's different, but they can provide some insightful tips not only on the act of writing itself, but on the environment conducive to writing, planning… Comparing completely different authors' experience could also be fun (this video of King and Martin is actually one of my fav)
Ah and many thanks for your ❤ and reblogs on my latest post ! UwU
Tips From a Beta Reading Writer #2
How to Write Dialogue That Doesn’t Sound Like a Script
Okay, so here's the thing. After years of trying to get dialogue right, I think I've finally cracked the code.
Read it aloud.
Yeah, you heard me. Just read your characters' lines out loud. You’ll be shocked at how quickly you can tell if something sounds natural or like you’re writing for a robot. If you’ve never said that line in your life, and if you’ve never heard someone say it in real life, it’s probably time for a change.
This simple trick has literally transformed my writing for the better. Dialogue that used to feel stiff and scripted now flows like a conversation between friends. Just try it. Your characters will thank you, and so will your readers.
Also, if you catch yourself saying “What?” after reading a line, that’s your cue. It’s gotta go.
GUIDE: NAMING A TOWN OR CITY
This post was originally from a FAQ, but since the original link is now defunct, I am re-posting it here.
There are many things to keep in mind when naming the town or city in your novel:
1) Genre/Theme/Tone
It’s very important to consider the genre and theme of your story when choosing a town name. Take these names for example, each of which indicates the genre or theme of the story: King’s Landing (sounds fantastical) Cloud City (sounds futuristic) Silent Hill (sounds scary) Sweet Valley (sounds happy and upbeat) Bikini Bottom (sounds funny) Radiator Springs (sounds car-related) Halloween Town (sounds Halloween-related) Storybrooke (sounds fairytale-related) 2) Time/Place It’s also important to consider the time and place where your story takes place. For example, you wouldn’t use “Vista Gulch” as a name for a town in Victorian England. You probably wouldn’t use it for a town in modern day North Carolina, either. Vista is a Spanish word and would normally be found in places where Spanish names are common, like Spain, Central and South America, the southwest United States (including southern California), Cuba, Puerto Rico, Dominican Republic, and Florida. 3) Size/Settlement Type An isolated town of 300 people probably won’t be Valley City, but a sprawling metropolis of 30 million could be called Windyville, because it could have started out as a small town and grew into a large city. 4) Geography Words like gulch, butte,and bayou tend to be regional terms. You probably wouldn’t find Berle’s Bayou in Idaho, or Windy Butte in Rhode Island. Words like mount, cape, and valley are dependent upon terrain. Most of the time, you won’t have a town named “mount” something unless there are hills or mountains nearby. You wouldn’t use “cape” unless the town was on a cape, which requires a large body of water. 5) History Is there a historical person or event that your town might be named after? The Simpsons’ hometown of Springfield is ironically named after its founder, Jebediah Springfield. Chattanooga, Tennessee is named after the Cherokee town that was there first. Nargothrond, in The Lord of the Rings, is an Elvish town with an Elvish name. 6) Combination of Words
person name + geographical term = Smithfield, Smith Creek
group name + geographical term = Pioneer Valley, Settlers’ Ridge
descriptive word + geographical term = Mystic Falls, Smoky Hill
person name + settlement type = Smithton, Claraville
landmark + settlement type = Bridgton, Beaconville
Word Lists
Types of Settlements

Geographical Features
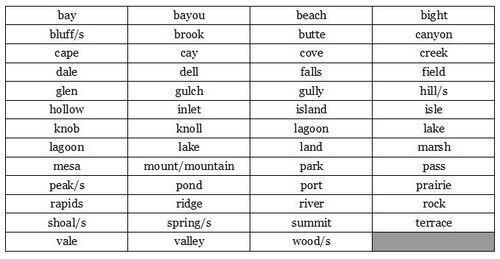
Place Words

Common Suffixes
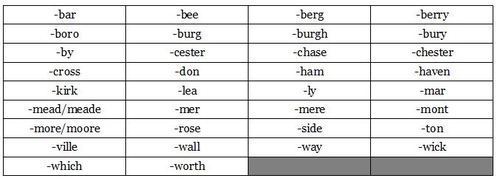
Other Descriptors
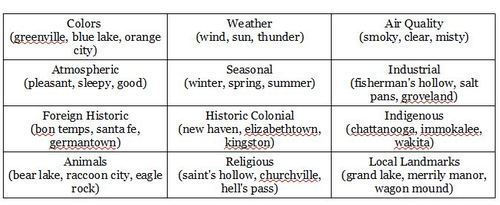
Tips on Making the Writing Process Easier
Use sticky notes to write down and organize major plot points
When inspiration for an idea strikes, write it down every single time. You never know if you might need that idea, and if you don’t write it, you will forget it.
Write the dialogue first. That way, you have a set up for a scene, but don’t have to focus too hard on narration.
Write your story by scene by scene. This way, you can focus on a scene at a time instead of an entire story. This does not mean you should stop focusing on writing a story
Remember to eat and drink
When you get stuck, stir up some conflicts.
Get The Emotion Thesaurus by Angela Ackerman and Becca Puglisi. It’s a guide for nearly every emotion you can write
Use a notebook and write by hand. I know it sounds awful (and for some, it might be awful) but writing with a pen and paper is drastically different than writing on a laptop, and this can make it so much easier
Remember to have a social life. Friends are important for your well-being (and possibly your wip)
Your outline is there to guide you through your story. But if your story disagrees with your outline, derail from the outline and come back to it when/if you get back on track
If you don’t get back on track, either continue with the story and hope you don’t get stuck, or tweak your outline
That’s it for now. Follow me for more writing tips and advice
Reactions to...
Reactions to… getting betrayed
Reactions to… getting kissed
Reactions to… the other being jealous
Reactions to… seeing someone again after a long time
Reactions to… being stuck somewhere
Reactions to… a love confession
Reactions to... being punched
If you like my blog and want to support me, you can buy me a coffee or become a member! And check out my Instagram! 🥰
Physical Contact Masterpost
Hand-Holding Dialogue
Hand-Holding
Touching
Hugs
Hugging Dialogue
Touch Starved Prompts
Touches Ask Games
Super soft intimacy
Casual Affections
Seeking out physical affection
Romantic, non-sexual intimacy prompts
Kisses
First Kisses
First Kiss Prompts
Accidental Kisses
Places for kissing
Angsty Kisses
If you like my blog and want to support me, you can buy me a coffee or become a member! And check out my Instagram! 🥰
How do I write a girldad? Because I saw a severe lack of girldad prompts in your writing prompts.
How to write a girldad
To create a multidimensional girldad character there are some things to consider:
Make the character show love and attention to his daughter(s).
He is proud of everything his daughters do and encourage them to achieve their dreams and simply do what they want to do.
Listening to his daughters concerns, and giving advice if it is wanted.
Being protective of his daughters, but knowing that they also need to respect their independence and the decisions they make.
Being involved in their lives, knowing who their friends are and how they are doing in school and in sports.
Treating other women in his life with respect, showing his daughters the right standard.
That the daughters are getting older may be difficult for the girldad, but he copes and learns to adapt to their new lives.
How to show their good relationship:
Including light-hearted and playful conversations to show their close bond.
Giving them sincere and loving exchanges.
Showing everyday interactions, like discussing school, friends, or plans for the weekend.
Having him give attention and affection to his daughters even in public.
Showing that the daughter's female friends also feel comfortable with the dad.
Having them share a hobby, especially one that is considered more feminine.
More: Masterpost: How to write a story
I hope you have fun with this! I'm thinking about making a prompt list for a girldad, so maybe there is something coming in the future.
- Jana
How to create an atmosphere: Forest
Sight
tall trees with thick canopies of leaves
alternating light coming in through the moving leafs of the trees
ground covered with a mix of grass, ferns, and fallen leaves
wildflowers adding splashes of colour
animals like deer, boars, squirrels, birds
insects like butterflies and bees add movement and life to the scene
Hearing
the air is filled with the melodious songs of birds
gentle rustling of leaves as the wind moves through the trees
constant hum and buzz of insects
the soft crunch of leaves, twigs, and soil while walking through the forest
Touch
the spongy feel and the soft coolness of moss
the rough texture of tree bark
the cooler temperature in the forest
with a gentle breeze that can be felt on your skin
Smell
the smell of fresh grass
the rich, earthy smell of soil and decaying leaves
the scent of fresh leaves, pine needles, and blooming flowers
the smell of the clean, slightly damp scent of water and wet earth from a nearby stream or pond
Taste
the clean taste of fresh air
the taste of sweet and tangy wildberries
the taste of self-picked mushrooms
the taste of edible wildflowers
the taste of a variety of nuts
the taste of wild greens
More: How to create an atmosphere
Writing Description Notes:
Updated 9th September 2024 More writing tips, review tips & writing description notes
Facial Expressions
Masking Emotions
Smiles/Smirks/Grins
Eye Contact/Eye Movements
Blushing
Voice/Tone
Body Language/Idle Movement
Thoughts/Thinking/Focusing/Distracted
Silence
Memories
Happy/Content/Comforted
Love/Romance
Sadness/Crying/Hurt
Confidence/Determination/Hopeful
Surprised/Shocked
Guilt/Regret
Disgusted/Jealous
Uncertain/Doubtful/Worried
Anger/Rage
Laughter
Confused
Speechless/Tongue Tied
Fear/Terrified
Mental Pain
Physical Pain
Tired/Drowsy/Exhausted
Eating
Drinking
Warm/Hot
20 Compelling Positive-Negative Trait Pairs
Here are 20 positive and negative trait pairs that can create compelling character dynamics in storytelling:
1. Bravery - Recklessness: A character is courageous in the face of danger but often takes unnecessary risks.
2. Intelligence - Arrogance: A character is exceptionally smart but looks down on others.
3. Compassion - Naivety: A character is deeply caring but easily deceived due to their trusting nature.
4. Determination - Stubbornness: A character is persistent in their goals but unwilling to adapt or compromise.
5. Charisma - Manipulativeness: A character is charming and persuasive but often uses these traits to exploit others.
6. Resourcefulness - Opportunism: A character is adept at finding solutions but is also quick to exploit situations for personal gain.
7. Loyalty - Blind Obedience: A character is fiercely loyal but follows orders without question, even when they're wrong.
8. Optimism - Denial: A character remains hopeful in difficult times but often ignores harsh realities.
9. Humor - Inappropriateness: A character lightens the mood with jokes but often crosses the line with their humor.
10. Generosity - Lack of Boundaries: A character is giving and selfless but often neglects their own needs and well-being.
11. Patience - Passivity: A character is calm and tolerant but sometimes fails to take action when needed.
12. Wisdom - Cynicism: A character has deep understanding and insight but is often pessimistic about the world.
13. Confidence - Overconfidence: A character believes in their abilities but sometimes underestimates challenges.
14. Honesty - Bluntness: A character is truthful and straightforward but often insensitive in their delivery.
15. Self-discipline - Rigidity: A character maintains strong control over their actions but is inflexible and resistant to change.
16. Adventurousness - Impulsiveness: A character loves exploring and trying new things but often acts without thinking.
17. Empathy - Overwhelm: A character deeply understands and feels others' emotions but can become overwhelmed by them.
18. Ambition - Ruthlessness: A character is driven to achieve great things but willing to do anything, even unethical, to succeed.
19. Resilience - Emotional Detachment: A character can endure hardships without breaking but often seems emotionally distant.
20. Strategic - Calculative: A character excels at planning and foresight but can be cold and overly pragmatic in their decisions.
These pairs create complex, multi-dimensional characters that can drive rich, dynamic storytelling.
---
+ If you find my content valuable, consider Support This Blog on Patreon!
The symbolism of flowers
Flowers have a long history of symbolism that you can incorporate into your writing to give subtext.
Symbolism varies between cultures and customs, and these particular examples come from Victorian Era Britain. You'll find examples of this symbolism in many well-known novels of the era!
Amaryllis: Pride
Black-eyed Susan: Justice
Bluebell: Humility
Calla Lily: Beauty
Pink Camellia: Longing
Carnations: Female love
Yellow Carnation: Rejection
Clematis: Mental beauty
Columbine: Foolishness
Cyclamen: Resignation
Daffodil: Unrivalled love
Daisy: Innocence, loyalty
Forget-me-not: True love
Gardenia: Secret love
Geranium: Folly, stupidity
Gladiolus: Integrity, strength
Hibiscus: Delicate beauty
Honeysuckle: Bonds of love
Blue Hyacinth: Constancy
Hydrangea: Frigid, heartless
Iris: Faith, trust, wisdom
White Jasmine: Amiability
Lavender: Distrust
Lilac: Joy of youth
White Lily: Purity
Orange Lily: Hatred
Tiger Lily: Wealth, pride
Lily-of-the-valley: Sweetness, humility
Lotus: Enlightenment, rebirth
Magnolia: Nobility
Marigold: Grief, jealousy
Morning Glory: Affection
Nasturtium: Patriotism, conquest
Pansy: Thoughtfulness
Peony: Bashfulness, shame
Poppy: Consolation
Red Rose: Love
Yellow Rose: Jealously, infidelity
Snapdragon: Deception, grace
Sunflower: Adoration
Sweet Willian: Gallantry
Red Tulip: Passion
Violet: Watchfulness, modesty
Yarrow: Everlasting love
Zinnia: Absent, affection
List of 40 character flaws
Stubbornness, Unyielding in one's own views, even when wrong.
Impatience, Difficulty waiting for long-term results.
Self-doubt, Constant uncertainty despite evident abilities.
Quick temper, Excessive reactions to provocations.
Selfishness, Prioritizing one's own needs over others'.
Arrogance, Overestimating one's own abilities.
Trust issues, Difficulty trusting others.
Perfectionism, Setting unreachable high standards.
Fear of change, Avoiding changes.
Haunted by the past, Old mistakes or traumas influencing the present.
Jealousy, Envious of others' successes.
Laziness, Hesitant to exert effort.
Vindictiveness, Strong desire for revenge.
Prejudice, Unfair biases against others.
Shyness, Excessive timidity.
Indecisiveness, Difficulty making decisions.
Vulnerability, Overly sensitive to criticism.
Greed, Strong desire for more (money, power, etc.).
Dishonesty, Tendency to distort the truth.
Recklessness, Ignoring the consequences of one's actions.
Cynicism, Negative attitude and distrust.
Cowardice, Lack of courage in critical moments.
Hotheadedness, Quick, often thoughtless reactions.
Contentiousness, Tendency to provoke conflicts.
Forgetfulness, Difficulty remembering important details.
Kleptomania, Compulsion to steal things.
Hypochondria, Excessive concern about one's health.
Pessimism, Expecting the worst in every situation.
Narcissism, Excessive self-love.
Control freak, Inability to let go or trust others.
Tactlessness, Inability to address sensitive topics sensitively.
Hopelessness, Feeling that nothing will get better.
Dogmatism, Rigidity in one's own beliefs.
Unreliability, Inability to keep promises.
Closed-offness, Difficulty expressing emotions.
Impulsiveness, Acting without thinking.
Wounded pride, Overly sensitive to criticism of oneself.
Isolation, Tendency to withdraw from others.
NEED HELP WRITING? (a masterlist)
I have likely not added many that I've reblogged to this list. Please feel free to roam my blog and/or ask/message me to add something you'd like to see on this list!
Synonym Lists
Look by @writers-potion
Descriptors
Voices by @saraswritingtipps
Show, Don't Tell by @lyralit
Tips & Tricks
5 Tips for Creating Intimidating Antagonists by @writingwithfolklore
How To (Realistically) Make a Habit of Writing by @byoldervine
Let's Talk About Misdirection by @deception-united
Tips to Improve Character Voice by @tanaor
Stephen King's Top 20 Rules for Writers posted by @toocoolformedschool
Fun Things to Add to a Fight Scene (Hand to Hand Edition) by @illarian-rambling
Questions I Ask My Beta Readers by @burntoutdaydreamer
Skip Google for Research by @s-n-arly
Breaking Writing Rules Right: Don't Write Direct Dialogue by @septemberercfawkes
Databases/Resources
International Clothing
Advice/Uplifting
Too Ashamed of Writing To Write by @writingquestionsanswered
"Said" is Beautiful by @blue-eyed-author
HOW TO WRITE A CHARACTER WHO IS IN PAIN
first thing you might want to consider: is the pain mental or physical?
if it’s physical, what type of pain is it causing? — sharp pain, white-hot pain, acute pain, dull ache, throbbing pain, chronic pain, neuropathic pain (typically caused by nerve damage), etc
if it’s mental, what is the reason your character is in pain? — grief, heartbreak, betrayal, anger, hopelessness, fear and anxiety, etc
because your character will react differently to different types of pain
PHYSICAL PAIN
sharp and white-hot pain may cause a character to grit their teeth, scream, moan, twist their body. their skin may appear pale, eyes red-rimmed and sunken with layers of sweat covering their forehead. they may have tears in their eyes (and the tears may feel hot), but they don’t necessarily have to always be crying.
acute pain may be similar to sharp and white-hot pain; acute pain is sudden and urgent and often comes without a warning, so your character may experience a hitched breathing where they suddenly stop what they’re doing and clench their hand at the spot where it hurts with widened eyes and open mouth (like they’re gasping for air).
dull ache and throbbing pain can result in your character wanting to lay down and close their eyes. if it’s a headache, they may ask for the lights to be turned off and they may be less responsive, in the sense that they’d rather not engage in any activity or conversation and they’d rather be left alone. they may make a soft whimper from their throat from time to time, depends on their personality (if they don’t mind others seeing their discomfort, they may whimper. but if your character doesn’t like anyone seeing them in a not-so-strong state, chances are they won’t make any sound, they might even pretend like they’re fine by continuing with their normal routine, and they may or may not end up throwing up or fainting).
if your character experience chronic pain, their pain will not go away (unlike any other illnesses or injuries where the pain stops after the person is healed) so they can feel all these types of sharp pain shooting through their body. there can also be soreness and stiffness around some specific spots, and it will affect their life. so your character will be lucky if they have caretakers in their life. but are they stubborn? do they accept help from others or do they like to pretend like they’re fine in front of everybody until their body can’t take it anymore and so they can no longer pretend?
neuropathic pain or nerve pain will have your character feeling these senses of burning, shooting and stabbing sensation, and the pain can come very suddenly and without any warning — think of it as an electric shock that causes through your character’s body all of a sudden. your character may yelp or gasp in shock, how they react may vary depends on the severity of the pain and how long it lasts.
EMOTIONAL PAIN
grief can make your character shut themself off from their friends and the world in general. or they can also lash out at anyone who tries to comfort them. (five states of grief: denial, anger, bargaining, depression and eventual acceptance.)
heartbreak — your character might want to lock themself in a room, anywhere where they are unseen. or they may want to pretend that everything’s fine, that they’re not hurt. until they break down.
betrayal can leave a character with confusion, the feelings of ‘what went wrong?’, so it’s understandable if your character blames themself at first, that maybe it’s their fault because they’ve somehow done something wrong somewhere that caused the other character to betray them. what comes after confusion may be anger. your character can be angry at the person who betrayed them and at themself, after they think they’ve done something wrong that resulted in them being betrayed, they may also be angry at themself next for ‘falling’ for the lies and for ‘being fooled’. so yes, betrayal can leave your character with the hatred that’s directed towards the character who betrayed them and themself. whether or not your character can ‘move on and forgive’ is up to you.
there are several ways a character can react to anger; they can simply lash out, break things, scream and yell, or they can also go complete silent. no shouting, no thrashing the place. they can sit alone in silence and they may cry. anger does make people cry. it mostly won’t be anything like ‘ugly sobbing’ but your character’s eyes can be bloodshot, red-rimmed and there will be tears, only that there won’t be any sobbing in most cases.
hopelessness can be a very valid reason for it, if you want your character to do something reckless or stupid. most people will do anything if they’re desperate enough. so if you want your character to run into a burning building, jump in front of a bullet, or confess their love to their archenemy in front of all their friends, hopelessness is always a valid reason. there’s no ‘out of character’ if they are hopeless and are desperate enough.
fear and anxiety. your character may be trembling, their hands may be shaky. they may lose their appetite. they may be sweaty and/or bouncing their feet. they may have a panic attack if it’s severe enough.
and I think that’s it for now! feel free to add anything I may have forgotten to mention here!
Other Words for "Look" + With meanings | List for writers
Many people create lists of synonyms for the word 'said,' but what about the word 'look'? Here are some synonyms that I enjoy using in my writing, along with their meanings for your reference. While all these words relate to 'look,' they each carry distinct meanings and nuances, so I thought it would be helpful to provide meanings for each one.
Gaze - To look steadily and intently, especially in admiration or thought.
Glance - A brief or hurried look.
Peek - A quick and typically secretive look.
Peer - To look with difficulty or concentration.
Scan - To look over quickly but thoroughly.
Observe - To watch carefully and attentively.
Inspect - To look at closely in order to assess condition or quality.
Stare - To look fixedly or vacantly at someone or something.
Glimpse - To see or perceive briefly or partially.
Eye - To look or stare at intently.
Peruse - To read or examine something with great care.
Scrutinize - To examine or inspect closely and thoroughly.
Behold - To see or observe a thing or person, especially a remarkable one.
Witness - To see something happen, typically a significant event.
Spot - To see, notice, or recognize someone or something.
Contemplate - To look thoughtfully for a long time at.
Sight - To suddenly or unexpectedly see something or someone.
Ogle - To stare at in a lecherous manner.
Leer - To look or gaze in an unpleasant, malicious way.
Gawk - To stare openly and stupidly.
Gape - To stare with one's mouth open wide, in amazement.
Squint - To look with eyes partially closed.
Regard - To consider or think of in a specified way.
Admire - To regard with pleasure, wonder, and approval.
Skim - To look through quickly to gain superficial knowledge.
Reconnoiter - To make a military observation of a region.
Flick - To look or move the eyes quickly.
Rake - To look through something rapidly and unsystematically.
Glare - To look angrily or fiercely.
Peep - To look quickly and secretly through an opening.
Focus - To concentrate one's visual effort on.
Discover - To find or realize something not clear before.
Spot-check - To examine something briefly or at random.
Devour - To look over with eager enthusiasm.
Examine - To inspect in detail to determine condition.
Feast one's eyes - To look at something with great enjoyment.
Catch sight of - To suddenly or unexpectedly see.
Clap eyes on - To suddenly see someone or something.
Set eyes on - To look at, especially for the first time.
Take a dekko - Colloquial for taking a look.
Leer at - To look or gaze in a suggestive manner.
Rubberneck - To stare at something in a foolish way.
Make out - To manage to see or read with difficulty.
Lay eyes on - To see or look at.
Pore over - To look at or read something intently.
Ogle at - To look at in a lecherous or predatory way.
Pry - To look or inquire into something in a determined manner.
Dart - To look quickly or furtively.
Drink in - To look at with great enjoyment or fascination.
Bask in - To look at or enjoy something for a period of time.


basic things you should know about your main characters
how is their relationship with their family
what are their beliefs, if they have any
what is their motivation (preferably something unrelated to their love interest/romantic feelings)
who were they raised to be vs. who they became/are becoming
what are their plans for the future, if they have any
how they feel about themselves and how it affects their behaviour
how do they feel about things they cannot control
and last but not least: Why is This Character the Protagonist??





I made these as a way to compile all the geographical vocabulary that I thought was useful and interesting for writers. Some descriptors share categories, and some are simplified, but for the most part everything is in its proper place. Not all the words are as useable as others, and some might take tricky wording to pull off, but I hope these prove useful to all you writers out there!
(save the images to zoom in on the pics)
Writing Resources List

I use my blog to share writing resources that I’ve collected over the years. I’ve recently gotten some new followers, so I thought I would make a list of many of these resources for easy reference.
(However, this is not a complete list of all the resources I’ve posted. For more writing resources, feel free to check out my blog.)
Encouragement for Writers
Writer’s Block & Procrastination
Writing Your Story’s Plot
How to Write a Scene
Choosing a Setting for Your Story
Character Arc & Character Development
Character Traits
How to Write Heroes & Villains
Elemental Magic & Superpowers
Writing Magic Systems
Fantasy Writing & World-Building
Writing Fight Scenes
Swords and Bows
Writing Mermaids
Writing Relationships & Romance
Romance & Relationship Prompts
+
I’m a writer, poet, and editor. I share writing resources that I’ve collected over the years and found helpful for my own writing. If you like my blog, follow me for more resources! ♡
How to Write a Character
↠ Start with the basics, because obviously. Name. Age. Gender. Maybe even a birthday if you’re feeling fancy. This is step one because, well, your character needs to exist before they can be interesting. But nobody cares if they’re 27 or 37 unless it actually matters to the story.
↠ Looks aren’t everything… but also, describe them. Yes, we know their soul is more important than their hair color, but readers still need something to visualize. Do they have the kind of face that makes babies cry? Do they always look like they just rolled out of bed? Give us details, not just “tall with brown hair.
↠ Personality isn’t just “kind but tough.” For the love of storytelling, give them more than two adjectives. Are they kind, or do they just pretend to be because they hate confrontation? Are they actually tough, or are they just too emotionally repressed to cry in public? Dig deeper.
↠ Backstory = Trauma (usually). Something shaped them. Maybe it was a messy divorce, maybe they were the middle child and never got enough attention, or maybe they once got humiliated in a spelling bee and never recovered. Whatever it is, make it matter to who they are today.
↠ Give them a goal. Preferably a messy one. If your character’s only motivation is to “be happy” or “do their best,” they’re boring. They need a real goal, one that conflicts with who they are, what they believe in, or what they think they deserve. Bonus points if it wrecks them emotionally.
↠ Make them suffer. Yes, I said it. A smooth, easy journey is not a story. Give them obstacles. Rip things away from them. Make them work for what they want. Nobody wants to read about a character who just gets everything handed to them (unless it’s satire, then carry on).
↠ Relationships = Depth. Nobody exists in a vacuum. Who do they love? Who annoys the hell out of them? Who do they have that messy, can’t-live-with-you-can’t-live-without-you tension with? People shape us. So, shape your character through the people in their life.
↠ Give them a voice that actually sounds like them. If all your characters talk the same, you’ve got a problem. Some people ramble, some overthink, some are blunt to the point of being offensive. Let their voice show who they are. You should be able to tell who’s talking without dialogue tags.
↠ If they don’t grow, what’s the point? People change. They learn things, make mistakes, get their hearts broken, and (hopefully) become a little wiser. If your character starts and ends the story as the same exact person, you just wasted everyone’s time.
↠ Flaws. Give. Them. Flaws. Nobody likes a perfect character. Give them something to struggle with, maybe they’re selfish, maybe they push people away, maybe they’re addicted to the thrill of self-destruction (fun!). Make them real. Make them human.
↠ Relatability is key. Your character doesn’t have to be likable, but they do have to be understandable. Readers need to get them, even if they don’t agree with them. If your character never struggles, never doubts, and never screws up, I have bad news: they’re not a character, they’re a mannequin.
↠ You’re never actually done. Characters evolve, not just in the story, but as you write them. If something feels off, fix it. If they feel flat, dig deeper. Keep refining, rewriting, and letting them surprise you. That’s how you create someone who feels real.
Now go forth and write characters that actually make people feel something. And if you need a reminder, just ask yourself: Would I care if this person existed in real life? If the answer is meh, start over.
How to Write Realistic Characters in Your Stories
Writing realistic characters can be challenging because there's a lot to consider. Even though I've touched on this subject before, it's a complex topic that requires vast knowledge to get it right. Here's a guide on what to consider when writing people in your stories:
1. Similarities to Real People: Just like in real life, your characters need to share traits with real people. This helps readers connect with your story and characters on a more personal level.
2. Negative Traits: It's important to explore your characters' negative traits to make them more believable. For example:
- People often think of themselves first because it's part of our DNA to protect and care for ourselves. Your characters should share these qualities.
- People pretend to be something they aren't or act differently in front of others due to fear of not being liked. This affects almost everyone at some point.
- People are easily distracted and often miss important lessons or moments that contribute to their growth.
- People are dishonest at times to protect themselves, making it hard to fully trust them.
3. Outside Influence: Your characters are also influenced by external factors, just like you are in real life. Consider these suggestions to help you along the way:
- People tell you what to think, feel, believe, and how to act. They often tell you that you're not good enough. These are common issues we go through as humans, making it important to your stories.
4. Realism vs. Idealism: While we sometimes want to write stories filled with fairy tales of a perfect world, sadly, that doesn't exist. There will always be someone who breaks your trust, and writing about this is important. You can take this information and practice cause, effect, and solutions to these situations to see what you come up with.
I hope this helps you on your writing journey. Happy writing!
Avoiding Plot Holes by Seeding Doubt
Having an “expert” character conveniently fuck up right when the plot needs it to happen, when they otherwise would never, always loudly looks like the hand of the author sabotaging things. Which is exactly what’s happening.
However, if you set up that scene in a way where that fuckup is possible and warranted, you can turn “this is so contrived” to “omg I knew that was going to happen”.
Some suggestions!
Firstly, if we’re dealing with humans, humans are not machines. Variability in skill even at the expert level happens. Go watch the Olympics or any professional sporting event and people have terrible days all the time.
In fiction, a conveniently terrible day because that’s just how this works doesn’t fly. Diablos ex machinas tend to go over easier than deus ex machinas, but a character failing at a critical challenge in the narrative for no reason screws with a lot of the tension and expectations. “For no reason” takes no effort by the author to set up and pay off, and it reads as cheap.
Behavioral variables
I am a novice archer. I write expert archers. I do not write supernaturally accurate archers. From the very beginning of my story, my expert, with four centuries of experience, isn’t nailing perfect kill shots with every hit. A) he doesn’t need to and B) leaving his enemy to die slowly and painfully is a low he will absolutely stoop to if he thinks it’s warranted.
He’s as good as he has to be and if he gets the job done, he doesn’t care if it’s a little messy. Him being messy and overconfident is what gets him in the end, too. If he’s trying, he’ll do better, but most of the time “eh, I got close enough, they’ll die eventually” is his mindset.
“Expert” in fiction being “this is a character who will reliably pass the challenges set up for them by the narrative”.
So if you have an “expert,” allowing them to get a little bit lazy and overconfident, or simply not think of themselves as needing to be perfect in a given situation, you allow yourself a lot of wiggle room for them to majorly fuck up.
Doesn’t work very well if I throw my archer into an archery tournament, but I haven’t done that, and I’ll get to that later.
Environmental variables
Using the archery example once again: Archery is finnicky and precision is key. So if you’ve got your archer, or any marksman, in a windy environment, they have to work that much harder to factor in the wind when setting up their shot.
If it’s rainy, or the sun’s in their face, or it’s dark, or it’s loud and they can’t focus, these things aren’t exact data points the audience is going to do the math on. Or, if they and their enemy are moving, which, in combat, is highly likely.
Physiological variables
Maybe your character didn’t get enough sleep, or they’re stressed about this moment, they’re cracking under the pressure, they’re doubting themselves, the enemy got into their head, or they’re distracted worrying about something else. Or they got drunk the night before, they ate too much or too little. They’re sick, their hands are sweaty, they’ve got a sinus headache. They’ve got cramps, or hot flashes, or earlier they pulled a muscle and it still tweaks.
These are all, once again, introducing doubt into the narrative so that, when they fuck up as the plot demands, the audience should consider “well they weren’t at their best, I believe it”.
—
The sloppy way to do this is to go, in the moment:
“But because it was windy, X missed his shot”.
Is this the first time the reader is learning that it’s windy? Pretty convenient to introduce it right as it becomes important.
Rather, establish your variable beforehand in a disconnected moment. Try to ground it to a different element, otherwise it might look like it’s being mentioned for no other reason than “this is important”. Or, if it’s environmental, bury it with the other sensory descriptors.
When establishing the scene and setting, casually mention how the wind is interacting with the characters—making their hair a mess, throwing pollen everywhere, making skirts billow, etc.
Have another character complain about this variable bothering them
Have the character instantly regret the decision they made the night before for unrelated reasons. Like, if they got drunk, now they’ve still got a headache.
Depends on the story and the audience, of course, but I personally think having the narrator explicitly call out the variable fuckery going on reads a bit hammy. I like letting the audience figure out what went wrong with the clues I give.
If the scene demands, I'll also let my characters get annoyed and upset about their shots going wrong and blaming the environment. So long as it's not "hand of the author here to tell you what went wrong" you've got options.
I wouldn’t pull this trick too many times, otherwise your “expert” ends up consistently not an expert and then their sudden success looks suspect and contrived.
If you are writing some sort of tournament where this character is deliberately setting themselves up for success and is considering all these variables… a great example I like is Todoroki vs Bakugo in My Hero Academia season 2.
Dude is an uncertain mess throughout the rest of his tournament once his “fuck you dad I’m gonna win by half-assing it” suddenly isn’t enough to beat Midoriya. He’s forced to face some Tragic Backstory and it throws him off his game—establishes doubt.
He has a string of successes once he starts taking baby steps with the other half of his powers, and in the finale, he’s up against someone where he really does have to give it his all if he wants to win. His brute force powers are up against someone who has honed his very specific and powerful abilities for a decade.
And he can’t do it.
The final fight stops being a matter of power metrics and who would win if they both were competing at their best with all the tricks in their playbook available, which is what most of the tournament had been up to this point.
Basically—it stops being a numbers game, and starts being an emotional one. If you have a character you need to fail at something, but who wouldn’t otherwise, consider shifting the battle from external to internal, so the task failure is just the catalyst for the real meat of the story: what this loss means to this person in the long run.
**Side note there are of course a ton of anime tournament fights probably better than this one, Rock Lee’s whole arc against Gaara is one of them, I just don’t remember it well enough to comment on it.
Not every reader is going to be savvy enough to go “well that’s going to be important later”. Use betas and editors to help gauge how vague or obvious your foreshadowing is.
But even if you have readers sussing out your foreshadowing: Part of the fun is figuring out how the journey will end, even if we know when and where. Otherwise tragedies and prequels wouldn’t be made.
The dramatic irony of knowing variable fuckery is at play when the character is unaware can be so fun as the audience. Horror films are kind of built on it.
so why should i care if people see my data
so glad you asked 😁 for one, any party holding information about the other shifts the power in their favor (rip rob kling i’m obsessed with him and think his work on the societal implications of technology should be mandatory reading for everyone <3) but most people don’t care about their data being stored because 1) “i’m not doing anything bad/illegal for me to be worried” 2) “idc if they know what i’m buying at target, what’s that going to tell them about me other than i like chocolate?” 3) “so what if they have my personal information? hows that going to impact me other than getting a few targeted ads?”
first off you need to understand that companies don’t just have access to what you do on their specific app. your data can be bought and sold to companies who aggregate all that information and put together a full picture of who you are. they get information about your spending habits, daily schedule, health, fitness, contact information, media preferences, etc etc so on and can sell that neat little package of information to anyone.
and let's not forget there is a historical precedent of certain demographics being targeted and criminalized! just look at the racial origins of loitering laws. who's to stop the government or other organizations from analyzing data and using it to silence and punish certain groups/people?
im too sleep deprived to be comprehensible rn but some articles
How Target Figured Out A Teen Girl Was Pregnant Before Her Father Did Facebook Releases New Research into How People Respond After a Break-Up Why we should collectively worry about Facebook and Google owning our data Facebook Manipulated 689,003 Users' Emotions For Science How Steve Bannon used Cambridge Analytica to further his alt-right vision for America
I once saw someone say
There are two kinds of writers
One's an architect
And the other's a gardener
The architect plans each careful window
While the gardener simply plants a seed and watches it grow
"Which one am I?" I wondered
Then I thought, I planned a house, but I plant seeds in the foundation
The vines grow
Through the windows
And the foundations are riddled with roots
I had a plan but lo behold
The tree that grows through the roof
Questions to Ask Yourself About Your Character
What is their relationship with their parents?
What is their favorite meal?
How do they identify?
What's their style?
Are they proud of themselves?
Are they patient or impatient?
Do they have siblings, and what's their relationship with them?
What are their standards?
Have they ever been in love?
When was the last time they felt loved?
Have they gotten their heart broken?
Do they know who they are?
What are their preferences?
What do they want?
What are their goals?
What would they do if they failed?
What would they save in a fire?
What's one childhood item they still love?
where can i find works that critique the porn industry and beauty industry that doesn’t come from radfems
Well, I happen to agree with radical feminists generally about beauty culture and the porn industry haha. Radical feminists aren't inherently trans exclusionary! I identify as a radical feminist and I believe trans people have a right to bodily autonomy, just like Andrea Dworkin and Catharine MacKinnon!
But, let me make you a list, just off the top of my head:
Pornography: Men Possessing Women by Andrea Dworkin: a classic and Dworkin is a former sex worker so I trust her takes on this stuff more than most others
OnlyFans Is Not a Safe Platform for ‘Sex Work.’ It’s a Pimp. by Catharine MacKinnon: Twitter leftists got furious at this article so clearly it's good
‘Sex without consent, I suppose that is rape’
"Talking to my Students About Porn" by Amia Srinivasan from her book, The Right to Sex, which apparently great although I haven't gotten around to reading it yet
Pornland: How Porn Has Hijacked Our Sexuality by Gail Dines
The Age of the Instagram Face by Jia Tolentino: I find Jia personally annoying but this piece is good
Everyone is Beautiful And No One Is Horny by RS Benedict
Emily Ratajkowski and the Burden of Looking Perfect by Carrie Battan
Appearance as a Feminist Issue by Deborah L. Rhode
The Skincare Con by Krithika Varagur
The Beauty Myth by Naomi Wolf: she's gone off the deep end but this book is classic
Perfect Girls, Starving Daughters by Courtney E. Martin: this book triggered my eating disorder recovery tbh
That should get you started!
Random Stuff for Your Story
I have bookmarks saved for random, different, interesting topics that don’t really fit into any single category, so I decided to just put them all together in one list.

A list of resources on miscellaneous topics to help make your stories more interesting.
Writing Accurate Heist Scenes A tumblr thread that discusses accurate heist scenes for heist movies, and what it’s like to work as a security guard.
Friends, Not Love Interests Helpful advice for anyone who is writing two characters as friends (particularly when one is female and the other is male), in order to help minimize the chance of readers wanting them to fall in love.
The Writer’s Guide to Distinguishing Marks on Characters A basic guide on different types of distinguishing marks for characters, such as freckles, birthmarks, scars, and tattoos.
Don’t Use Specific Numbers in Your Story A tumblr thread that explains if your story doesn’t need a specific number for something (whether a date, age, span of time, etc.), then you don’t need to use a number. Includes helpful examples.
Pet Peeves in TV Shows and Movies A tumblr thread with different lists of things that people find annoying in TV shows and movies. Many of these things can also apply to situations in stories.
Types of Paperwork That Characters Could Do A tumblr thread that discusses how fanfiction writers often give their characters “large amounts of paperwork they hate doing,” but don’t describe the type of paperwork. Provides a list of different types of paperwork that characters could be working on.
In Time Travel Movies, When the Time Traveler Asks... A tumblr thread that discusses more realistic responses for when a time traveler asks what year it is or where they are, instead of people automatically thinking they are weird or crazy for asking.
Reasons for a Character’s Death Explains the reasons why you might kill off a character, and offers advice on how to make a character’s death meaningful.
Dialogue Responses to “I Thought You Were Dead!” A list of different responses that a character could give when someone else says, “I thought you were dead.”
+
I’m a writer, poet, and editor. I share writing resources that I’ve collected over the years and found helpful for my own writing. If you like my blog, follow me for more resources! ♡
Soooo maybe an oddly specific question. Could you recommend your favorite books about politics in the last decade? Or even in the last 20 years? My school sucked and I'm trying to learn about modern politics on my own but there's so much content available that I'm lost. And you're very smart and read a lot, so I'm hoping you have recommendations. Thanks!!!
Omg thank you, I do read a lot so I’m glad someone appreciates it.
Here are my top 20 books on politics and related sociological issues. I included some of these in a list I made over Christmas but I'll add to it here, and most are from the last 20 years.
This Town: Two Parties and a Funeral — plus plenty of valet parking! — in America’s Gilded Capital by Mark Leibovich
They Were Her Property: White Women as Slave Owners in the American South by Stephanie E. Jones-Rogers
The Destruction of Hillary Clinton by Susan Bordo (pair with What Happened by Hillary Rodham Clinton)
All the President's Men by Carl Bernstein
We Were Eight Years in Power: An American Tragedy by Ta-Nehisi Coates
Caste: The Origins of Our Discontents by Isabel Wilkerson
The Cruelty is the Point by Adam Serwer
Why We're Polarized by Ezra Klein
Women & Power: A Manifesto by Mary Beard
The Soul of America: The Battle for our Better Angels by Jon Meacham
This Will Not Pass: Trump, Biden, and the Battle for America's Future by Jonathan Martin and Alexander Burns
Political Fictions by Joan Didion
A Promised Land by Barack Obama
The Origins of Totalitarianism by Hannah Arendt
Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham Lincoln by Doris Kearns Goodwin
The Optimistic Leftist: Why the 21st Century Will Be Better Than You Think by Ruy Teixeira
The Perils of “Privilege” by Phoebe Maltz Bovy
Both/And by Huma Abedin
Renegades by Barack Obama and Bruce Springsteen (usual recommendation to listen to their podcast)
Beautiful Things by Hunter Biden (As you can tell by the below excerpt, Hunter Biden is me fr fr)

Excellent tips and habits for writers
The advice I've given before is to write every scene you think of, no matter if it gets used or not. Its always a great idea to go back every once and a while and edit these scenes, or revise them.
Never force inspiration or a scene. If it isn't coming naturally, take a break and come back later or the next day. it's important to give yourself time to think. use your break to day dream about your story and what could come next. if your brain is happy, this should be relatively simple. If your brain isn't happy, then you need to take a longer break, stop writing for the day all together, or write something else.
if you're a pantser, like me, and it's hard to plot. You can practice reverse plotting, and plot your story as you go. make notes of things that happen in your story, changes in a character, changes in the plot, changes in the setting, dates for events, timelines, important information that's been revealed, anything you deem important to your story.
always reread what you've already written. don't try to edit it. turn off your editor brain and reread your story so far before you resume writing, so you can get into the voice and tone that you've already established.
if you're finding it difficult to start writing or keep writing. try turning off your internal editor and free write. it's good practice to be able to write down your unfiltered thoughts or daydreams without having to stop and edit while you're writing. it helps with your writing flow, getting the scene down onto the page, and increases your writing intuition.
before you write, always take time to daydream or think about your story beforehand. it helps things go much smoother in the long run.
if you've been working on something for a long time, don't pressure yourself into confinement. if you want to work on something new but you're worried about what you've been working on, don't. stop worrying and write what you want. forcing yourself to keep writing something when you don't want to is just going to make you burn out faster.
don't be afraid to create visuals or playlists that help you with what you're writing. It's an enviable talent to be able to write something off a photo you saw on pinterest, or a song you really like.
if you find yourself in a mood where you want to write really badly, but you have no idea what you want to write, and none of the prompts you find are appealing enough. find an activity you use to destress, whether its listening to music, listening to asmr, doom scrolling on social media, or browsing pinterest. go do that. chances are, you'll find something that will inspire you what to write when you're not looking for it.