195 posts
Latest Posts by t-b-a-blr-blog - Page 3



Medically Important Bacteria: Clasification
Normal Flora
Blood, Spinal Fluid, Urine: sterile
Cutaneous surfaces (urethra, outer ear included): Staph epidermidis, Staph aureus, Corynobacteria (dyphteroids),Streptocci, Candida spp
Nose: Staph aureus, Staph epidermidis, dyphteroids, assorted streptococci
Gingival crevices: anaerobes = Bacterioides/Prevotella, Fusobacterium, Streotococci, Actinomyces
Oropharynx: Viridans group (alpha hemolytic strep), Neisseria (non pathogenic), H. influenzae (non typeable, meaning, w/o capsule), Candida albicans
Stomach: none
Breast-fed babies colon: microaerophilic/anaerobic = Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus, streptococci.
Adult Colon: microaerophilic/anaerobic = Bacteroides/Prevotella, E.coli, Bifidobacterium, Eubacterium, Fusobacterium, Gram- anaerobic rods, Lactobacillus, E.faecalis, streptococci
Vagina: Lactobacillus, streptococci, diphteroids, yeasts, Veillonella, Gram- rods

MICROBIOLOGY MNEMONIC
My favorite band: the Killers (and I’m gonna see them for the second time in 3 weeks!!!!!!! I’m SO excited!!!!!!)
There’s this mnemonic to remember encapsulated organisms that use capsule layers as their major mechanism of pathogenicity.
Capsules are slippery layers and can not be phagocyte. To remember that, just remember this Killer’s song called “All the pretty faces”
This is the only way I can remember this mnemonic, here it goes…
S ome K illers H ave P retty N ice Capsules
S treptococcus pneumoniae
K lebsiella pneumoniae
H aemophilus influenzae
P seudomona aeuroginosa
N eisseria meningitidis
C riptococcus neoformans
Tularemia
An infection common in wild rodents that is passed to humans through contact with infected animal tissues or by ticks, biting flies, and mosquitoes.
Also known as rabbit fever and deer fly fever, amongst others.

Microbiology Mnemonic
STD: Chlamydia Trachomatis’ serotypes
“Eye Don't Know why people don’t use condoms”
Most common BACTERIAL STD in the US
Serotypes: D-K : nongonococcal urethritis, cervicitis, PID
Eye: Inclusion conjunctivitis.
Pneumonia (staccato cough) / Inclussion conjunctivitis in neonates / infants

STD: L imphogranuloma Venereum
L1,2,3
Africa, Asia, South America
Swollen lymph nodes, ulcers, fistulas -> Genital elephantiasis

tr AC homa
A-C serotypes (A,B,Ba,C)
Follicular conjuntivitis -> Conjuntival scarring -> inturned eyelashes -> corneal scarring -> BLINDNESS



Recurrente infections with catalase positive organisms in Chronic Granulomatose Disease (CGD)

Staphylococcus epidermidis is a coagulase negative, Gram-positive coccus. The organism uses sophisticated regulatory networks to adapt its metabolism to suit varying environmental conditions. S. epidermidis relies on biofilm formation to protect cells from the host immune system and other anti-microbial molecules.
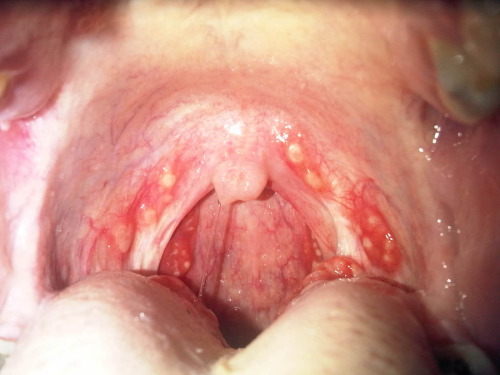
Strep throat.
What is Acute or Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis?
Acute or Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis is an infection of the heart’s endocardium. The endocardium is the inner lining of the heart muscle, which also covers the heart valves. Bacterial Endocarditis can damage or even destroy your heart valves. The difference between acute and subacute bacterial endocarditis is acute bacterial endocarditis is a sudden onset, whereas subacute bacterial endocarditis is a gradual onset.
Acute endocarditis most often occurs when an aggressive species of skin bacteria, especially a staphylococcus (staph), enters the bloodstream and attacks a normal, undamaged heart valve. Once staph bacteria begin to multiply inside the heart, they may send small clumps of bacteria called septic emboli into the bloodstream to spread the infection to other organs, especially to the kidneys, lungs and brain. Intravenous (IV) drug users are at very high risk of acute endocarditis, because numerous needle punctures give aggressive staph bacteria many opportunities to enter the blood.If untreated, this form of endocarditis can be fatal in less than six weeks.
Subacute endocarditis is caused by one of the viridans group of streptococci (Streptococcus sanguis, mutans, mitis or milleri) that normally live in the mouth and throat. Streptococcus bovis or Streptococcus equinus also can cause subacute endocarditis, typically in patients who have some form of gastrointestinal cancer, usually colon cancer. Subacute endocarditis tends to involve heart valves that already are damaged in some way, and it usually is less likely to cause septic emboli than acute endocarditis. If untreated, subacute bacterial endocarditis can worsen for as long as one year before it is fatal.
Tularemia as a biological weapon
It was viewed as an attractive agent because:
it is easy to aerosolize,
it is highly infective; 10-50 bacteria are required to infect,
it is nonpersistent and easy to decontaminate (unlike anthrax),
it is highly incapacitating to infected persons,
it has comparatively low lethality, which is useful where enemy soldiers are in proximity to noncombatants, e.g. civilians
can you see the irony……we are working our ass off to kill these bugs.At th same time some weirdo working in one lab is making bio weapon.

CAMP test for the identification of Streptococcus agalactiae (group B).
(A) Streptococcus (group B) shows a positive CAMP reaction arrow-shaped zone of enhanced hemolysis .
(B) Streptococcus pyogenes (group A) shows a negative reaction when inoculated at a right angle to
© Staphylococcus aureus.

Anaerobic ABC
A ctinomyces
B acteroides
C lostridium
Clostridium perfringes
Nagler reaction: C. perfringens phospholipase causes turbidity around the colonies on egg-yolk medium. Inhibited by specific antiserum.
Anaerobic stormy fermetantion in milk media

Food poisoning strains produce heat resistant spores.
Type A spores producing gas gangrene are inactivated by heat quickly.

Clostridium tetani
Gram+, anaerobe, spore forming, motile, rod.
Neurotoxin: Tetanus Toxin blocks glycine and GABA and produces a SPASTIC PARALYSIS.
TETANUS
Opisthotonus

Risus Sardonicus

Severe mucle spasm

Clostridium botulinum
Gram+, anaerobe, spore forming, motile rods
Botulin toxin (botox) inhibits the release of ACh and produces a flacid paralysis.
Adults ingest the toxin from poorly heated canned food (labile toxin, 60° 10minutes): weakness, diplopia, flacid paralysis and respiratory muscles involved, vomiting, diarrhea.
Infants ingest the spore from the dust or honey and form the toxins in the gut: constipation, weak crying, weak feeding, flacid paralysis and rapid respiratory involvement
Wound: traumatic implantation (assoc. w/ IVDA; uncommon), same symptoms without GI symptoms. Debridement, no closure.





Colon: pseudomembranous colitis due to Clostridium difficile (pseudomembranous inflammation) Note the gray-yellow pseudomembrane covering the entire mucosal surface. Damage is due to a toxin produced by C. difficile. Similar to diphtheria, the toxin produces necrosis of the mucosa and submucosa without actual invasion by the bacteria. A toxin assay of stool is the best method for diagnosing the disease. Ampicillin is the MC drug causing pseudomembranous colitis and does so by destroying colonic bacteria that normally keep C. difficile in check.
Amazing web site!
Listeria with tumbling motility (by Pathmass)
Listeria monocytogenes
Gram+, aerobic, motile rod, facultative intracellular, beta hemolytic on blood agar
Tumbling motility in broth (as seen in video)
Jet motility in cells by actin filament formation
Listeriolysin O (Beta hemolysin): pathogenic factor, facilitates it scape from phagosome before phagolysosome formation and “jets” into another cell.
Diseases:
Lysteriosis: asymptomatic or diarrhea.
Lysteriosis in pregnant women septicimia, crosses placenta.
Granulomatosis infantisepticum: neonatal disease, in utero transmission, sepsis, diseminated granulomas and high mortality.
Neonatal sepsis and meningitis (3° most common cause) 2-3 weeks after birth (fecal exposure)
Septicemia and meningitis in immunocompromised pts
Meningitis in renal transplant pts, cancer pts
Elek test to document toxi production of Corynobacterium diphteriae

volutin granules are an intracytoplasmic storage form of complexed inorganic polyphosphate, the production of which is used as one of the identifying criteria when attempting to isolate Corynebacterium diphtheriae on Löffler’s medium….look like chines letters…as given below
Difference between Blood Agar and Chocolate Agar
Hi everyone!
I’ll tell you in short about Nutrient agar first
It is a simple basal medium used for growth of common pathogens
It constitutes peptone water, meat extract and agar
Difference between Blood Agar and Chocolate Agar
What is common between Blood agar and Chocolate agar?
Both are enriched media
Used for the growth of Gram positive cocci and fastidious organisms like Neisseria & Haemophilus species
Can be used to indicate hemolysis
What are fastidious organisms?
They require specialized environments due to complex nutritional requirement
What is the difference between Blood agar and Chocolate agar?
The difference lies in how the media are made
How is Blood agar made?
Nutrient agar is sterilized by autoclave, cooled to 50°C and sterile sheep blood (5-10%) is added gradually and poured into plates
How is Chocolate agar made?
Nutrient agar is sterilized by autoclave, cooled to 75-80°C and sterile sheep blood (5-10%) is added gradually and poured into plates
How is the difference in temperature significant?
Certain organisms such as Haemophilus species require V factor for growth (complex nutritional requirement)
Factor V is present in blood but it is present inside the red blood cells (RBC)
These organisms can not utilize V factor which is trapped inside the RBC’s in Blood agar
When Blood agar is heated to 80-90°C for a few minutes (boiled blood agar), the V factor is released from within the erythrocytes and made available to the organism for utilization
Some strains of Neisseriae and Diphtheroids require V factor too
That’s why these media are superior to plain Blood agar for growing organisms requiring V factor
What is V fatcor?
V fatcor is a coenzyme, Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) or Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate (NADP) which acts as a hydrogen acceptor in the metabolism of cell
So to conclude, Chocolate agar is a type of blood agar in which the blood cells have been lysed by heating for growing fastidious organisms :)
Did you know?
Modified Thayer Martin is a type of chocolate agar which contains antibiotics (Vancomycin, Nystatin & Colistin) to suppress growth of other bacteria and promote growth of N gonorrhoeae
*phew* That’s all for today!
The image is my first photoshop work on the site, hope you like it =D
Just to remind you guys, Chocolate agar contains no chocolate, they simply named it after the yummy color :P
-IkaN
Indwelling catheter associated UTI
Catheter induced UTI
Typical :e.coli,Klebsella pneumonia,staph.saprophticus,proteus.mirabilis(lactose fermenters)(eat protein to be the cool member of the sapron staff club)
Atypical opportunistic:Pseudomonas aeroginasa.(non lactose fermenter)
Summery of UTIs
E.coli and klebsella are leading cause of uti..
staph saprophticus uti in sexually active women.
Enterococi(strptococcus family ) oppurtunistic uti
U.urealyticu known cause of urithritis but needs special media rich in urea and cholestrol
Actinomyces israelii
Gram+, anaerobic, non-spore forming, branching rod
Endogenous transmission (dental crevices -bad higiene, dental trauma- ; female genital tract -IUD-)
Dx: branching rods in “sulfur granules”; colonies resemble a molar tooth.


Not painful but very invasive penetrating tissues, including bone.
Draining abscess (sinus tracts) CULTURE THAT PUS
Disease: ACTINOMYCOSIS in low O2 tissues
Cervicofacil: “Lumpy jaw”, mycetoma on jaw line
Pelvic: from IUD
CNS: solitary abscess
Abdominal: qx, trauma
Thoracic: aspiration

How to remember Lysteria monocytogenes tumbling motility?
MICROBIOLOGY MNEMONIC
So, Lysteria rhymes with Hysteria, and when I think of hysteria I think of someone dancing Hysterically…..(actually, me dancing hysterically..)
I also googled Hysteria, and found this:

HYSTERIA RADIO!
So here it goes: “Lysteria dances to Hysteria Radio”
If I don’t come up with all these silly associations my brain melts and confuses all the freakin bacterias, so bear with me…
Nocardia
Gram+, aerobic, non-spore forming, non- motile, branching filamentous rod.

Partially acid fast
Immunocompromised pts, cancer pts.
DISEASES
Cavitary broncopulmonary Nocardiosis: > N. asteroides, fever, cough, dyspnea, localized or diffuse pneumonia (symptoms very similar to TBC) If spreads hematogenously => multiple brain abscesses.

Cutaneous, subcutaneous Nocardiosis: > N. brasiliensis,cellulitis => subcutaneous draining abscess with granules (mycetoma)


Diphtheria is known for creating a slimy/sticky/smelly exudate in the throat and mouth, but there are quite a few variations on its etiology and presentation.
A. Common type of diphtheria. Child three years old, seen on fourth day of illness. Exudate covering pharynx, tonsils, and uvula. Received 16,000 units of antitoxin. Throat clear on sixth day. Discharged cured.
B. Follicular type of diphtheria. Child seven years old, seen on second day of illness. The membrane involved the lacunae of the tonsils. Resembles follicular tonsillitis. Received 6,000 units of antitoxin total.
C. Hemorrhagic type of diphtheria. Child seven-and-a-half years old, seen on sixth day of illness. Tonsillar and post-pharyngeal exudate. Severe nasal and post-pharyngeal hemorrhages during exfoliation of membrane. Received in all 15,000 units of antitoxin. Throat clear on ninth day of illness. Myocarditis developed. Case discharged cured four weeks after admission.
D. Septic type of diphtheria. Child eight years old, seen on fifth day of illness. The pseudo-membrane in this case covered the hard palate and extended in one large mass down the pharynx, completely hiding the tonsils.
Diseases of Infancy and Childhood. Louis Fischer, M.D., 1917.
Mycobaterium tuberculosis PATHOGENESIS
Facultative intracellular

Sulfatides: inhibit PHAGOLYSOSOME FORMATION allowing intracellular survival.
Cord Factor (serpentine growth in vitro): disrupts mithochondrial respiration and oxidative phosphorilation and inhibits leukocyte migration.

Tuberculin + Mycolic Acid: type IV hypersensitivity (delayed hs), Cellular Mediated Immunity (CMI)
Micobacterium tuberculosis DX
Auramine-Rhodamine staining bacilli: fluorescent apple green (sensitive but not specific). If positive, do acid fast.

Acid Fast

Lowenstein-Jensen medium: aerobic, slow growing (2-3weeks)

PPD or Mantoux Test: measure 48-72h after. POSITIVE: >/= 5mm in VIH+ pts, >/=10mm in high risk population (IVDA, poverty, immigrants from high TB area, physicians, nurses), >/=15mm in low risk population

Positive indicates exposure, but not necessarily active disease.
Quantiferon-TB Gold Test: measures IF-gamma

Niacin producers
Catalase negative at 68° and catalase active at body T°
No serodiagnosis