Clostridium Perfringes
Clostridium perfringes
Nagler reaction: C. perfringens phospholipase causes turbidity around the colonies on egg-yolk medium. Inhibited by specific antiserum.
Anaerobic stormy fermetantion in milk media

Food poisoning strains produce heat resistant spores.
Type A spores producing gas gangrene are inactivated by heat quickly.

More Posts from T-b-a-blr-blog and Others



MORE MIXED MNEMONICS
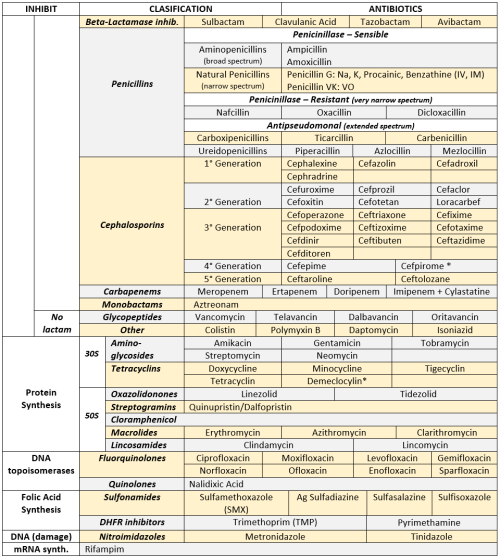
ANTIBIOTICS CHEAT SHEET :)
Also, REMEMBER!!!!
* Sulfonamides compete for albumin with:
Bilirrubin: given in 2°,3°T, high risk or indirect hyperBb and kernicterus in premies
Warfarin: increases toxicity: bleeding
* Beta-lactamase (penicinillase) Suceptible:
Natural Penicillins (G, V, F, K)
Aminopenicillins (Amoxicillin, Ampicillin)
Antipseudomonal Penicillins (Ticarcillin, Piperacillin)
* Beta-lactamase (penicinillase) Resistant:
Oxacillin, Nafcillin, Dicloxacillin
3°G, 4°G Cephalosporins
Carbapenems
Monobactams
Beta-lactamase inhibitors
* Penicillins enhanced with:
Clavulanic acid & Sulbactam (both are suicide inhibitors, they inhibit beta-lactamase)
Aminoglycosides (against enterococcus and psedomonas)
* Aminoglycosides enhanced with Aztreonam
* Penicillins: renal clearance EXCEPT Oxacillin & Nafcillin (bile)
* Cephalosporines: renal clearance EXCEPT Cefoperazone & Cefrtriaxone (bile)
* Both inhibited by Probenecid during tubular secretion.
* 2°G Cephalosporines: none cross BBB except Cefuroxime
* 3°G Cephalosporines: all cross BBB except Cefoperazone bc is highly highly lipid soluble, so is protein bound in plasma, therefore it doesn’t cross BBB.
* Cephalosporines are "LAME“ bc they do not cover this organisms
L isteria monocytogenes
A typicals (Mycoplasma, Chlamydia)
M RSA (except Ceftaroline, 5°G)
E nterococci

* Disulfiram-like effect: Cefotetan & Cefoperazone (mnemonic)
* Cefoperanzone: all the exceptions!!!
All 3°G cephalosporins cross the BBB except Cefoperazone.
All cephalosporins are renal cleared, except Cefoperazone.
Disulfiram-like effect
* Against Pseudomonas:
3°G Cef taz idime (taz taz taz taz)
4°G Cefepime, Cefpirome (not available in the USA)
Antipseudomonal penicillins
Aminoglycosides (synergy with beta-lactams)
Aztreonam (pseudomonal sepsis)
* Covers MRSA: Ceftaroline (rhymes w/ Caroline, Caroline the 5°G Ceph), Vancomycin, Daptomycin, Linezolid, Tigecycline.
* Covers VRSA: Linezolid, Dalfopristin/Quinupristin
* Aminoglycosides: decrease release of ACh in synapse and act as a Neuromuscular blocker, this is why it enhances effects of muscle relaxants.
* DEMECLOCYCLINE: tetracycline that’s not used as an AB, it is used as tx of SIADH to cause Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus (inhibits the V2 receptor in collecting ducts)
* Phototoxicity: Q ue S T ion?
Q uinolones
Sulfonamides
T etracyclines

* p450 inhibitors: Cloramphenicol, Macrolides (except Azithromycin), Sulfonamides
* Macrolides SE: Motilin stimulation, QT prolongation, reversible deafness, eosinophilia, cholestatic hepatitis
* Bactericidal: beta-lactams (penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams, carbapenems), aminoglycosides, fluorquinolones, metronidazole.
* Baceriostatic: tetracyclins, streptogramins, chloramphenicol, lincosamides, oxazolidonones, macrolides, sulfonamides, DHFR inhibitors.
* Pseudomembranous colitis: Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Clindamycin, Lincomycin.
* QT prolongation: macrolides, sometimes fluoroquinolones





11.19.17
2 more days until break
Music mood: Mili - Miracle Milk
Nocardia
Gram+, aerobic, non-spore forming, non- motile, branching filamentous rod.

Partially acid fast
Immunocompromised pts, cancer pts.
DISEASES
Cavitary broncopulmonary Nocardiosis: > N. asteroides, fever, cough, dyspnea, localized or diffuse pneumonia (symptoms very similar to TBC) If spreads hematogenously => multiple brain abscesses.

Cutaneous, subcutaneous Nocardiosis: > N. brasiliensis,cellulitis => subcutaneous draining abscess with granules (mycetoma)

What is Acute or Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis?
Acute or Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis is an infection of the heart’s endocardium. The endocardium is the inner lining of the heart muscle, which also covers the heart valves. Bacterial Endocarditis can damage or even destroy your heart valves. The difference between acute and subacute bacterial endocarditis is acute bacterial endocarditis is a sudden onset, whereas subacute bacterial endocarditis is a gradual onset.
Acute endocarditis most often occurs when an aggressive species of skin bacteria, especially a staphylococcus (staph), enters the bloodstream and attacks a normal, undamaged heart valve. Once staph bacteria begin to multiply inside the heart, they may send small clumps of bacteria called septic emboli into the bloodstream to spread the infection to other organs, especially to the kidneys, lungs and brain. Intravenous (IV) drug users are at very high risk of acute endocarditis, because numerous needle punctures give aggressive staph bacteria many opportunities to enter the blood.If untreated, this form of endocarditis can be fatal in less than six weeks.
Subacute endocarditis is caused by one of the viridans group of streptococci (Streptococcus sanguis, mutans, mitis or milleri) that normally live in the mouth and throat. Streptococcus bovis or Streptococcus equinus also can cause subacute endocarditis, typically in patients who have some form of gastrointestinal cancer, usually colon cancer. Subacute endocarditis tends to involve heart valves that already are damaged in some way, and it usually is less likely to cause septic emboli than acute endocarditis. If untreated, subacute bacterial endocarditis can worsen for as long as one year before it is fatal.








Medically Important Bacteria: Clasification
Without immunity, we’RE JUST BAGS OF NUTRIENTS!
Microbiology lecturer (via scienceprofessorquotes)

volutin granules are an intracytoplasmic storage form of complexed inorganic polyphosphate, the production of which is used as one of the identifying criteria when attempting to isolate Corynebacterium diphtheriae on Löffler’s medium….look like chines letters…as given below
-
 the24hrtherapist liked this · 3 years ago
the24hrtherapist liked this · 3 years ago -
 angelaellar reblogged this · 5 years ago
angelaellar reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 live-love-lightly liked this · 6 years ago
live-love-lightly liked this · 6 years ago -
 t-b-a-blr-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
t-b-a-blr-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 t-b-a-blr-blog liked this · 6 years ago
t-b-a-blr-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 paolocabeza-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
paolocabeza-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 paolocabeza-blog liked this · 8 years ago
paolocabeza-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 srgcpzz liked this · 12 years ago
srgcpzz liked this · 12 years ago -
 lilikoi--boy-blog liked this · 12 years ago
lilikoi--boy-blog liked this · 12 years ago -
 mynotes4usmle reblogged this · 12 years ago
mynotes4usmle reblogged this · 12 years ago