Medically Important Bacteria: Clasification



Medically Important Bacteria: Clasification
More Posts from T-b-a-blr-blog and Others

(Day 4/100 days of productivity) - Haemophilus Influenzae card!
Today was mostly spent working on research, textbooks, but and making flashcards like this for microbiology!

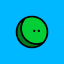
Schematic of gram positive diplococci (Streptococcus pneumoniae): Note that the diplococci are lancet shaped
Tularemia
An infection common in wild rodents that is passed to humans through contact with infected animal tissues or by ticks, biting flies, and mosquitoes.
Also known as rabbit fever and deer fly fever, amongst others.


13.02.18 Revision
I’ve always got my trusty reference book with me at work, but sometimes I like to read over a few topics just in case anything ever shows up :) and oml trying to write referral letter templates be like: …has been measuring … measured between 5-12 mmol/L … BGL measuring between 5-12 mmol/L OTL
🎼 The Boots - Gugudan 구구단
Follow optomstudies for daily original posts and study masterposts! Links: all originals + langblr posts + 15-part college 101 series + web directory!
Penicillin

Penicillin is a widely used antibiotic prescribed to treat staphylococci and streptococci bacterial infections.
beta-lactam family
Gram-positive bacteria = thick cell walls containing high levels of peptidoglycan
gram-negative bacteria = thinner cell walls with low levels of peptidoglycan and surrounded by a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) layer that prevents antibiotic entry
penicillin is most effective against gram-positive bacteria where DD-transpeptidase activity is highest.
Examples of penicillins include:
amoxicillin
ampicillin
bacampicillin
oxacillin
penicillin
Mechanism(s)
Penicillin inhibits the bacterial enzyme transpeptidase, responsible for catalysing the final peptidoglycan crosslinking stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis.
Cells wall is weakened and cells swell as water enters and then burst (lysis)
Becomes permanently covalently bonded to the enzymes’s active site (irreversible)


Alternative theory: penicillin mimics D-Ala D-Ala

Or may act as an umbrella inhibitor

Resistance
production of beta-lactamase - destroys the beta-lactam ring of penicillin and makes it ineffective (eg Staphylococcus aureus - most are now resistant)
In response, synthetic penicillin that is resistant to beta-lactamase is in use including egdicloxacillin, oxacillin, nafcillin, and methicillin.
Some is resistant to methicillin - methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Demonstrating blanket resistance to all beta-lactam antibiotics -extremely serious health risk.

Different anatomy notes form this semester Supplies used (not all at once, I mix and match): Faber-Castell Coloured Pencils (48 Pack) - https://amzn.to/2Kd1mUy Staedtler Triplus Fineliners - http://amzn.to/2pghonI Stabilo Point 88 Fineliner - https://amzn.to/2qU8fC9 Sharpie Pens - https://amzn.to/2HTRmP2 Uni Pin 0.1 Fineliner - https://amzn.to/2HmXp1z Crayola Supertips - https://amzn.to/2HVW1jr Bic Ballpoint Pen - https://amzn.to/2HmCjk0 Stabilo Swing Cool Highlighters - https://amzn.to/2HKxPTu

Positives are violet in color and negatives are red or pink on gram stain! My untidy handwritten notes here.



Medically Important Fungi
Cryptosporidium
Cryptosporidium is a microscopic parasite that causes the diarrhoeal disease cryptosporidiosis. Both the parasite and the disease are commonly known as “Crypto.”
The parasite is protected by an outer shell (oocyst)
Allows survival outside the body for long periods of time
Very tolerant to chlorine disinfection.
Water is the most common form of spread
Poses serious risk to immunocompromised individuals, eg AIDS; cancer and transplant patients who are taking certain immunosuppressive drugs.

Symptoms
Symptoms of cryptosporidiosis generally begin 2 to 10 days (average 7 days) after infection.
Watery diarrhea
Stomach cramps or pain
Dehydration
Nausea
Vomiting
Fever
Weight loss
Some people with Crypto will have no symptoms at all.
Symptoms usually last about 1 to 2 weeks (with a range of a few days to 4 or more weeks) in persons with healthy immune systems. Occasionally, people may experience a recurrence of symptoms after a brief period of recovery before the illness ends. Symptoms can come and go for up to 30 days.
In immunocompromised persons Cryptosporidium infections could possibly affect other areas of the digestive tract or the respiratory tract.
Diagnosis & Detection

Cryptosporidium oocysts in a modified acid-fast stain. (CDC Photo; DPDx)
Examination of stool samples.
Detection can be difficult - several stool samples over several days.
acid-fast staining, direct fluorescent antibody [DFA] , and/or enzyme immunoassays
Molecular methods (e.g., polymerase chain reaction – PCR) are increasingly used in reference diagnostic labs,
Treatment
Most people who have healthy immune systems will recover without treatment. Young children and pregnant women may be more susceptible to dehydration resulting from diarrhoea.
For those persons with AIDS, anti-retroviral therapy (improves the immune status) will also decrease or eliminate symptoms of cryptosporidiosis. However, even if symptoms disappear, cryptosporidiosis is often not curable and the symptoms may return if the immune status worsens.
Cryptosporidium and AIDS
Advanced immunosuppression — typically CD4 T lymphocyte cell (CD4) counts of <100 cells/µL — is associated with the greatest risk for prolonged, severe, or extraintestinal cryptosporidiosis.
The three species that most commonly infect humans are Cryptosporidium hominis, Cryptosporidium parvum, and Cryptosporidium meleagridis. Infections are usually caused by one species, but a mixed infection is possible.
Up to 74% of diarrhoea stools in AIDS patients demonstrating the organism in less developed countries where potent antiretroviral therapy is not widely available,
cryptosporidiosis has decreased and occurs at an incidence of <1 case per 1000 person-years in patients with AIDS.4 Infection occurs through ingestion of Cryptosporidium oocysts. Viable oocysts in feces can be transmitted directly through contact with infected humans or animals, particularly those with diarrhea. Oocysts can contaminate recreational water sources such as swimming pools and lakes, and public water supplies and may persist despite standard chlorination (see Appendix: Food and Water-Related Exposures). Person-to-person transmission is common, especially among sexually active men who have sex with men.
Fever is present in approximately one-third of patients and malabsorption is common.
The epithelium of the biliary tract and the pancreatic duct can be infected with Cryptosporidium, leading to sclerosing cholangitis and to pancreatitis secondary to papillary stenosis,
Pulmonary infections also have been reported, and may be under-recognized.
Treatment
ART with immune restoration to a CD4 count >100 cells/µL usually leads to resolution
Treatment of diarrhoea with anti-motility agents (AIII) may be necessary.
Patients with biliary tract involvement may require endoscopic retrograde choledocoduodenoscopy for diagnosis.
Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) has not been described in association with treatment of cryptosporidiosis.
No pharmacologic interventions are known to be effective in preventing the recurrence of cryptosporidiosis.
No therapy has been shown to be effective without ART.
-
 docpink reblogged this · 5 months ago
docpink reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 medusa2411 liked this · 1 year ago
medusa2411 liked this · 1 year ago -
 soethura007 liked this · 1 year ago
soethura007 liked this · 1 year ago -
 aloe-enriched liked this · 3 years ago
aloe-enriched liked this · 3 years ago -
 the24hrtherapist liked this · 3 years ago
the24hrtherapist liked this · 3 years ago -
 strangeflowerhumanoiddonkey liked this · 4 years ago
strangeflowerhumanoiddonkey liked this · 4 years ago -
 jonelroos liked this · 4 years ago
jonelroos liked this · 4 years ago -
 jonelroos reblogged this · 4 years ago
jonelroos reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 tahirazoni liked this · 4 years ago
tahirazoni liked this · 4 years ago -
 strawberrynot liked this · 4 years ago
strawberrynot liked this · 4 years ago -
 expect0-patronum liked this · 4 years ago
expect0-patronum liked this · 4 years ago -
 devinfreetime liked this · 4 years ago
devinfreetime liked this · 4 years ago -
 angelaellar reblogged this · 5 years ago
angelaellar reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 littlepotatosack reblogged this · 5 years ago
littlepotatosack reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 theecatran liked this · 5 years ago
theecatran liked this · 5 years ago -
 meowicee reblogged this · 5 years ago
meowicee reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 godismymedicine liked this · 6 years ago
godismymedicine liked this · 6 years ago -
 betagranoz93-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
betagranoz93-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 the-bell-jar-illiteracy reblogged this · 6 years ago
the-bell-jar-illiteracy reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 lostquerencia-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
lostquerencia-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 futuremls-blog liked this · 6 years ago
futuremls-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 doctornimsblog liked this · 6 years ago
doctornimsblog liked this · 6 years ago -
 bajiraokaushal-blog liked this · 6 years ago
bajiraokaushal-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 danipixel liked this · 6 years ago
danipixel liked this · 6 years ago -
 t-b-a-blr-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
t-b-a-blr-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 t-b-a-blr-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
t-b-a-blr-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 t-b-a-blr-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
t-b-a-blr-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 t-b-a-blr-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
t-b-a-blr-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 t-b-a-blr-blog liked this · 6 years ago
t-b-a-blr-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 nukeeeeeeeeeee-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
nukeeeeeeeeeee-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 onshchk-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
onshchk-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 sessizbimelek reblogged this · 7 years ago
sessizbimelek reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 meenatabasum-blog liked this · 7 years ago
meenatabasum-blog liked this · 7 years ago -
 3rdyearsucks-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
3rdyearsucks-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 dreaminginretrospect liked this · 7 years ago
dreaminginretrospect liked this · 7 years ago -
 mystudynotes5-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
mystudynotes5-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 mystudynotes5-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
mystudynotes5-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 mystudynotes1-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
mystudynotes1-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 mahrukh05-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
mahrukh05-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 lydiapas-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago
lydiapas-blog reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 microtech84 liked this · 7 years ago
microtech84 liked this · 7 years ago -
 trickmaster29 liked this · 7 years ago
trickmaster29 liked this · 7 years ago -
 mewixtine-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
mewixtine-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 mewixtine-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
mewixtine-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago